Camera
Overview
Camera
The OpenHarmony camera driver model implements the camera hardware device interface (HDI) and the camera pipeline model to manage camera devices. The camera driver model consists of the following layers:
- HDI implementation layer: implements standard ohos (OpenHarmony operating system) APIs for cameras.
- Framework layer: connects to the HDI implementation layer for control instruction and stream transfer, establishes data channels, and manages camera devices.
- Device adaptation layer: shields the differences between underlying chips and OSs for multi-platform adaptation.
Working Principles
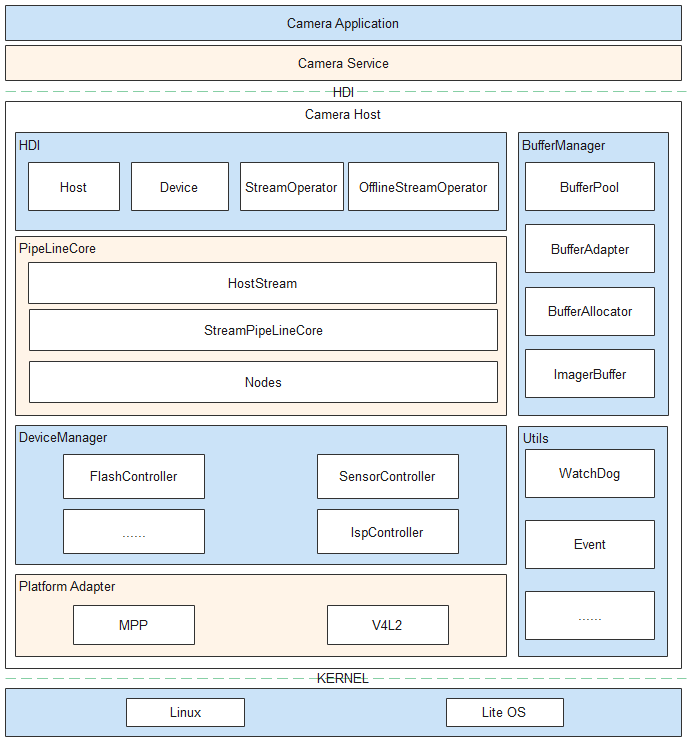
The camera module is used to initialize services and devices, set up data channels, and configure, create, deliver, and capture streams. The figure below illustrates camera driver model.
Figure 1 HDF-based camera driver model
-
When the system starts, the camera_host process is created. The process enumerates underlying devices, creates a DeviceManager instance that manages the device tree, an object for each underlying device, and a CameraHost instance, and registers the CameraHost instance with the UHDF service. Through the UHDF service, the camera service can obtain the underlying CameraDeviceHost services to operate the hardware devices. Note that the DeviceManager instance can also be created by using the configuration table.
-
The Camera Service obtains the CameraHost instance through the CameraDeviceHost service. The CameraHost instance can be used to obtain the bottom-layer camera capabilities, turn on the flashlight, call the Open() interface to start the camera and create a connection, create a DeviceManager instance (powering on the bottom-layer hardware modules), and create a CameraDevice instance (providing the device control interface for the upper layer). When the CameraDevice instance is created, each submodule of PipelineCore is instantiated. Among the submodules, StreamPipelineCore is responsible for creating pipelines, and MetaQueueManager is responsible for reporting metadata.
-
The Camera Service configures stream and creates a Stream class through the CameraDevice module. The StreamPipelineStrategy module creates the node connection mode of the corresponding stream by using the mode issued by the upper layer and querying the configuration table. The StreamPipelineBuilder module creates a node and returns the pipeline to the StreamPipelineDispatcher module through the connection. The StreamPipelineDispatcher module dispatches pipelines.
-
The Camera Service controls the stream operations through the Stream instance. The AttachBufferQueue() interface is used to deliver the buffer queue requested from the display module to the bottom layer. The CameraDeviceDriverModel manages the buffer. After the Capture() interface is called to deliver commands, the bottom layer transfers the buffer to the upper layer. The Image Signal Processor (ISP) node obtains a specified number of buffers from the buffer queue and delivers the buffers to the bottom-layer ISP hardware. After filling the buffers, the ISP hardware transfers the buffers to the CameraDeviceDriverModel. The CameraDeviceDriverModel fills the created pipeline with the received buffers by using a loop thread. Each node processes the pipeline data and transfers the data to the upper layer by using a callback. At the same time, the buffers are freed for reuse.
