UART
Overview
The Universal Asynchronous Receiver/Transmitter (UART) is a universal serial data bus used for asynchronous communication. It enables bi-directional communication between devices in full-duplex mode.
UART is widely used to print information for debugging or to connect to various external modules such as GPS and Bluetooth.
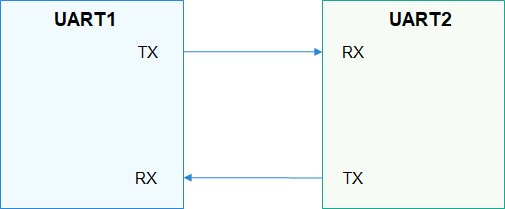
A UART is connected to other modules through two wires (as shown in Figure 1) or four wires (as shown in Figure 2).
-
TX: TX pin of the transmitting UART. It is connected to the RX pin of the peer UART.
-
RX: RX pin of the receiving UART. It is connected to the TX pin of the peer UART.
-
RTS: Request to Send signal pin. It is connected to the CTS pin of the peer UART and is used to indicate whether the local UART is ready to receive data.
-
CTS: Clear to Send signal pin. It is connected to the RTS pin of the peer UART and is used to indicate whether the local UART is allowed to send data to the peer end.
Figure 1 Two-wire UART communication
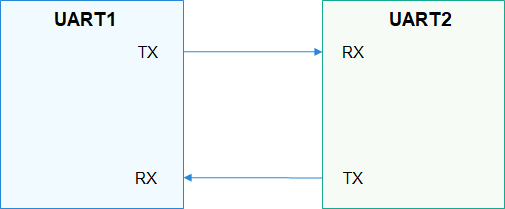
Figure 2 Four-wire UART communication
-
The transmitting and receiving UARTs must ensure that they have the same settings on particular attributes such as the baud rate and data format (start bit, data bit, parity bit, and stop bit) before they start to communicate. During data transmission, a UART sends data to the peer end over the TX pin and receives data from the peer end over the RX pin. When the size of the buffer used by a UART for storing received data reaches the preset threshold, the RTS signal of the UART changes to 1 (data cannot be received), and the peer UART stops sending data to it because its CTS signal does not allow it to send data.
-
The UART interface defines a set of common functions for operating a UART port, including obtaining and releasing device handles, reading and writing data of a specified length, and obtaining and setting the baud rate, as well as the device attributes.
Available APIs
Table 1 UART driver APIs
| API | Description |
|---|---|
| UartOpen | Obtains a UART device handle. |
| UartClose | Releases a UART device handle. |
| UartRead | Reads data of the specified length from a UART device. |
| UartWrite | Writes data of the specified length to a UART device. |
| UartGetBaud | Obtains the UART baud rate. |
| UartSetBaud | Sets the UART baud rate. |
| UartGetAttribute | Obtains UART device attributes. |
| UartSetAttribute | Sets UART device attributes. |
| UartSetTransMode | Sets the UART transmission mode. |
NOTE
All APIs described in this document can be called only in kernel mode.
Usage Guidelines
How to Use
The figure below illustrates how to use the APIs.
Figure 3 Using UART driver APIs
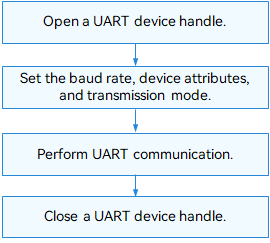
Opening a UART Device Handle
Before performing UART communication, call UartOpen to obtain a UART device handle. This function returns the pointer to the UART device handle with the specified port number.
DevHandle UartOpen(uint32_t port);
Table 2 Description of UartOpen
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| port | UART port number. |
| Return Value | Description |
| NULL | The operation failed. |
| Device handle | The operation is successful. The obtained UART device handle is returned. |
Example: Obtain the device handle of UART port 3.
