SDIO
Overview
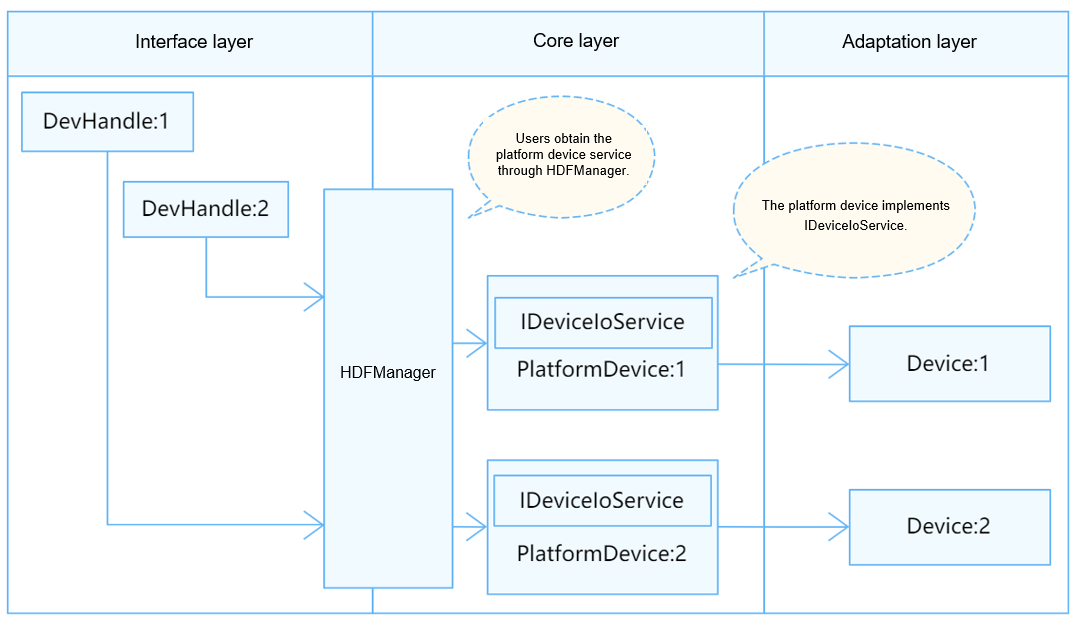
A Secure Digital Input Output (SDIO) card is an extension of the SD specification to cover I/O functions. SD and SDIO are called multimedia card (MMCs). In the Hardware Driver Foundation (HDF) framework, the SDIO module uses the independent service mode for API adaptation. In this mode, each device independently publishes a device service to handle external access requests. After receiving an access request from an API, the device manager extracts the parameters in the request to call the internal method of the target device. In the independent service mode, the service management capabilities of the HDFDeviceManager can be directly used. However, you need to configure a device node for each device, which increases the memory usage.
Figure 1 Independent service mode
Available APIs
SdioDeviceOps
// Function template
struct SdioDeviceOps {
int32_t (*incrAddrReadBytes)(struct SdioDevice *dev, uint8_t *data, uint32_t addr, uint32_t size);
int32_t (*incrAddrWriteBytes)(struct SdioDevice *dev, uint8_t *data, uint32_t addr, uint32_t size);
int32_t (*fixedAddrReadBytes)(struct SdioDevice *dev, uint8_t *data, uint32_t addr, uint32_t size, uint32_t scatterLen);
int32_t (*fixedAddrWriteBytes)(struct SdioDevice *dev, uint8_t *data, uint32_t addr, uint32_t size, uint32_t scatterLen);
int32_t (*func0ReadBytes)(struct SdioDevice *dev, uint8_t *data, uint32_t addr, uint32_t size);
int32_t (*func0WriteBytes)(struct SdioDevice *dev, uint8_t *data, uint32_t addr, uint32_t size);
int32_t (*setBlockSize)(struct SdioDevice *dev, uint32_t blockSize);
int32_t (*getCommonInfo)(struct SdioDevice *dev, SdioCommonInfo *info, uint32_t infoType);
int32_t (*setCommonInfo)(struct SdioDevice *dev, SdioCommonInfo *info, uint32_t infoType);
int32_t (*flushData)(struct SdioDevice *dev);
int32_t (*enableFunc)(struct SdioDevice *dev);
int32_t (*disableFunc)(struct SdioDevice *dev);
int32_t (*claimIrq)(struct SdioDevice *dev, SdioIrqHandler *irqHandler);
int32_t (*releaseIrq)(struct SdioDevice *dev);
int32_t (*findFunc)(struct SdioDevice *dev, struct SdioFunctionConfig *configData);
int32_t (*claimHost)(struct SdioDevice *dev);
int32_t (*releaseHost)(struct SdioDevice *dev);
};
Table 1 Callbacks for the members in the SdioDeviceOps structure
NOTE
CommonInfo includes the following information:
- maxBlockNum: specifies the maximum number of blocks in a request.
- maxBlockSize: specifies the maximum number of bytes in a block.
- maxRequestSize: specifies the maximum number of bytes in a request.
