PWM
Overview
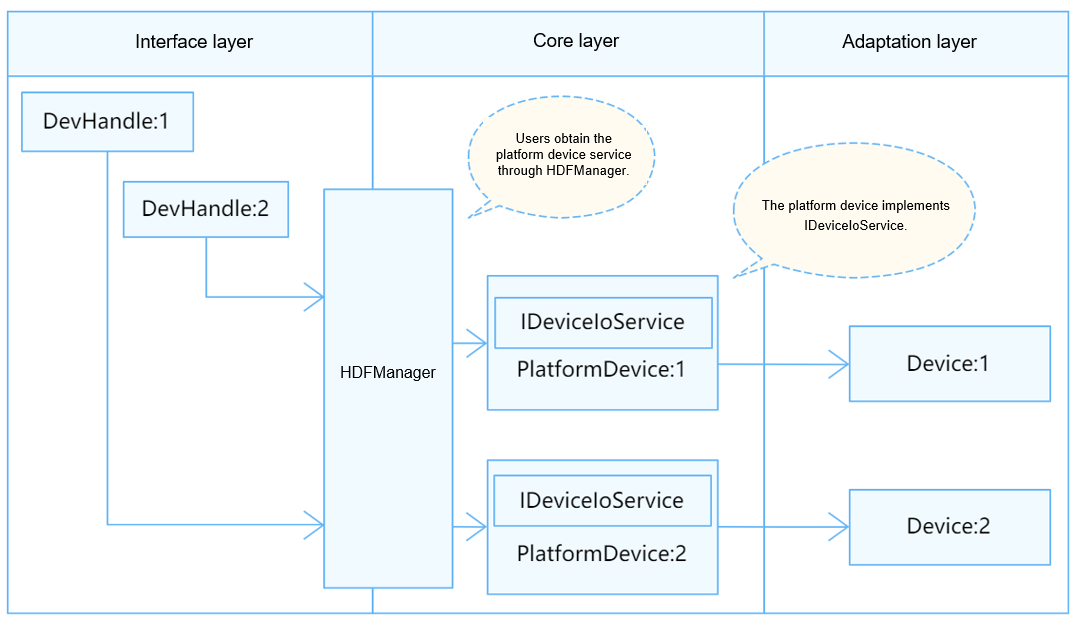
In the Hardware Driver Foundation (HDF), the Pulse Width Modulator (PWM) uses the independent service mode for API adaptation. In this mode, each device independently publishes a device service to handle external access requests. After receiving an access request from an API, the device manager extracts the parameters in the request to call the internal method of the target device. In the independent service mode, the service management capabilities of the HDF Device Manager can be directly used. However, you need to configure a device node for each device, which increases the memory usage.
Figure 1 Independent service mode
Available APIs
PwmMethod
struct PwmMethod {
int32_t (*setConfig)(struct PwmDev *pwm, struct PwmConfig *config);
int32_t (*open)(struct PwmDev *pwm);
int32_t (*close)(struct PwmDev *pwm);
};
Table 1 Callbacks for the members in the PwmMethod structure
pwm: structure pointer to the PWM controller at the core layer. |
|||
pwm: structure pointer to the PWM controller at the core layer. |
|||
pwm: structure pointer to the PWM controller at the core layer. |
How to Develop
The PWM module adaptation involves the following steps:
-
Instantiate the driver entry.
- Instantiate the HdfDriverEntry structure.
- Call HDF_INIT to register the HdfDriverEntry instance with the HDF.
-
Configure attribute files.
- Add the deviceNode information to the device_info.hcs file.
- (Optional) Add the pwm_config.hcs file.
-
Instantiate the PWM controller object.
-
Initialize PwmDev.
-
Instantiate PwmMethod in the PwmDev object.
 NOTE
NOTEFor details, see Available APIs.
-
-
Debug the driver.
- (Optional) For new drivers, verify the basic functions, such as the PWM control status and response to interrupts.
Development Example
The following uses pwm_hi35xx.c as an example to present the contents that need to be provided by the vendor to implement device functions.