-
The Camera Service delivers the photographing command through the Capture() interface. The ChangeToOfflineStream() interface is used to query the position of the photographing buffer. If the ISP hardware has output an image and sent the image data to the IPP node, the common photographing streams can be converted into offline streams. Otherwise, the close process is executed. The ChangeToOfflineStream() interface transfers StreamInfo to enable the offline stream to obtain the stream information of the common stream, confirms the node connection mode of the offline stream based on the configuration table, and creates the node connection of the offline stream. If the node connection has been created, the interface releases the node required by the non-offline stream through CloseCamera(). It then waits for the buffer to return from the bottom-layer pipeline to the upper layer and then releases the pipeline resources.
-
The Camera Service sends the CaptureSetting parameter to the CameraDeviceDriverModel through the UpdateSettings() interface of the CameraDevice instance. The CameraDeviceDriverModel forwards the parameter to each node through the StreamPipelineDispatcher module. The CaptureSetting parameter carried in StartStreamingCapture() and Capture() is forwarded to the node to which the stream belongs through the StreamPipelineDispatcher module.
-
The Camera Service controls underlying metadata reporting through the EnableResult() and DisableResult() interfaces. If the underlying metadata needs to be reported, the pipeline creates a buffer queue in the CameraDeviceDriverModel to collect and transfer metadata, queries the configuration table based on the StreamPipelineStrategy module, and creates and connects to the specified node through the StreamPipelineBuilder module. The MetaQueueManager module delivers the buffer to the bottom layer, and the bottom-layer node fills in data. The MetaQueueManager module then invokes the upper-layer callback to transfer the data to the upper layer.
-
The Camera Service calls the Close() interface of the CameraDevice class, and the CameraDevice instance calls the corresponding DeviceManager module to power off each hardware. If an offline stream exists in the subpipeline of the IPP node, the offline stream must be reserved until the execution is complete.
-
To implement dynamic frame control, a CollectBuffer thread is started in the StreamOperator. The CollectBuffer thread obtains a buffer from the buffer queue of each stream. If the frame rate of a stream needs to be controlled (1/n of the sensor output frame rate), the CollectBuffer thread can control the buffer packaging of each frame as required, and determine whether to collect the buffer of the stream. For example, if the output frame rate of the sensor is 120 fps and the preview stream frame rate is 30 fps, the CollectBuffer thread collects the buffer of the preview stream every 4 fps.
Development Guidelines
When to Use
The camera module encapsulates camera operations in camera preview, photographing, and video streams to facilitate camera hardware operations and improve development efficiency.
Available APIs
- icamera_device.h
| API | Description |
|---|---|
| CamRetCode GetStreamOperator( const OHOS::sptr OHOS::sptr |
Obtains the stream controller. |
| CamRetCode UpdateSettings(const std::shared_ptr |
Updates device control parameters. |
| CamRetCode SetResultMode(const ResultCallbackMode &mode) | Sets the result callback mode and function. |
| CamRetCode GetEnabledResults(std::vector |
Obtains the enabled ResultMeta. |
| CamRetCode EnableResult(const std::vector |
Enables specific ResultMeta. |
| CamRetCode DisableResult(const std::vector |
Disables specific ResultMeta. |
| void Close() | Closes the camera device. |
- icamera_device_callback.h
| API | Description |
|---|---|
| void OnError(ErrorType type, int32_t errorCode) | Called when an error occurs on the device to return error information. You need to implement this interface. |
| void OnResult(uint64_t timestamp, const std::shared_ptr |
Callback invoked to report metadata related to the camera device. |
- icamera_host.h
| API | Description |
|---|---|
| CamRetCode SetCallback(const OHOS::sptr |
Sets the ICameraHostCallback API. |
