Application Framework
Introduction
The application framework of OpenHarmony consists of two modules: ability management framework and bundle management framework.
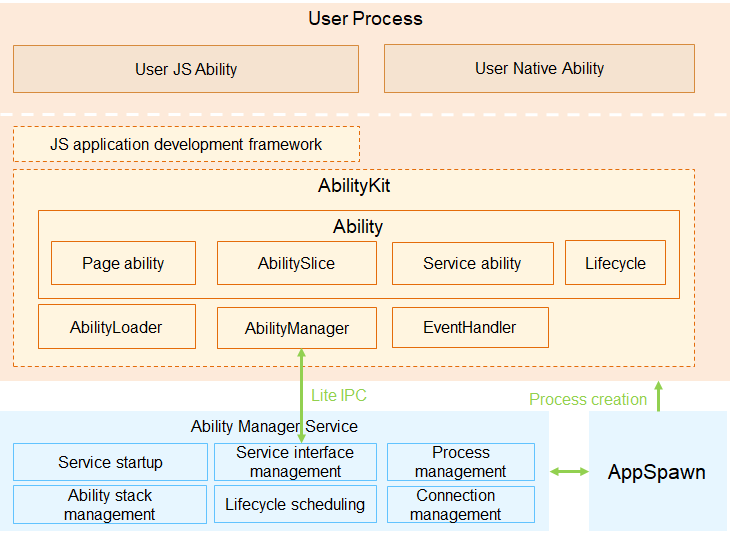
1. Ability management framework: This framework is provided by OpenHarmony for you to develop OpenHarmony applications. The following figure shows the sub-modules in the ability management framework.
Figure 1 Architecture of the ability management framework
-
AbilityKit is a development kit provided by the ability management framework. You can use this kit to develop applications based on the Ability component. There are two types of applications developed based on the Ability component: JS Ability developed using the JavaScript language and Native Ability developed using the C/C++ language. The JS application development framework encapsulates JavaScript UI components on the basis of the AbilityKit and is used to help you quickly develop JS Ability-based applications.
-
Ability is the minimum unit for the system to schedule applications. It is a component that can implement an independent functionality. An application can contain one or more Ability instances. There are two types of templates that you can use to create an Ability instance: Page and Service.
- An Ability using the Page template (Page ability for short) provides a UI for interacting with users.
- An Ability using the Service template (Service ability for short) does not have a UI and is used for running background tasks.
-
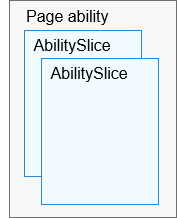
An AbilitySlice represents a single screen and its control logic. It is specific to Page abilities. A Page ability may contain one ability slice or multiple ability slices that provide highly relevant capabilities. The following figure shows the relationship between a Page ability and its ability slices.
Figure 2 Relationship between a Page ability and its ability slices
-
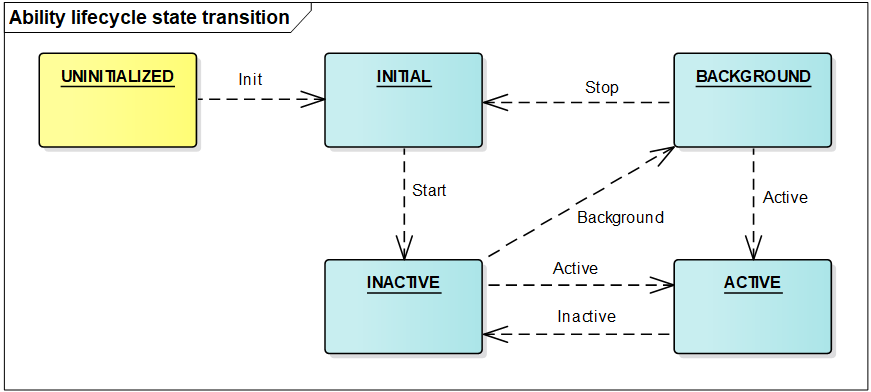
Lifecycle is a general term for all states of an ability, including UNINITIALIZED, INITIAL, INACTIVE, ACTIVE, and BACKGROUND. The following figure shows the lifecycle state transition of an ability.
-
Description of ability lifecycle states:
-
UNINITIALIZED: The ability is not initialized. This state is a temporary state. An ability changes directly to the INITIAL state upon its creation.
-
INITIAL: This state refers to the initial or stopped state. The ability in this state is not running. The ability enters the INACTIVE state after it is started.
-
INACTIVE: The ability is visible but does not gain focus. This state is the same as the ACTIVE state because the concept of window focus is not supported currently.