- enTimeout: specifies the maximum timeout period, in milliseconds.
- funcNum: specifies the function number, which ranges from 1 to 7.
- irqCap: specifies the interrupt request (IRQ) capabilities.
- (void *)data
How to Develop
The SDIO module adaptation involves the following steps:
-
Instantiate the driver entry.
- Instantiate the HdfDriverEntry structure.
- Call HDF_INIT to register the HdfDriverEntry instance with the HDF.
-
Configure attribute files.
- Add the deviceNode information to the device_info.hcs file.
- (Optional) Add the sdio_config.hcs file.
-
Instantiate the SDIO controller object.
-
Initialize SdioDevice.
-
Instantiate SdioDeviceOps in the SdioDevice object.
 NOTE
NOTEFor details, see Available APIs.
-
-
Debug the driver.
- (Optional) For new drivers, verify the basic functions, such as the SDIO control status and response to interrupts.
Development Example
The following uses sdio_adapter.c as an example to present the contents that need to be provided by the vendor to implement device functions.
-
Instantiate the driver entry. The driver entry must be a global variable of the HdfDriverEntry type (defined in hdf_device_desc.h), and the value of moduleName must be the same as that in device_info.hcs. In the HDF, the start address of each HdfDriverEntry object of all loaded drivers is collected to form a segment address space similar to an array for the upper layer to invoke.
Generally, HDF calls the Bind function and then the Init function to load a driver. If Init fails to be called, HDF calls Release to release driver resources and exit.
-
SDIO driver entry reference
struct HdfDriverEntry g_sdioDriverEntry = { .moduleVersion = 1, .Bind = Hi35xxLinuxSdioBind, // See the Bind function. .Init = Hi35xxLinuxSdioInit, // See the Init function. .Release = Hi35xxLinuxSdioRelease// See the Release function. .moduleName = "HDF_PLATFORM_SDIO",// (Mandatory) The value must be the same as that of moduleName in the .hcs file. }; // Call HDF_INIT to register the driver entry with the HDF. HDF_INIT(g_sdioDriverEntry);
-
-
Add the deviceNode information to the device_info.hcs file and configure the device attributes in the sdio_config.hcs file. The deviceNode information is related to registration of the driver entry. The device attribute values are closely related to the default values or value ranges of the SdioDevice members at the core layer.
In this example, there is only one SDIO controller. If there are multiple SDIO controllers, you need to add the deviceNode information to the device_info file and add the corresponding device attributes to the sdio_config file.
-
device_info.hcs configuration reference
root { device_info { match_attr = "hdf_manager"; platform :: host { hostName = "platform_host"; priority = 50; device_sdio :: device { device0 :: deviceNode { policy = 1; priority = 70; permission = 0644; moduleName = "HDF_PLATFORM_SDIO"; // (Mandatory) Driver name, which must be the same as the moduleName in the driver entry. serviceName = "HDF_PLATFORM_MMC_2"; // (Mandatory) Unique name of the service published by the driver deviceMatchAttr = "hisilicon_hi35xx_sdio_0";// (Mandatory) Used to configure the private data of the controller. The value must be the same as the controller in sdio_config.hcs. } } } } } -
sdio_config.hcs configuration reference
root { platform { sdio_config { template sdio_controller { match_attr = ""; hostId = 2; // (Mandatory) It is set to 2. For details, see mmc_config.hcs. devType = 2; // (Mandatory) It is set to 2. For details, see mmc_config.hcs. } controller_0x2dd1 :: sdio_controller { match_attr = "hisilicon_hi35xx_sdio_0";// (Mandatory) The value must be the same as that of deviceMatchAttr in device_info.hcs. } } }
-
-
Initialize the SdioDevice object at the core layer, including initializing the vendor custom structure (transferring parameters and data), instantiating SdioDeviceOps (used to call underlying functions of the driver) in SdioDevice, and implementing the HdfDriverEntry member functions (Bind, Init, and Release).
-
Custom structure reference
To the driver, the custom structure carries parameters and data. The values in the sdio_config.hcs file are read by HDF, and the structure members are initialized through DeviceResourceIface. Some important values are also passed to the objects at the core layer.
typedef struct { uint32_t maxBlockNum; // Maximum number of blocks in a request. uint32_t maxBlockSize; // Maximum number of bytes in a block. The value range is 1 to 2048. uint32_t maxRequestSize; // Maximum number of bytes in a request. The value range is 1 to 2048. uint32_t enTimeout; // Maximum timeout period in milliseconds. The value cannot exceed one second. uint32_t funcNum; // Function number, which ranges from 1 to 7. uint32_t irqCap; // IRQ capabilities. void *data; // Private data. } SdioFuncInfo; // SdioDevice is the core layer controller structure. Its members are assigned with values by using the Bind function. struct SdioDevice { struct SdDevice sd; struct SdioDeviceOps *sdioOps; struct SdioRegister sdioReg; uint32_t functions; struct SdioFunction *sdioFunc[SDIO_MAX_FUNCTION_NUMBER]; struct SdioFunction *curFunction; struct OsalThread thread; /* irq thread */ struct OsalSem sem; bool irqPending; bool threadRunning; }; -
Instantiate the callback function structure SdioDeviceOps in SdioDevice. Other members are initialized by using the Init function.