| CamRetCode GetCameraIds(std::vector<std::string> &cameraIds) | Obtains the IDs of available camera devices. |
| CamRetCode GetCameraAbility(const std::string &cameraId, std::shared_ptr |
Obtains the abilities of a camera device. |
| CamRetCode OpenCamera(const std::string &cameraId, const OHOS::sptr OHOS::sptr |
Opens a camera. |
| CamRetCode SetFlashlight(const std::string &cameraId, bool &isEnable) | Turns on or off the flash. |
- icamera_host_callback.h
| API | Description |
|---|---|
| void OnCameraStatus(const std::string &cameraId, CameraStatus status) | Reports camera status changes. |
| void OnFlashlightStatus(const std::string &cameraId, FlashlightStatus status) | Callback invoked to report the flash status changes. |
- ioffline_stream_operator.h
| API | Description |
|---|---|
| CamRetCode CancelCapture(int captureId) | Cancels a capture request. |
| CamRetCode ReleaseStreams(const std::vector |
Releases streams. |
| CamRetCode Release() | Releases all offline streams. |
- istream_operator.h
| API | Description |
|---|---|
| CamRetCode IsStreamsSupported( OperationMode mode, const std::shared_ptr<Camera::CameraMetadata> &modeSetting, const std::vector<std::shared_ptr<StreamInfo>> &info, StreamSupportType &type) |
Checks whether a stream can be added. |
| CamRetCode CreateStreams(const std::vector<std::shared_ptr |
Creates streams. |
| CamRetCode ReleaseStreams(const std::vector |
Releases streams. |
| CamRetCode CommitStreams(OperationMode mode, const std::shared_ptr |
Configure streams. |
| CamRetCode GetStreamAttributes( std::vector<std::shared_ptr |
Obtain stream attributes. |
| CamRetCode AttachBufferQueue(int streamId, const OHOS::sptr<OHOS::IBufferProducer> &producer) | Attaches a producer handle to a stream. |
| CamRetCode DetachBufferQueue(int streamId) | Detaches a producer handle from a stream. |
| CamRetCode Capture(int captureId, const std::shared_ptr |
Captures images. |
| CamRetCode CancelCapture(int captureId) | Cancels a capture. |
| CamRetCode ChangeToOfflineStream(const std::vector OHOS::sptr OHOS::sptr |
Changes a stream into an offline stream. |
- istream_operator_callback.h
| API | Description |
|---|---|
| void OnCaptureStarted(int32_t captureId, const std::vector<int32_t> &streamIds) | Called when a capture starts. |
| void OnCaptureEnded(int32_t captureId, const std::vector<std::shared_ptr |
Called when a capture ends. |
| void OnCaptureError(int32_t captureId, const std::vector<std::shared_ptr |
Called when an error occurs during the capture. |
| void OnFrameShutter(int32_t captureId, const std::vector<int32_t> &streamIds, uint64_t timestamp) |
Called when a frame is captured. |
How to Develop
To camera driver development procedure is as follows:
-
Register a CameraHost.
Define the HdfDriverEntry structure to define the method for initializing a CameraHost.
struct HdfDriverEntry g_cameraHostDriverEntry = { .moduleVersion = 1, .moduleName = "camera_service", .Bind = HdfCameraHostDriverBind, .Init = HdfCameraHostDriverInit, .Release = HdfCameraHostDriverRelease, }; HDF_INIT(g_cameraHostDriverEntry); // Register the HdfDriverEntry structure with the HDF. -
Initialize the CameraHost.
HdfCameraHostDriverBind defined in the HdfDriverEntry structure provides the registration of CameraServiceDispatch() and CameraHostStubInstance(). CameraServiceDispatch() is used to remotely call a method of the CameraHost, such as OpenCamera() and SetFlashlight(). CameraHostStubInstance() is used to initialize the camera device, which is called during system startup.
int HdfCameraHostDriverBind(HdfDeviceObject *deviceObject)
{
HDF_LOGI("HdfCameraHostDriverBind enter!");
if (deviceObject == nullptr) {
HDF_LOGE("HdfCameraHostDriverBind: HdfDeviceObject is NULL !");
return HDF_FAILURE;
}
HdfCameraService *hdfCameraService = reinterpret_cast<HdfCameraService *>(OsalMemAlloc(sizeof(HdfCameraService)));
if (hdfCameraService == nullptr) {
HDF_LOGE("HdfCameraHostDriverBind OsalMemAlloc HdfCameraService failed!");
return HDF_FAILURE;
}
hdfCameraService->ioservice.Dispatch = CameraServiceDispatch; // Used to call methods of the CameraHost.
hdfCameraService->ioservice.Open = nullptr;
hdfCameraService->ioservice.Release = nullptr;
hdfCameraService->instance = CameraHostStubInstance(); // Initialize the camera device.
