Data Synchronization Between UIAbility and UI
Based on the OpenHarmony application model, you can use any of the following ways to implement data synchronization between the UIAbility component and UI:
- Using EventHub for Data Synchronization: The EventHub object is provided by the base class Context. Events are transferred using the publish/subscribe (pub/sub) pattern. Specifically, after subscribing to an event, your application will receive the event and process it accordingly when the event is published.
- Using globalThis for Data Synchronization: globalThis is a global object inside the ArkTS engine instance and can be accessed by components such as UIAbility, ExtensionAbility, and Page.
- Using AppStorage or LocalStorage for Data Synchronization: ArkUI provides two application-level state management solutions: AppStorage and LocalStorage, which implement application- and UIAbility-level data synchronization, respectively.
Using EventHub for Data Synchronization
EventHub provides an event mechanism for the UIAbility or ExtensionAbility component so that they can subscribe to, unsubscribe from, and trigger events.
Before using the APIs provided by EventHub, you must obtain an EventHub object, which is provided by the base class Context. This section uses EventHub as an example to describe how to implement data synchronization between the UIAbility component and the UI.
-
Call eventHub.on() in the UIAbility in either of the following ways to register a custom event event1.
import UIAbility from '@ohos.app.ability.UIAbility'; const TAG: string = '[Example].[Entry].[EntryAbility]'; export default class EntryAbility extends UIAbility { func1(...data) { // Trigger the event to complete the service operation. console.info(TAG, '1. ' + JSON.stringify(data)); } onCreate(want, launch) { // Obtain an eventHub object. let eventhub = this.context.eventHub; // Subscribe to the event. eventhub.on('event1', this.func1); eventhub.on('event1', (...data) => { // Trigger the event to complete the service operation. console.info(TAG, '2. ' + JSON.stringify(data)); }); } } -
Call eventHub.emit() on the UI to trigger the event, and pass the parameters as required.
import common from '@ohos.app.ability.common'; @Entry @Component struct Index { private context = getContext(this) as common.UIAbilityContext; eventHubFunc() { // Trigger the event without parameters. this.context.eventHub.emit('event1'); // Trigger the event with one parameter. this.context.eventHub.emit('event1', 1); // Trigger the event with two parameters. this.context.eventHub.emit('event1', 2, 'test'); // You can design the parameters based on your service requirements. } // Page display. build() { ... } } -
Obtain the event trigger result from the subscription callback of UIAbility. The run log result is as follows:
[] [1] [2,'test'] -
After event1 is used, you can call eventHub.off() to unsubscribe from the event.
// context is the AbilityContext of the UIAbility instance. this.context.eventHub.off('event1');
Using globalThis for Data Synchronization
globalThis is a global object inside the ArkTS engine instance and can be used by UIAbility, ExtensionAbility, and Page inside the engine. Therefore, you can use globalThis for data synchronization.
Figure 1 Using globalThis for data synchronization
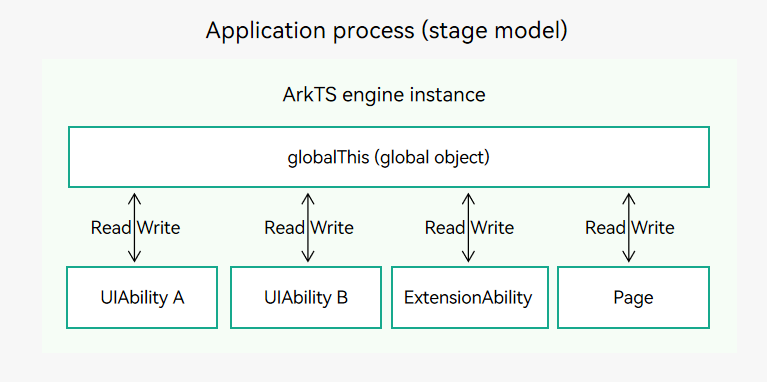
The following describes how to use globalThis in three scenarios. Precautions are provided as well.
- Using globalThis Between UIAbility and Page
- Using globalThis Between UIAbility and UIAbility
- Use globalThis Between UIAbility and ExtensionAbility
- Precautions for Using globalThis
Using globalThis Between UIAbility and Page
By binding attributes or methods to globalThis, you can implement data synchronization between the UIAbility component and UI. For example, if you bind the want parameter in the UIAbility component, you can use the want parameter information on the UI corresponding to the UIAbility component.
-
When startAbility() is called to start a UIAbility instance, the onCreate() callback is invoked, and the want parameter can be passed in the callback. Therefore, you can bind the want parameter to globalThis.
import UIAbility from '@ohos.app.ability.UIAbility'; export default class EntryAbility extends UIAbility { onCreate(want, launch) { globalThis.entryAbilityWant = want; ... } ... } -
Use globalThis on the UI to obtain the want parameter information.
let entryAbilityWant; @Entry @Component struct Index { aboutToAppear() { entryAbilityWant = globalThis.entryAbilityWant; } // Page display. build() { ... } }
Using globalThis Between UIAbility and UIAbility
To implement data synchronization between two UIAbility components in the same application, you can bind data to globalThis. For example, you can save data in globalThis in UIAbilityA and obtain the data from UIAbilityB.