DevHandle handle = NULL; /* UART device handle */
uint32_t port = 3; /* UART port number */
handle = UartOpen(port);
if (handle == NULL) {
HDF_LOGE("UartOpen: failed!\n");
return;
}
Setting the UART Baud Rate
Call UartSetBaud() to set the UART baud rate.
int32_t UartSetBaud(DevHandle handle, uint32_t baudRate);
Table 3 Description of UartSetBaud
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| handle | UART device handle. |
| baudRate | Baud rate to set. |
| Return Value | Description |
| 0 | The operation is successful. |
| Negative value | The operation failed. |
Example: Set the UART baud rate to 9600.
int32_t ret;
/* Set the UART baud rate to 9600. */
ret = UartSetBaud(handle, 9600);
if (ret != 0) {
HDF_LOGE("UartSetBaud: failed, ret %d\n", ret);
}
Obtaining the UART Baud Rate
Call UartGetBaud() to obtain the UART baud rate.
int32_t UartGetBaud(DevHandle handle, uint32_t *baudRate);
Table 4 Description of UartGetBaud
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| handle | UART device handle. |
| baudRate | Pointer to the UART baud rate obtained. |
| Return Value | Description |
| 0 | The operation is successful. |
| Negative value | The operation failed. |
Example: Obtain the UART baud rate.
int32_t ret;
uint32_t baudRate;
/* Obtain the UART baud rate. */
ret = UartGetBaud(handle, &baudRate);
if (ret != 0) {
HDF_LOGE("UartGetBaud: failed, ret %d\n", ret);
}
Setting UART Device Attributes
Call UartSetAttribute() to set UART device attributes.
int32_t UartSetAttribute(DevHandle handle, struct UartAttribute *attribute);
Table 5 Description of UartSetAttribute
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| handle | UART device handle. |
| attribute | Pointer to the UART device attributes to set. |
| Return Value | Description |
| 0 | The operation is successful. |
| Negative value | The operation failed. |
Example: Set UART device attributes.
int32_t ret;
struct UartAttribute attribute;
attribute.dataBits = UART_ATTR_DATABIT_7; /* Enable 7 bits to be transferred each time. */
attribute.parity = UART_ATTR_PARITY_NONE; /* Disable parity check. */
attribute.stopBits = UART_ATTR_STOPBIT_1; /* Set the stop bit to 1. */
attribute.rts = UART_ATTR_RTS_DIS; /* Disable the RTS signal. */
attribute.cts = UART_ATTR_CTS_DIS; /* Disable the CTS signal. */
attribute.fifoRxEn = UART_ATTR_RX_FIFO_EN; /* Enable RX FIFO. */
attribute.fifoTxEn = UART_ATTR_TX_FIFO_EN; /* Enable TX FIFO. */
/* Set UART device attributes. */
ret = UartSetAttribute(handle, &attribute);
if (ret != 0) {
HDF_LOGE("UartSetAttribute: failed, ret %d\n", ret);
}
Obtaining UART Device Attributes
Call UartGetAttribute() to obtain the current UART device attributes.
int32_t UartGetAttribute(DevHandle handle, struct UartAttribute *attribute);
Table 6 Description of UartGetAttribute
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| handle | UART device handle. |
| attribute | Pointer to the UART device attributes obtained. |
| Return Value | Description |
| 0 | The operation is successful. |
| Negative value | The operation failed. |
Example: Obtain UART device attributes.
int32_t ret;
struct UartAttribute attribute;
/* Obtain UART device attributes. */
ret = UartGetAttribute(handle, &attribute);
if (ret != 0) {
HDF_LOGE("UartGetAttribute: failed, ret %d\n", ret);
}
Setting the UART Transmission Mode
Call UartSetTransMode() to set the UART transmission mode.
int32_t UartSetTransMode(DevHandle handle, enum UartTransMode mode);
Table 7 Description of UartSetTransMode
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| handle | UART device handle. |
| mode | UART transmission mode to set. |
| Return Value | Description |
| 0 | The operation is successful. |
| Negative value | The operation failed. |
Example: Set the UART transmission mode to UART_MODE_RD_BLOCK.
int32_t ret;
/* Set the UART transmission mode. */
ret = UartSetTransMode(handle, UART_MODE_RD_BLOCK);
if (ret != 0) {
HDF_LOGE("UartSetTransMode: failed, ret %d\n", ret);
}
Writing Data to a UART Device
Call UartWrite() to write data of the specified length to a UART device.
int32_t UartWrite(DevHandle handle, uint8_t *data, uint32_t size);
Table 8 Description of UartWrite
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| handle | UART device handle. |
| data | Pointer to the data to write. |
| size | Length of the data to write. |
| Return Value | Description |
| 0 | The operation is successful. |
| Negative value | The operation failed. |
Example: Write data to a UART device.