deviceObject->service = &hdfCameraService->ioservice;
return HDF_SUCCESS;
}
The following functions are the implementation of the methods of the CameraHost:
int32_t CameraHostStub::CameraHostServiceStubOnRemoteRequest(int cmdId, MessageParcel &data,
MessageParcel &reply, MessageOption &option)
{
switch(cmdId) {
case CMD_CAMERA_HOST_SET_CALLBACK: {
return CameraHostStubSetCallback(data, reply, option);
}
case CMD_CAMERA_HOST_GET_CAMERAID: {
return CameraHostStubGetCameraIds(data, reply, option);
}
case CMD_CAMERA_HOST_GET_CAMERA_ABILITY: {
return CameraHostStubGetCameraAbility(data, reply, option);
}
case CMD_CAMERA_HOST_OPEN_CAMERA: {
return CameraHostStubOpenCamera(data, reply, option);
}
case CMD_CAMERA_HOST_SET_FLASH_LIGHT: {
return CameraHostStubSetFlashlight(data, reply, option);
}
default: {
HDF_LOGE("%s: not support cmd %d", __func__, cmdId);
return HDF_ERR_INVALID_PARAM;
}
}
return HDF_SUCCESS;
}
CameraHostStubInstance() finally calls CameraHostImpl::Init() to obtain the physical camera and initialize the DeviceManager and PipelineCore modules.
- Obtain the CameraHost.
Call the Get() interface to obtain the CameraHost from the CameraService. The Get() interface is as follows:
sptr<ICameraHost> ICameraHost::Get(const char *serviceName)
{
do {
using namespace OHOS::HDI::ServiceManager::V1_0;
auto servMgr = IServiceManager::Get();
if (servMgr == nullptr) {
HDF_LOGE("%s: IServiceManager failed!", __func__);
break;
}
auto remote = servMgr->GetService(serviceName); // Obtain the CameraHost based on serviceName.
if (remote != nullptr) {
sptr<CameraHostProxy> hostSptr = iface_cast<CameraHostProxy>(remote); // Return the CameraHostProxy object that contains interfaces such as OpenCamera() to the caller.
return hostSptr;
}
HDF_LOGE("%s: GetService failed! serviceName = %s", __func__, serviceName);
} while(false);
HDF_LOGE("%s: get %s failed!", __func__, serviceName);
return nullptr;
}
- Implement the OpenCamera() interface.
The CameraHostProxy class provides five interfaces: SetCallback(), GetCameraIds(), GetCameraAbility(), OpenCamera(), and SetFlashlight(). The following describes OpenCamera(). The OpenCamera() interface calls the remote CameraHostStubOpenCamera() interface through the CMD_CAMERA_HOST_OPEN_CAMERA to obtain an ICameraDevice object.
CamRetCode CameraHostProxy::OpenCamera(const std::string &cameraId, const OHOS::sptr<ICameraDeviceCallback> &callback, OHOS::sptr<ICameraDevice> &pDevice)
{
int32_t ret = Remote()->SendRequest(CMD_CAMERA_HOST_REMOTE_OPEN_CAMERA, data, reply, option);
if (ret != HDF_SUCCESS) {
HDF_LOGE("%{public}s: SendRequest failed, error code is %{public}d", __func__, ret);
return INVALID_ARGUMENT;
}
CamRetCode retCode = static_cast<CamRetCode>(reply.ReadInt32());
bool flag = reply.ReadBool();
if (flag) {
sptr<IRemoteObject> remoteCameraDevice = reply.ReadRemoteObject();
if (remoteCameraDevice == nullptr) {
HDF_LOGE("%{public}s: CameraHostProxy remoteCameraDevice is null", __func__);
}
pDevice = OHOS::iface_cast<ICameraDevice>(remoteCameraDevice);
}
return retCode;
}
Remote()->SendRequest calls CameraHostServiceStubOnRemoteRequest(), enters the CameraHostStubOpenCamera() interface based on cmdId, and finally calls CameraHostImpl::OpenCamera() to obtain a CameraDevice and power on the camera hardware.
CamRetCode CameraHostImpl::OpenCamera(const std::string &cameraId, const OHOS::sptr<ICameraDeviceCallback> &callback, OHOS::sptr<ICameraDevice> &device)
{
std::shared_ptr<CameraDeviceImpl> cameraDevice = std::static_pointer_cast<CameraDeviceImpl>(itr->second);
if (cameraDevice == nullptr) {
CAMERA_LOGE("camera device is null.");
return INSUFFICIENT_RESOURCES;
}
CamRetCode ret = cameraDevice->SetCallback(callback);
if (ret != NO_ERROR) {
CAMERA_LOGW("set camera device callback failed.");
return ret;
}
CameraHostConfig *config = CameraHostConfig::GetInstance();
if (config == nullptr) {
return INVALID_ARGUMENT;
}
std::vector<std::string> phyCameraIds;
RetCode rc = config->GetPhysicCameraIds(cameraId, phyCameraIds);
if (rc != RC_OK) {
CAMERA_LOGE("get physic cameraId failed.");
return DEVICE_ERROR;
}
if (CameraPowerUp(cameraId, phyCameraIds) != RC_OK) { // Power on the camera hardware.