-
Instantiate the driver entry. The driver entry must be a global variable of the HdfDriverEntry type (defined in hdf_device_desc.h), and the value of moduleName must be the same as that in device_info.hcs. In the HDF, the start address of each HdfDriverEntry object of all loaded drivers is collected to form a segment address space similar to an array for the upper layer to invoke.
Generally, HDF calls the Bind function and then the Init function to load a driver. If Init fails to be called, HDF calls Release to release driver resources and exits.
-
PWM driver entry reference
struct HdfDriverEntry g_hdfPwm = { .moduleVersion = 1, .moduleName = "HDF_PLATFORM_PWM",// (Mandatory) The value must be the same as that of moduleName in the .hcs file. .Bind = HdfPwmBind, .Init = HdfPwmInit, .Release = HdfPwmRelease, }; // Call HDF_INIT to register the driver entry with the HDF. HDF_INIT(g_hdfPwm);
-
-
Add the deviceNode information to the device_info.hcs file and configure the device attributes in the pwm_config.hcs file. The deviceNode information is related to registration of the driver entry. The device attribute values are closely related to the default values or value ranges of the PwmDev members at the core layer. If there are multiple devices, you need to add the deviceNode information to the device_info file and add the corresponding device attributes to the pwm_config file.
-
device_info.hcs configuration reference
root { device_info { platform :: host { hostName = "platform_host"; priority = 50; device_pwm :: device {// Configure an HDF device node for each PWM controller. Set this parameter only when there are multiple PWM controllers. device0 :: deviceNode { policy = 1; // Publish kernel-mode services. priority = 80; // Driver startup priority permission = 0644; // Permission to create device nodes for the driver moduleName = "HDF_PLATFORM_PWM"; // (Mandatory) Driver name, which must be the same as the moduleName in the driver entry. serviceName = "HDF_PLATFORM_PWM_0";// (Mandatory) Unique name of the service published by the driver deviceMatchAttr = "hisilicon_hi35xx_pwm_0";// (Mandatory) Used to configure the private data of the controller. The value must be the same as the controller information in pwm_config.hcs. // For details about the controller information, see pwm_config.hcs. } device1 :: deviceNode { policy = 1; priority = 80; permission = 0644; moduleName = "HDF_PLATFORM_PWM"; serviceName = "HDF_PLATFORM_PWM_1"; deviceMatchAttr = "hisilicon_hi35xx_pwm_1"; } } } } } -
pwm_config.hcs configuration reference
root { platform { pwm_config { template pwm_device {// (Mandatory) Template configuration. In the template, you can configure the common parameters shared by service nodes. serviceName = ""; match_attr = ""; num = 0; // (Mandatory) Device number base = 0x12070000; // (Mandatory) Used for address mapping } device_0x12070000 :: pwm_device { match_attr = "hisilicon_hi35xx_pwm_0";// (Mandatory) The value must be the same as that of deviceMatchAttr in device_info.hcs. } device_0x12070020::pwm_device {// Set this parameter only when there are multiple devices. match_attr = "hisilicon_hi35xx_pwm_1"; num = 1; base = 0x12070020; // (Mandatory) Used for address mapping } } } }
-
-
Initialize the PwmDev object at the core layer, including initializing the vendor custom structure (transferring parameters and data), instantiating PwmMethod (used to call underlying functions of the driver) in PwmDev, and implementing the HdfDriverEntry member functions (Bind, Init, and Release).
-
Custom structure reference
To the driver, the custom structure carries parameters and data. The values in the pwm_config.hcs file are read by HDF, and the structure members are initialized through DeviceResourceIface. Some important values, such as the device number, are also passed to the objects at the core layer.
