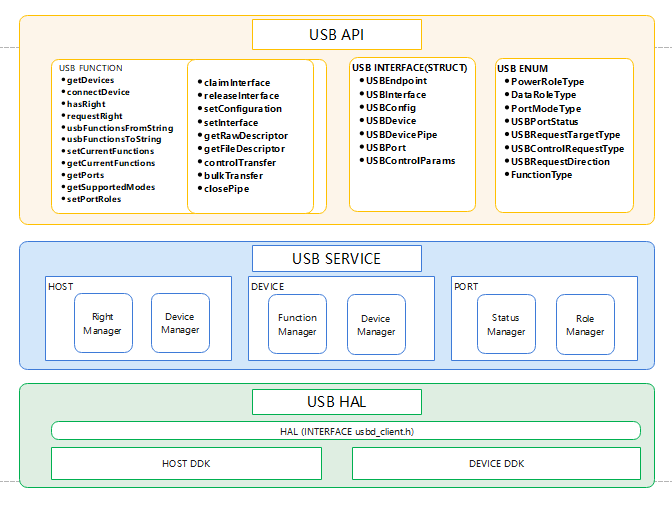
usb_srv_client.h
|
int32_t OpenDevice(const UsbDevice &device, USBDevicePipe &pip);
|
Opens a USB device to set up a connection.
|
int32_t HasRight(std::string deviceName);
|
Checks whether the user has the permission to access the USB device.
|
int32_t RequestRight(std::string deviceName);
|
Requests the temporary permission for a given application to access the USB device.
|
int32_t GetDevices(std::vector &deviceList);
|
Obtains the USB device list.
|
int32_t ClaimInterface(USBDevicePipe &pip, const UsbInterface &interface, bool force);
|
Claims a USB interface exclusively. This must be done before data transfer.
|
int32_t ReleaseInterface(USBDevicePipe &pip, const UsbInterface &interface);
|
Releases a USB interface. This is usually done after data transfer.
|
int32_t BulkTransfer(USBDevicePipe &pip, const USBEndpoint &endpoint, std::vector &vdata, int32_t timeout);
|
Performs a bulk transfer on a specified endpoint. The data transfer direction is determined by the endpoint direction.
|
int32_t ControlTransfer(USBDevicePipe &pip, const UsbCtrlTransfer &ctrl, std::vector &vdata);
|
Performs a control transfer for endpoint 0 of the device. The transmission direction is determined by the request type.
|
int32_t SetConfiguration(USBDevicePipe &pip, const USBConfig &config);
|
Sets the current configuration of the USB device.
|
int32_t SetInterface(USBDevicePipe &pipe, const UsbInterface &interface);
|
Sets the alternate settings for the specified USB interface. This allows you to switch between two interfaces with the same ID but different alternate settings.
|
int32_t GetRawDescriptors(std::vector &vdata);
|
Obtains the raw USB descriptor.
|
int32_t GetFileDescriptor();
|
Obtains the file descriptor.
|
bool Close(const USBDevicePipe &pip);
|
Closes a USB device to release all system resources related to the device.
|
int32_t PipeRequestWait(USBDevicePipe &pip, int64_t timeout, UsbRequest &req);
|
Obtains the isochronous transfer result.
|
int32_t RequestInitialize(UsbRequest &request);
|
Initializes the isochronous transfer request.
|
int32_t RequestFree(UsbRequest &request);
|
Frees the isochronous transfer request.
|
|
| int32_t RequestAbort(UsbRequest &request);
|
Cancels the data transfer requests to be processed.
|
int32_t RequestQueue(UsbRequest &request);
|
Sends or receives isochronous transfer requests on a specified endpoint. The data transfer direction is determined by the endpoint direction.
|
int32_t BulkRequstDataSize(const UsbDev &dev, const UsbPipe &pipe, uint32_t &length);
|
Reads bulk data during isochronous transfer. This method is applicable to transfer of a huge amount of data.
|
int32_t BulkReadData(const UsbDev &dev, const UsbPipe &pipe, std::vector &data);
|
Obtains the data reading result. Use this method together with BulkReadData.
|
int32_t BulkWriteData(const UsbDev &dev, const UsbPipe &pipe, const std::vector &data);
|
Writes bulk data during isochronous transfer. This method is applicable to transfer of a huge amount of data.
|
int32_t BulkGetWriteCompleteLength(const UsbDev &dev, const UsbPipe &pipe, uint32_t &length);
|
Obtains the data writing status based on length. Use this method together with BulkWriteData.
|