CAMERA_LOGE("camera powerup failed.");
CameraPowerDown(phyCameraIds);
return DEVICE_ERROR;
}
auto sptrDevice = deviceBackup_.find(cameraId);
if (sptrDevice == deviceBackup_.end()) {
deviceBackup_[cameraId] = cameraDevice.get();
}
device = deviceBackup_[cameraId];
cameraDevice->SetStatus(true);
return NO_ERROR;
}
- Implement the GetStreamOperator() interface.
CameraDeviceImpl defines interfaces such as GetStreamOperator(), UpdateSettings(), SetResultMode(), and GetEnabledResult(). The following is an example of implementing the GetStreamOperator() interface:
CamRetCode CameraDeviceImpl::GetStreamOperator(const OHOS::sptr<IStreamOperatorCallback> &callback,
OHOS::sptr<IStreamOperator> &streamOperator)
{
if (callback == nullptr) {
CAMERA_LOGW("input callback is null.");
return INVALID_ARGUMENT;
}
spCameraDeviceCallback_ = callback;
if (spStreamOperator_ == nullptr) {
// Here, an spStreamOperator object is created and passed to the caller for stream operations.
spStreamOperator_ = new(std::nothrow) StreamOperatorImpl(spCameraDeviceCallback_, shared_from_this());
if (spStreamOperator_ == nullptr) {
CAMERA_LOGW("create stream operator failed.");
return DEVICE_ERROR;
}
ismOperator_ = spStreamOperator_;
}
streamOperator = ismOperator_;
spStreamOperator_->SetRequestCallback([this](){
spCameraDeviceCallback_->OnError(REQUEST_TIMEOUT, 0);
});
}
- Create a stream.
Fill in the StreamInfo structure before creating a stream by calling CreateStreams().
using StreamInfo = struct _StreamInfo {
int streamId_;
int width_; // Stream width
int height_; // Stream height
int format_; // Stream format, for example, PIXEL_FMT_YCRCB_420_SP
int dataSpace_;
StreamIntent intent_; // StreamIntent, for example, PREVIEW
bool tunneledMode_;
OHOS::sptr<OHOS::IBufferProducer> bufferQueue_; // The stream buffer queue can be created by using the streamCustomer->CreateProducer() interface.
int minFrameDuration_;
EncodeType encodeType_;
};
The CreateStreams() interface in the StreamOperatorImpl class is used to create a StreamBase instance, which can then be used to initialize operations such as CreateBufferPool() by using the init() interface.
RetCode StreamOperatorImpl::CreateStream(const std::shared_ptr<StreamInfo>& streamInfo)
{
static std::map<StreamIntent, std::string> typeMap = {
{PREVIEW, "PREVIEW"},
{VIDEO, "VIDEO"},
{STILL_CAPTURE, "STILL_CAPTURE"},
{POST_VIEW, "POST_VIEW"}, {ANALYZE, "ANALYZE"},
{CUSTOM, "CUSTOM"}
};
auto itr = typeMap.find(streamInfo->intent_);
if (itr == typeMap.end()) {
CAMERA_LOGE("do not support stream type. [type = %{public}d]", streamInfo->intent_);
return RC_ERROR;
}
std::shared_ptr<StreamBase> stream = StreamFactory::Instance().CreateShared(itr->second); // Create a StreamBase instance.
RetCode rc = stream->Init(streamInfo);
return RC_OK;
}
-
Configure the stream.
Use the CommitStreams() interface to configure the stream, including PipelineCore initialization and creation. It must be called after the stream is created.
CamRetCode StreamOperatorImpl::CommitStreams(OperationMode mode, const std::shared_ptr<Camera::CameraMetadata>& modeSetting) { auto cameraDevice = cameraDevice_.lock(); if (cameraDevice == nullptr) { CAMERA_LOGE("camera device closed."); return CAMERA_CLOSED; } std::shared_ptr<IPipelineCore> PipelineCore = std::static_pointer_cast<CameraDeviceImpl>(cameraDevice)->GetPipelineCore(); if (PipelineCore == nullptr) { CAMERA_LOGE("Failed to obtain PipelineCore."); return CAMERA_CLOSED; } streamPipeCore_ = PipelineCore->GetStreamPipelineCore(); if (streamPipeCore_ == nullptr) { CAMERA_LOGE("Failed to obtain the stream PipelineCore."); return DEVICE_ERROR; } RetCode rc = streamPipeCore_->Init(); // Initialize the PipelineCore. if (rc != RC_OK) { CAMERA_LOGE("Failed to initialize the stream PipelineCore."); return DEVICE_ERROR; } rc = streamPipeCore_->CreatePipeline(mode); // Create a pipeline. if (rc != RC_OK) { CAMERA_LOGE("Failed to create pipeline."); return INVALID_ARGUMENT; } return NO_ERROR; } -
Capture images.