static struct SdioDeviceOps g_sdioDeviceOps = { .incrAddrReadBytes = Hi35xxLinuxSdioIncrAddrReadBytes, .incrAddrWriteBytes = Hi35xxLinuxSdioIncrAddrWriteBytes, .fixedAddrReadBytes = Hi35xxLinuxSdioFixedAddrReadBytes, .fixedAddrWriteBytes = Hi35xxLinuxSdioFixedAddrWriteBytes, .func0ReadBytes = Hi35xxLinuxSdioFunc0ReadBytes, .func0WriteBytes = Hi35xxLinuxSdioFunc0WriteBytes, .setBlockSize = Hi35xxLinuxSdioSetBlockSize, .getCommonInfo = Hi35xxLinuxSdioGetCommonInfo, .setCommonInfo = Hi35xxLinuxSdioSetCommonInfo, .flushData = Hi35xxLinuxSdioFlushData, .enableFunc = Hi35xxLinuxSdioEnableFunc, .disableFunc = Hi35xxLinuxSdioDisableFunc, .claimIrq = Hi35xxLinuxSdioClaimIrq, .releaseIrq = Hi35xxLinuxSdioReleaseIrq, .findFunc = Hi35xxLinuxSdioFindFunc, .claimHost = Hi35xxLinuxSdioClaimHost, .releaseHost = Hi35xxLinuxSdioReleaseHost, }; -
Bind function
Input parameters:
HdfDeviceObject, an interface parameter exposed by the driver, contains the .hcs configuration file information.
Return values:
HDF_STATUS (The following table lists some status. For details about other status, see HDF_STATUS in the //drivers/framework/include/utils/hdf_base.h file.)
Table 2 Input parameters and return values of the Bind function
Function description:
Initializes the custom structure object and SdioCntlr, calls the SdioCntlrAdd function at the core layer, and performs other initialization operations customized by the vendor.
static int32_t Hi35xxLinuxSdioBind(struct HdfDeviceObject *obj) { struct MmcCntlr *cntlr = NULL; int32_t ret; ... cntlr = (struct MmcCntlr *)OsalMemCalloc(sizeof(struct MmcCntlr));// Apply for memory. ... cntlr->ops = &g_sdioCntlrOps; // (Mandatory) struct MmcCntlrOps g_sdioCntlrOps={ // .rescanSdioDev = Hi35xxLinuxSdioRescan,}; cntlr->hdfDevObj = obj; // (Mandatory) Enable conversion between HdfDeviceObject and MmcCntlr. obj->service = &cntlr->service; // (Mandatory) Enable conversion between HdfDeviceObject and MmcCntlr. ret = Hi35xxLinuxSdioCntlrParse(cntlr, obj);// (Mandatory) Initialize the index and devType of cntlr. If the initialization fails, execute goto _ERR. ... ret = MmcCntlrAdd(cntlr); // (Mandatory) Call the mmc_core.c function at the core layer. If the function fails to be called, execute goto _ERR. ... ret = MmcCntlrAllocDev(cntlr, (enum MmcDevType)cntlr->devType);// (Mandatory) Call the mmc_core.c function at the core layer. If the function fails to be called, execute goto _ERR. ... MmcDeviceAddOps(cntlr->curDev, &g_sdioDeviceOps);// (Mandatory) Call the function of mmc_core.c at the core layer to instantiate the hook. HDF_LOGD("Hi35xxLinuxSdioBind: Success!"); return HDF_SUCCESS; _ERR: Hi35xxLinuxSdioDeleteCntlr(cntlr); HDF_LOGE("Hi35xxLinuxSdioBind: Fail!"); return HDF_FAILURE; } -
Init function
Input parameters:
HdfDeviceObject, an interface parameter exposed by the driver, contains the .hcs configuration file information.
Return values:
HDF_STATUS
Function description:
No operation. The vendor can add operations as required.
static int32_t Hi35xxLinuxSdioInit(struct HdfDeviceObject *obj) { (void)obj;// No operation. The vendor can add operations as required. HDF_LOGD("Hi35xxLinuxSdioInit: Success!"); return HDF_SUCCESS; } -
Release function
Input parameters:
HdfDeviceObject, an interface parameter exposed by the driver, contains the .hcs configuration file information.
Return values:
–
Function description:
Releases the memory and deletes the controller. This function assigns a value to the Release API in the driver entry structure. When the HDF fails to call the Init function to initialize the driver, the Release function can be called to release driver resources. All forced conversion operations for obtaining the corresponding object can be successful only when the Bind function has the corresponding value assignment operations.
static void Hi35xxLinuxSdioRelease(struct HdfDeviceObject *obj) { if (obj == NULL) { return; } Hi35xxLinuxSdioDeleteCntlr((struct MmcCntlr *)obj->service);// (Mandatory) Custom function for releasing memory. A forced conversion from HdfDeviceObject to MmcCntlr is involved. } -