-
ACTIVE: The ability is in the foreground and has focus. The ability changes from the ACTIVE state to the INACTIVE state before returning to the background.
-
BACKGROUND: The ability returns to the background. After being re-activated, the ability enters the ACTIVE state. After being destroyed, the ability enters the INITIAL state.
-
-
AbilityLoader is used to register and load Ability classes. After creating an Ability class, you should first call the registration API defined in AbilityLoader to register the Ability class name with the ability management framework so that this Ability can be instantiated when being started.
-
AbilityManager enables inter-process communication (IPC) between the AbilityKit and the Ability Manager Service.
-
EventHandler is provided by the AbilityKit to enable inter-thread communication between abilities.
-
The Ability Manager Service is a system service used to coordinate the running relationships and lifecycle states of Ability instances. It consists of the following sub-modules:
- The service startup sub-module starts and registers the Ability Manager Service.
- The service interface management sub-module manages external capabilities provided by the Ability Manager Service.
- The process management sub-module starts and destroys processes where Ability instances are running, and maintains the process information.
- The ability stack management sub-module maintains the presentation sequence of abilities in the stack.
- The lifecycle scheduling sub-module changes an ability to a particular state based on the current operation of the system.
- The connection management sub-module manages connections to Service abilities.
-
AppSpawn is a system service used to create the process for running an ability. This service has high permissions. It sets permissions for Ability instances and pre-loads some common modules to accelerate application startup.
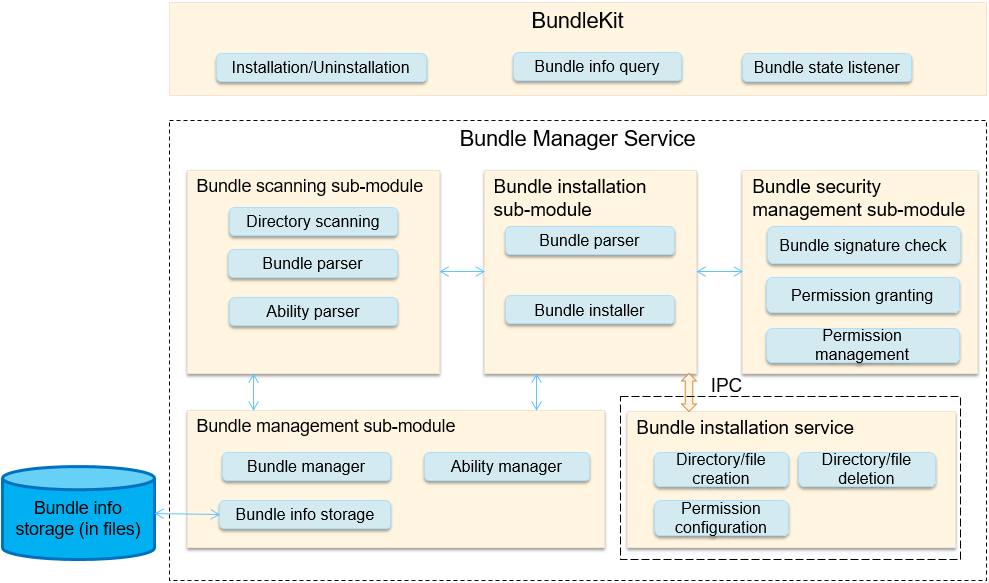
2. Bundle management framework: This framework is provided by OpenHarmony for you to manage application bundles (installation packages). The following figure shows the sub-modules in the bundle management framework.
Figure 4 Architecture of the bundle management framework
-
BundleKit includes external APIs provided by the Bundle Manager Service, including the APIs for application installation and uninstallation, bundle information query, and bundle state change listeners.
-
The bundle scanning sub-module parses pre-installed or installed bundles on the local device and extracts information from them for the bundle management sub-module to manage and make the information persistent for storage.
-
The bundle installation sub-module installs, uninstalls, and updates a bundle.
-
The bundle installation service is an independent process used to create or delete installation directories and has high permissions.
-
The bundle management sub-module manages information related to application bundles and stores persistent bundle information.
-
The bundle security management sub-module verifies signatures, and grants and manages permissions.