Fill in the CaptureInfo structure before calling the Capture() method.
using CaptureInfo = struct _CaptureInfo { std::vector<int> streamIds_; // IDs of streams to be captured std::shared_ptr<Camera::CameraMetadata> captureSetting_; // Camera ability can be obtained through the GetCameraAbility() interface of CameraHost. bool enableShutterCallback_; };Use the Capture() interface in StreamOperatorImpl to call the CreateCapture() interface to capture streams.
CamRetCode StreamOperatorImpl::Capture(int captureId, const std::shared_ptr<CaptureInfo>& captureInfo, bool isStreaming) { if (!ValidCaptureInfo(captureId, captureInfo)) { CAMERA_LOGE("capture streamIds is empty. [captureId = %d]", captureId); return INVALID_ARGUMENT; } std::shared_ptr<CameraCapture> cameraCapture = nullptr; RetCode rc = CreateCapture(captureId, captureInfo, isStreaming, cameraCapture); if (rc != RC_OK) { CAMERA_LOGE("create capture is failed."); return DEVICE_ERROR; } { std::unique_lock<std::mutex> lock(captureMutex_); camerCaptureMap_.insert(std::make_pair(captureId, cameraCapture)); } rc = StartThread(); if (rc != RC_OK) { CAMERA_LOGE("preview start failed."); return DEVICE_ERROR; } return NO_ERROR; } -
Cancel the capture and release the offline stream.
Use the CancelCapture() interface in the StreamOperatorImpl class to cancel the stream capture based on captureId.
CamRetCode StreamOperatorImpl::CancelCapture(int captureId) { auto itr = camerCaptureMap_.find(captureId); // Search for the CameraCapture object in the Map based on the captureId. RetCode rc = itr->second->Cancel(); // Call the Cancel() interface in CameraCapture to cancel the stream capture. std::unique_lock<std::mutex> lock(captureMutex_); camerCaptureMap_.erase(itr); // Erase the CameraCapture object. return NO_ERROR; }Use the ReleaseStreams() interface in the StreamOperatorImpl class t release the streams created by using CreateStream() and CommitStreams() and destroy the pipeline.
CamRetCode StreamOperatorImpl::ReleaseStreams(const std::vector<int>& streamIds) { RetCode rc = DestroyStreamPipeline(streamIds); // Destroy the pipeline based on streamIds. rc = DestroyHostStreamMgr(streamIds); rc = DestroyStreams(streamIds); // Destroy the stream specified by streamIds. return NO_ERROR; } -
Close the camera device.
Use the Close() interface in the CameraDeviceImpl class to close the camera device. This interface calls PowerDown() in the DeviceManager to power off the device.
Development Example
There is a camera demo in the /drivers/peripheral/camera/hal/init directory. After system startup, the executable file ohos_camera_demo is generated in the /vendor/bin directory. This demo can implement basic camera capabilities such as preview and photographing. The following uses the demo as an example to describe how to use the HDI to write the PreviewOn() and CaptureON() instances. For details, see ohos_camera_demo.
-
Construct a CameraDemo object in the main function. This object contains methods for initializing the camera and starting, stopping, and releasing streams. The mainDemo->InitSensors() function is used to initialize the CameraHost, and the mainDemo->InitCameraDevice() function is used to initialize the CameraDevice.
