RDB Overview
The relational database (RDB) manages data based on relational models. With the underlying SQLite database, the RDB provides a complete mechanism for managing local databases. To satisfy different needs in complicated scenarios, the RDB offers a series of methods for performing operations such as adding, deleting, modifying, and querying data, and supports direct execution of SQL statements.
You do not need to care about the implementation of the database locking mechanism.
Basic concepts
-
RDB
A type of database created on the basis of relational models. The RDB stores data in rows and columns. A RDB is also called RDB store.
-
Predicate
A representation of the property or feature of a data entity, or the relationship between data entities. It is mainly used to define operation conditions.
-
Result set
A set of query results used to access data. You can access the required data in a result set in flexible modes.
-
SQLite database
A lightweight open-source relational database management system that complies with Atomicity, Consistency, Isolation, and Durability (ACID).
Working Principles
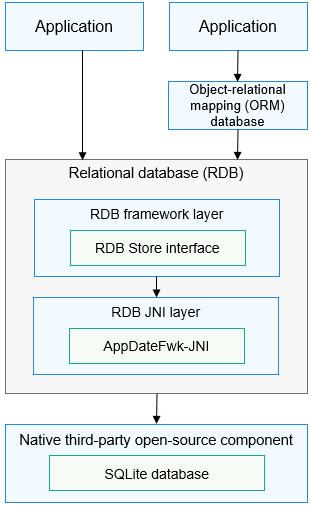
The RDB provides common operation APIs for external systems. It uses the SQLite as the underlying persistent storage engine, which supports all SQLite database features.
Figure 1 How RDB works
Default Settings
- The default RDB logging mode is Write Ahead Log (WAL).
- The default data flushing mode is FULL mode.
- The default size of the shared memory used by an OpenHarmony database is 2 MB.
Constraints
-
A maximum of four connection pools can be connected to an RDB to manage read and write operations.
-
To ensure data accuracy, the RDB supports only one write operation at a time.