struct HiPwm { struct PwmDev dev; // (Mandatory) Core layer structure volatile unsigned char *base; struct HiPwmRegs *reg; // Device attribute structure, which can be customized. bool supportPolarity; }; // PwmDev is the controller structure at the core layer. Its members are assigned with values by using the Init function. struct PwmDev { struct IDeviceIoService service; struct HdfDeviceObject *device; struct PwmConfig cfg; // Attribute structure. For details, see the description of PwmConfig. struct PwmMethod *method; // Hook function template bool busy; uint32_t num; // Device number OsalSpinlock lock; void *priv; // Private data. Generally, the start address of the custom structure is stored to facilitate invoking of the structure. }; struct PwmConfig { uint32_t duty; // Time (in ns) when a signal is in the on state. uint32_t period; // Regular interval (in ns) of PWM uint32_t number; // Number of consecutive PWMs uint8_t polarity; // Polarity // ------------------- | -------------- // PWM_NORMAL_POLARITY | Normal polarity // PWM_INVERTED_POLARITY | Inverted polarity // uint8_t status; // Running status // ------------------ | ----------------- // PWM_DISABLE_STATUS | Disabled // PWM_ENABLE_STATUS | Enabled }; -
Instantiate the callback function structure PwmMethod in PwmDev. Other members are initialized by using the Init function.
// Example in pwm_hi35xx.c: fill the hook function struct PwmMethod g_pwmOps = { .setConfig = HiPwmSetConfig,// Configure attributes. }; -
Init function
Input parameters:
HdfDeviceObject, an interface parameter exposed by the driver, contains the .hcs configuration file information.
Return values:
HDF_STATUS (The following table lists some status. For details about other status, see HDF_STATUS in the //drivers/framework/include/utils/hdf_base.h file.)
Function description:
Initializes the custom structure object and PwmDev, and calls the PwmDeviceAdd function at the core layer.
// The bind function is empty. It can be combined with the init function or implement related operations based on the vendor's requirements. static int32_t HdfPwmBind(struct HdfDeviceObject *obj) { (void)obj; return HDF_SUCCESS; } static int32_t HdfPwmInit(struct HdfDeviceObject *obj) { int ret; struct HiPwm *hp = NULL; ... hp = (struct HiPwm *)OsalMemCalloc(sizeof(*hp)); ... ret = HiPwmProbe(hp, obj); // (Mandatory) The implementation is as follows: ... return ret; } static int32_t HiPwmProbe(struct HiPwm *hp, struct HdfDeviceObject *obj) { uint32_t tmp; struct DeviceResourceIface *iface = NULL; iface = DeviceResourceGetIfaceInstance(HDF_CONFIG_SOURCE);// Initialize the custom structure HiPwm. ... hp->reg = (struct HiPwmRegs *)hp->base; // Initialize the custom structure HiPwm. hp->supportPolarity = false; // Initialize the custom structure HiPwm. hp->dev.method = &g_pwmOps; // Connect to the instantiated object of PwmMethod. hp->dev.cfg.duty = PWM_DEFAULT_DUTY_CYCLE; // Initialize PwmDev. hp->dev.cfg.period = PWM_DEFAULT_PERIOD; // Initialize PwmDev. hp->dev.cfg.polarity = PWM_DEFAULT_POLARITY; // Initialize PwmDev. hp->dev.cfg.status = PWM_DISABLE_STATUS; // Initialize PwmDev. hp->dev.cfg.number = 0; // Initialize PwmDev. hp->dev.busy = false; // Initialize PwmDev. if (PwmDeviceAdd(obj, &(hp->dev)) ) != HDF_SUCCESS) {// (Important) Call the core layer function to initialize the hp->dev devices and services. OsalIoUnmap((void *)hp->base); return HDF_FAILURE; } return HDF_SUCCESS; } -
Release function
Input parameters:
HdfDeviceObject, an interface parameter exposed by the driver, contains the .hcs configuration file information.
Return values:
–
Function description:
Releases the memory and deletes the controller. This function assigns a value to the Release API in the driver entry structure. When the HDF fails to call the Init function to initialize the driver, the Release function can be called to release driver resources.
static void HdfPwmRelease(struct HdfDeviceObject *obj) { struct HiPwm *hp = NULL; ... hp = (struct HiPwm *)obj->service;// A forced conversion from HdfDeviceObject to HiPwm is involved. ... PwmDeviceRemove(obj, &(hp->dev));// (Mandatory) Call the core layer functions to release PwmDev devices and services. A forced conversion from HiPwm to PwmDev is involved in the process. HiPwmRemove(hp); //Release HiPwm. }
-