Directory Structure
/foundation
├── aafwk
│ └── aafwk_lite
│ ├── frameworks
│ │ ├── ability_lite # Core implementation code of AbilityKit
│ │ ├── abilitymgr_lite # Client code used for communication between the AbilityKit and Ability Manager Service
│ │ └── want_lite # Implementation code of the information carrier for interaction between abilities
│ ├── interfaces
│ │ ├── kits
│ │ │ ├── ability_lite # AbilityKit APIs exposed externally
│ │ │ └── want_lite # External APIs of the information carrier for interaction between abilities
│ │ └── innerkits
│ │ └── abilitymgr_lite # Internal APIs provided by the Ability Manager Service for other subsystems
│ └── services
│ └── abilitymgr_lite # Implementation code of the Ability Manager Service
└── appexecfwk
└── appexecfwk_lite
├── frameworks
│ └── bundle_lite # Client code used for communication between the BundleKit and Bundle Manager Service
├── interfaces
│ ├── kits
│ │ └── bundle_lite # BundleKit APIs exposed externally
│ └── innerkits
│ └── bundlemgr_lite # Core implementation code of BundleKit and internal APIs provided by the Bundle Manager Service for other subsystems
├── services
│ └── bundlemgr_lite # Implementation code of the Bundle Manager Service
└── utils
└── bundle_lite # Utility code used during the implementation of the Bundle Manager Service
Constraints
-
Language version
- C++ 11 or later
-
The specifications of the application framework vary depending on the System-on-a-Chip (SoC) and underlying OS capabilities.
-
Cortex-M RAM and ROM
- RAM: greater than 20 KB (recommended)
- ROM: greater than 300 KB (for the JS application development framework and related subsystems, such as UIKit and engine)
-
Cortex-A RAM and ROM
- RAM: greater than 2 MB (recommended)
- ROM: greater than 2 MB (for the JS application development framework and related subsystems, such as UIKit and engine)
-
Usage
-
Running the Two Services in the Application Framework
- The application framework has two system services Ability Manager Service and Bundle Manager Service. They are running in the foundation process.
- Ability Manager Service and Bundle Manager Service are registered with sa_manager. sa_manager runs in the foundation process and sets up a thread runtime environment for the two services. For details about how to create and use the Ability Manager Service and Bundle Manager Service, see SA Framework.
-
The demo code of the ability developed based on the AbilityKit is stored in the foundation/aafwk/aafwk_lite/frameworks/ability_lite/example directory. If you need to modify the functionality, modify the code in the entry/src/main/cpp files or add a new code file, and update the configuration in BUILD.gn accordingly.
-
Add the configuration for the ability demo for compilation in the build/lite/config/subsystem/aafwk/BUILD.gn file.
import("//build/lite/config/subsystem/lite_subsystem.gni") lite_subsystem("aafwk") { subsystem_components = [ "......", "//foundation/aafwk/aafwk_lite/frameworks/ability_lite/example:hiability", "......", ] } -
Run the following commands in the shell to build the demo. (For more building details, see the description of the compilation and building subsystem.) After the building is successful, the libhiability.so file is generated in out/ipcamera_hi3516dv300_liteos_a/dev_tools/example.
hb set hb build -
Compile the config.json file. For details, see the config.json file in the foundation/aafwk/aafwk_lite/frameworks/ability_lite/example directory. The file content is as follows:
{ "app": { "bundleName": "com.xxxxxx.hiability", "vendor": "xxxxxx", "version": { "code": 1, "name": "1.0" }, "apiVersion": { "compatible": 3, "target": 3 } }, "deviceConfig": { "default": { "keepAlive": false }, }, "module": { "deviceType": [ "smartVision" ], "distro": { "deliveryWithInstall": true, "moduleName": "hiability", "moduleType": "entry" }, "abilities": [{ "name": "MainAbility", "icon": "assets/entry/resources/base/media/icon.png", "label": "test app 1", "launchType": "standard", "type": "page", "visible": true }, { "name": "SecondAbility", "icon": "", "label": "test app 2", "launchType": "standard", "type": "page", "visible": true }, { "name": "ServiceAbility", "icon": "", "label": "test app 2", "launchType": "standard", "type": "service", "visible": true } ] } } -
Generate a HAP.
-
Add resource files to the assets/entry/resources/base/media directory based on the following directory structure.

-
Compress the preceding files into a ZIP package and change the file name extension to .hap, for example, hiability.hap.
-
-
Install the HAP.
- Place the preceding HAP file in a particular directory (/nfs/hap/ in this example).
- Run the following command to install the HAP. (Taking hispark_taurus as an example, you can obtain the bm tool from the out/hispark_taurus/ipcamera_hispark_taurus/dev_tools/bin directory after the version building.)
./bin/bm install -p /nfs/hiability.hap -
After the installation is complete, use the aa tool to run the demo through the following command. (Taking hispark_taurus as an example, you can obtain the aa tool from the out/hispark_taurus/ipcamera_hispark_taurus/dev_tools/bin directory after the version building.)
./bin/aa start -p com.xxxxxx.hiability -n MainAbility
Repositories Involved
Application framework