int32_t ret;
uint8_t wbuff[5] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
/* Write 5-byte data to the UART device. */
ret = UartWrite(handle, wbuff, 5);
if (ret != 0) {
HDF_LOGE("UartWrite: failed, ret %d\n", ret);
}
Reading Data from a UART Device
Call UartRead() to read data of the specified length from a UART device.
int32_t UartRead(DevHandle handle, uint8_t *data, uint32_t size);
Table 9 Description of UartRead
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| handle | UART device handle. |
| data | Pointer to the buffer for receiving the data. |
| size | Length of the data to read. |
| Return Value | Description |
| Non-negative value | The operation is successful. The length of the data read is returned. |
| Negative value | The operation failed. |
Example: Read data of the specified length from a UART device.
int32_t ret;
uint8_t rbuff[5] = {0};
/* Read 5-byte data from the UART device. */
ret = UartRead(handle, rbuff, 5);
if (ret < 0) {
HDF_LOGE("UartRead: failed, ret %d\n", ret);
}
CAUTION
Data is successfully read from the UART device if a non-negative value is returned. If 0 is returned, no valid data can be read from the UART device. A value greater than 0 indicates the length of the data read from the UART device. The data length must be less than or equal to the value of size and cannot exceed the maximum length of the data to read at a time specified by the UART controller in use.
Closing a UART Device Handle
Call UartClose() to close a UART device handle.
void UartClose(DevHandle handle);
This function releases the resources requested by UartOpen.
Table 10 Description of UartClose
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| handle | UART device handle to close. |
Example: Close a UART device handle.
UartClose(handle); /* Close the UART device handle. */
Example
The following example shows how to open a UART device handle, set the baud rate, device attributes, and transmission mode, read data from or write data into the UART device, and then close the UART device handle.
#include "hdf_log.h"
#include "uart_if.h"
void UartTestSample(void)
{
int32_t ret;
uint32_t port;
DevHandle handle = NULL;
uint8_t wbuff[5] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 };
uint8_t rbuff[5] = { 0 };
struct UartAttribute attribute;
attribute.dataBits = UART_ATTR_DATABIT_7; /* Enable 7 bits to be transferred each time. */
attribute.parity = UART_ATTR_PARITY_NONE; /* Disable parity check. */
attribute.stopBits = UART_ATTR_STOPBIT_1; /* Set the stop bit to 1. */
attribute.rts = UART_ATTR_RTS_DIS; /* Disable the RTS signal. */
attribute.cts = UART_ATTR_CTS_DIS; /* Disable the CTS signal. */
attribute.fifoRxEn = UART_ATTR_RX_FIFO_EN; /* Enable RX FIFO. */
attribute.fifoTxEn = UART_ATTR_TX_FIFO_EN; /* Enable TX FIFO. */
/* Enter the UART port number. */
port = 1;
/* Open the UART device handle based on the port number. */
handle = UartOpen(port);
if (handle == NULL) {
HDF_LOGE("UartOpen: failed!\n");
return;
}
/* Set the UART baud rate to 9600. */
ret = UartSetBaud(handle, 9600);
if (ret != 0) {
HDF_LOGE("UartSetBaud: failed, ret %d\n", ret);
goto _ERR;
}
/* Set UART device attributes. */
ret = UartSetAttribute(handle, &attribute);
if (ret != 0) {
HDF_LOGE("UartSetAttribute: failed, ret %d\n", ret);
goto _ERR;
}
/* Set the UART transmission mode to non-blocking mode. */
ret = UartSetTransMode(handle, UART_MODE_RD_NONBLOCK);
if (ret != 0) {
HDF_LOGE("UartSetTransMode: failed, ret %d\n", ret);
goto _ERR;
}
/* Write 5-byte data to the UART device. */
ret = UartWrite(handle, wbuff, 5);
if (ret != 0) {
HDF_LOGE("UartWrite: failed, ret %d\n", ret);
goto _ERR;
}
/* Read 5-byte data from the UART device. */
ret = UartRead(handle, rbuff, 5);
if (ret < 0) {
HDF_LOGE("UartRead: failed, ret %d\n", ret);
goto _ERR;
}
_ERR:
/* Close the UART device handle. */
UartClose(handle);
}