int main(int argc, char** argv) { RetCode rc = RC_OK; auto mainDemo = std::make_shared<CameraDemo>(); rc = mainDemo->InitSensors(); // Initialize the CameraHost. if (rc == RC_ERROR) { CAMERA_LOGE("main test: mainDemo->InitSensors() error\n"); return -1; } rc = mainDemo->InitCameraDevice(); // Initialize the CameraDevice. if (rc == RC_ERROR) { CAMERA_LOGE("main test: mainDemo->InitCameraDevice() error\n"); return -1; } rc = PreviewOn(0, mainDemo); // Configure and enable streams. if (rc != RC_OK) { CAMERA_LOGE("main test: PreviewOn() error demo exit"); return -1; } ManuList(mainDemo, argc, argv); // Print the menu to the console. return RC_OK; }The function used to initialize the CameraHost is implemented as follows, where the HDI ICameraHost::Get() is called to obtain the demoCameraHost and set the callback:
RetCode CameraDemo::InitSensors() { demoCameraHost_ = ICameraHost::Get(DEMO_SERVICE_NAME); if (demoCameraHost_ == nullptr) { CAMERA_LOGE("demo test: ICameraHost::Get error"); return RC_ERROR; } hostCallback_ = new CameraHostCallback(); rc = demoCameraHost_->SetCallback(hostCallback_); return RC_OK; }The implementation of the function for initializing the CameraDevice is as follows, where the GetCameraIds(cameraIds_), GetCameraAbility(cameraId, ability_), and OpenCamera(cameraIds_.front(), callback, demoCameraDevice_) interfaces are called to obtain the demoCameraHost.
RetCode CameraDemo::InitCameraDevice() { (void)demoCameraHost_->GetCameraIds(cameraIds_); const std::string cameraId = cameraIds_.front(); demoCameraHost_->GetCameraAbility(cameraId, ability_); sptr<CameraDeviceCallback> callback = new CameraDeviceCallback(); rc = demoCameraHost_->OpenCamera(cameraIds_.front(), callback, demoCameraDevice_); return RC_OK; } -
Implement the PreviewOn() interface to configure streams, enable preview streams, and start stream capture. After this interface is called, the camera preview channel starts running. Two streams are enabled: preview stream and capture or video stream. Only the preview stream will be captured.
static RetCode PreviewOn(int mode, const std::shared_ptr<CameraDemo>& mainDemo) { rc = mainDemo->StartPreviewStream(); // Configure the preview stream. if (mode == 0) { rc = mainDemo->StartCaptureStream(); // Configure the capture stream. } else { rc = mainDemo->StartVideoStream(); // Configure the video stream. } rc = mainDemo->CaptureON(STREAM_ID_PREVIEW, CAPTURE_ID_PREVIEW, CAPTURE_PREVIEW); // Capture the preview stream. return RC_OK; }The StartCaptureStream(), StartVideoStream(), and StartPreviewStream() interfaces call the CreateStream() interface with different input parameters.
RetCode CameraDemo::StartVideoStream() { RetCode rc = RC_OK; if (isVideoOn_ == 0) { isVideoOn_ = 1; rc = CreateStream(STREAM_ID_VIDEO, streamCustomerVideo_, VIDEO); // To enable the preview stream or capture stream, change the input parameters. } return RC_OK; }The CreateStream() interface calls the HDI to configure and create a stream. Specifically, the interface first calls the HDI to obtain a StreamOperation object and then creates a StreamInfo object. Call CreateStreams() and CommitStreams() to create and configure a stream.
RetCode CameraDemo::CreateStreams(const int streamIdSecond, StreamIntent intent) { std::vector<std::shared_ptr<StreamInfo>> streamInfos; std::vector<std::shared_ptr<StreamInfo>>().swap(streamInfos); GetStreamOpt(); // Obtain a StreamOperator object. std::shared_ptr<StreamInfo> previewStreamInfo = std::make_shared<StreamInfo>(); SetStreamInfo(previewStreamInfo, streamCustomerPreview_, STREAM_ID_PREVIEW, PREVIEW); // Fill in the StreamInfo. if (previewStreamInfo->bufferQueue_ == nullptr) { CAMERA_LOGE("demo test: CreateStream CreateProducer(); is nullptr\n"); return RC_ERROR; } streamInfos.push_back(previewStreamInfo); std::shared_ptr<StreamInfo> secondStreamInfo = std::make_shared<StreamInfo>(); if (streamIdSecond == STREAM_ID_CAPTURE) { SetStreamInfo(secondStreamInfo, streamCustomerCapture_, STREAM_ID_CAPTURE, intent); } else { SetStreamInfo(secondStreamInfo, streamCustomerVideo_, STREAM_ID_VIDEO, intent); } if (secondStreamInfo->bufferQueue_ == nullptr) { CAMERA_LOGE("demo test: CreateStreams CreateProducer() secondStreamInfo is nullptr\n"); return RC_ERROR; } streamInfos.push_back(secondStreamInfo); rc = streamOperator_->CreateStreams(streamInfos); // Create a stream. if (rc != Camera::NO_ERROR) { CAMERA_LOGE("demo test: CreateStream CreateStreams error\n"); return RC_ERROR; } rc = streamOperator_->CommitStreams(Camera::NORMAL, ability_); if (rc != Camera::NO_ERROR) { CAMERA_LOGE("demo test: CreateStream CommitStreams error\n"); std::vector<int> streamIds = {STREAM_ID_PREVIEW, streamIdSecond}; streamOperator_->ReleaseStreams(streamIds); return RC_ERROR; } return RC_OK; }The CaptureON() interface calls the Capture() interface of StreamOperator to obtain camera data, rotate the buffer, and start a thread to receive data of the corresponding type.