-
UIAbilityA stores a string and binds it to globalThis.
import UIAbility from '@ohos.app.ability.UIAbility' export default class UIAbilityA extends UIAbility { onCreate(want, launch) { globalThis.entryAbilityStr = 'UIAbilityA'; // UIAbilityA stores the string "UIAbilityA" to globalThis. ... } } -
Obtain the data from UIAbilityB.
import UIAbility from '@ohos.app.ability.UIAbility' export default class UIAbilityB extends UIAbility { onCreate(want, launch) { // UIAbilityB reads name from globalThis and outputs it. console.info('name from entryAbilityStr: ' + globalThis.entryAbilityStr); ... } }
Using globalThis Between UIAbility and ExtensionAbility
To implement data synchronization between the UIAbility and ExtensionAbility components in the same application, you can bind data to globalThis. For example, you can save data in globalThis in UIAbilityA and obtain the data from ServiceExtensionAbility.
-
UIAbilityA stores a string and binds it to globalThis.
import UIAbility from '@ohos.app.ability.UIAbility' export default class UIAbilityA extends UIAbility { onCreate(want, launch) { // UIAbilityA stores the string "UIAbilityA" to globalThis. globalThis.entryAbilityStr = 'UIAbilityA'; ... } } -
Obtain the data from ExtensionAbility.
import Extension from '@ohos.app.ability.ServiceExtensionAbility' export default class ServiceExtAbility extends Extension { onCreate(want) { / / ServiceExtAbility reads name from globalThis and outputs it. console.info('name from entryAbilityStr: ' + globalThis.entryAbilityStr); ... } }
Precautions for Using globalThis
Figure 2 Precautions for globalThis
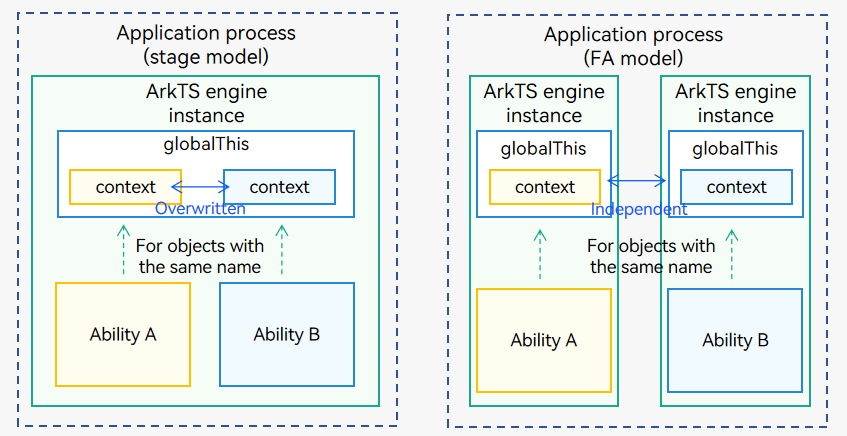
-
In the stage model, all the UIAbility components in a process share one ArkTS engine instance. When using globalThis, do not store objects with the same name. For example, if UIAbilityA and UIAbilityB use globalThis to store two objects with the same name, the object stored earlier will be overwritten.
-
This problem does not occur in the FA model because each UIAbility component uses an independent engine.
-
The lifecycle of an object bound to globalThis is the same as that of the ArkTS engine instance. You are advised to assign the value null after using the object to minimize memory usage.
The following provides an example to describe the object overwritten problem in the stage model.
-
In the UIAbilityA file, UIAbilityContext is stored in globalThis.
import UIAbility from '@ohos.app.ability.UIAbility' export default class UIAbilityA extends UIAbility { onCreate(want, launch) { globalThis.context = this.context; // UIAbilityA stores the context in globalThis. ... } } -
Obtain and use UIAbilityContext on the page of UIAbilityA. After the UIAbilityA instance is used, switch it to the background.
@Entry @Component struct Index { onPageShow() { let ctx = globalThis.context; // Obtain the context from globalThis and use it. } // Page display. build() { ... } } -
In the UIAbilityB file, UIAbilityContext is stored in globalThis and has the same name as that in the UIAbilityA file.
import UIAbility from '@ohos.app.ability.UIAbility' export default class UIAbilityB extends UIAbility { onCreate(want, launch) { // UIAbilityB overwrites the context stored by UIAbilityA in globalThis. globalThis.context = this.context; ... } } -
Obtain and use UIAbilityContext on the page of UIAbilityB. The obtained globalThis.context is the value of UIAbilityContext in UIAbilityB.
@Entry @Component struct Index { onPageShow() { let ctx = globalThis.context; // Obtain the context from globalThis and use it. } // Page display. build() { ... } } -
Switch the UIAbilityB instance to the background and switch the UIAbilityA instance to the foreground. In this case, UIAbilityA will not enter the onCreate() lifecycle again.
import UIAbility from '@ohos.app.ability.UIAbility' export default class UIAbilityA extends UIAbility { onCreate(want, launch) { // UIAbilityA will not enter this lifecycle. globalThis.context = this.context; ... } } -
When the page of UIAbilityA is displayed, the obtained globalThis.context is UIAbilityContext of UIAbilityB instead of UIAbilityA. An error occurs.
@Entry @Component struct Index { onPageShow() { let ctx = globalThis.context; // The context in globalThis is the context of UIAbilityB. } // Page display. build() { ... } }
Using AppStorage or LocalStorage for Data Synchronization
ArkUI provides AppStorage and LocalStorage to implement application- and UIAbility-level data synchronization, respectively. Both solutions can be used to manage the application state, enhance application performance, and improve user experience. The AppStorage is a global state manager and is applicable when multiple UIAbilities share the same state data. The LocalStorage is a local state manager that manages state data used inside a single UIAbility. They help you control the application state more flexibly and improve the maintainability and scalability of applications. For details, see State Management of Application-Level Variables.