RetCode CameraDemo::CaptureON(const int streamId, const int captureId, CaptureMode mode) { std::shared_ptr<Camera::CaptureInfo> captureInfo = std::make_shared<Camera::CaptureInfo>(); // Create and fill in CaptureInfo. captureInfo->streamIds_ = {streamId}; captureInfo->captureSetting_ = ability_; captureInfo->enableShutterCallback_ = false; int rc = streamOperator_->Capture(captureId, captureInfo, true);// The stream capture starts, and buffer recycling starts. if (mode == CAPTURE_PREVIEW) { streamCustomerPreview_->ReceiveFrameOn(nullptr); // Create a preview thread to receive the passed buffers. } else if (mode == CAPTURE_SNAPSHOT) { streamCustomerCapture_->ReceiveFrameOn([this](void* addr, const uint32_t size) { // Create a capture thread to receive the passed buffers through the StoreImage callback. StoreImage(addr, size); }); } else if (mode == CAPTURE_VIDEO) { OpenVideoFile(); streamCustomerVideo_->ReceiveFrameOn([this](void* addr, const uint32_t size) {// Create a video thread to receive the passed buffer by calling the StoreVideo callback. StoreVideo(addr, size); }); } return RC_OK; } -
Implement the ManuList() function to obtain characters from the console through the fgets() interface. Different characters correspond to different capabilities provided by the demo, and the functionality menu is printed.
static void ManuList(const std::shared_ptr<CameraDemo>& mainDemo, const int argc, char** argv) { int idx, c; int awb = 1; constexpr char shortOptions[] = "h:cwvaqof:"; c = getopt_long(argc, argv, shortOptions, longOptions, &idx); while(1) { switch (c) { case 'h': c = PutMenuAndGetChr(); // Print the menu. break; case 'f': FlashLightTest(mainDemo); // Test the flashlight capability. c = PutMenuAndGetChr(); break; case 'o': OfflineTest(mainDemo); // Test the offline capability. c = PutMenuAndGetChr(); break; case 'c': CaptureTest(mainDemo); // Test the capture capability. c = PutMenuAndGetChr(); break; case 'w': // Test the AWB capability. if (awb) { mainDemo->SetAwbMode(OHOS_CAMERA_AWB_MODE_INCANDESCENT); } else { mainDemo->SetAwbMode(OHOS_CAMERA_AWB_MODE_OFF); } awb = !awb; c = PutMenuAndGetChr(); break; case 'a': // Test the AE capability. mainDemo->SetAeExpo(); c = PutMenuAndGetChr(); break; case 'v': // Test the video capability. VideoTest(mainDemo); c = PutMenuAndGetChr(); break; case 'q': // Exit the demo. PreviewOff(mainDemo); mainDemo->QuitDemo(); exit(EXIT_SUCCESS); default: CAMERA_LOGE("main test: command error please retry input command"); c = PutMenuAndGetChr(); break; } } }The PutMenuAndGetChr() interface prints the menu of the demo and calls fgets() to wait for commands from the console.
static int PutMenuAndGetChr(void) { constexpr uint32_t inputCount = 50; int c = 0; char strs[inputCount]; Usage(stdout); CAMERA_LOGD("pls input command(input -q exit this app)\n"); fgets(strs, inputCount, stdin); for (int i = 0; i < inputCount; i++) { if (strs[i] != '-') { c = strs[i]; break; } } return c; }The console outputs the menu details as follows:
"Options:\n" "-h | --help Print this message\n" "-o | --offline stream offline test\n" "-c | --capture capture one picture\n" "-w | --set WB Set white balance Cloudy\n" "-v | --video capture Video of 10s\n" "-a | --Set AE Set Auto exposure\n" "-f | --Set Flashlight Set flashlight ON 5s OFF\n" "-q | --quit stop preview and quit this app\n");