MMC
Overview
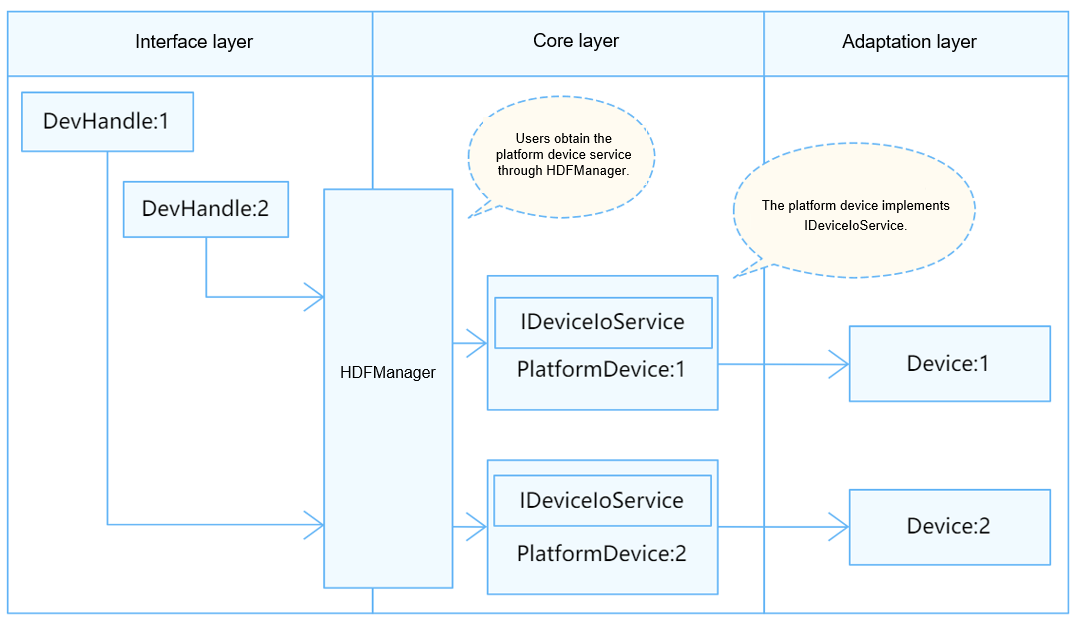
In the Hardware Driver Foundation (HDF) framework, the MultiMedia Card (MMC) uses the independent service mode for API adaptation. In this mode, each device independently publishes a device service to handle external access requests. After receiving an access request from an API, the device manager extracts the parameters in the request to call the internal method of the target device. In the independent service mode, the service management capabilities of the HDFDeviceManager can be directly used. However, you need to configure a device node for each device, which increases the memory usage.
Figure 1 Independent service mode
Available APIs
MmcCntlrOps
struct MmcCntlrOps {
int32_t (*request)(struct MmcCntlr *cntlr, struct MmcCmd *cmd);
int32_t (*setClock)(struct MmcCntlr *cntlr, uint32_t clock);
int32_t (*setPowerMode)(struct MmcCntlr *cntlr, enum MmcPowerMode mode);
int32_t (*setBusWidth)(struct MmcCntlr *cntlr, enum MmcBusWidth width);
int32_t (*setBusTiming)(struct MmcCntlr *cntlr, enum MmcBusTiming timing);
int32_t (*setSdioIrq)(struct MmcCntlr *cntlr, bool enable);
int32_t (*hardwareReset)(struct MmcCntlr *cntlr);
int32_t (*systemInit)(struct MmcCntlr *cntlr);
int32_t (*setEnhanceSrobe)(struct MmcCntlr *cntlr, bool enable);
int32_t (*switchVoltage)(struct MmcCntlr *cntlr, enum MmcVolt volt);
bool (*devReadOnly)(struct MmcCntlr *cntlr);
bool (*devPluged)(struct MmcCntlr *cntlr);
bool (*devBusy)(struct MmcCntlr *cntlr);
int32_t (*tune)(struct MmcCntlr *cntlr, uint32_t cmdCode);
int32_t (*rescanSdioDev)(struct MmcCntlr *cntlr);
};
Table 1 Callbacks for the members in the MmcCntlrOps structure
How to Develop
The MMC module adaptation involves the following steps:
-
Instantiate the driver entry.
- Instantiate the HdfDriverEntry structure.
- Call HDF_INIT to register the HdfDriverEntry instance with the HDF framework.
-
Configure attribute files.
- Add the deviceNode information to the device_info.hcs file.
- (Optional) Add the mmc_config.hcs file.
-
Instantiate the MMC controller object.
-
Initialize MmcCntlr.
-
Instantiate MmcCntlrOps in the MmcCntlr object.
 NOTE
NOTEFor details, see Available APIs.
-
-
Debug the driver.
- (Optional) For new drivers, verify basic functions, for example, verify the information returned after the mount operation and whether the device starts successfully.
Development Example
The following uses himci.c as an example to present the contents that need to be provided by the vendor to implement device functions.
-
Instantiate the driver entry. The driver entry must be a global variable of the HdfDriverEntry type (defined in hdf_device_desc.h), and the value of moduleName must be the same as that in device_info.hcs. In the HDF framework, the start address of each HdfDriverEntry object of all loaded drivers is collected to form a segment address space similar to an array for the upper layer to invoke.
Generally, HDF calls the Bind function and then the Init function to load a driver. If Init fails to be called, HDF calls Release to release driver resources and exit.
-
MMC driver entry reference
struct HdfDriverEntry g_mmcDriverEntry = { .moduleVersion = 1, .Bind = HimciMmcBind, // See the Bind function. .Init = HimciMmcInit, // See the Init function. .Release = HimciMmcRelease, //See the Release function. .moduleName = "hi3516_mmc_driver",// (Mandatory) The value must be the same as that of moduleName in the .hcs file. }; HDF_INIT(g_mmcDriverEntry); // Call HDF_INIT to register the driver entry with the HDF framework.
-
-
Add the deviceNode information to the device_info.hcs file and configure the device attributes in the mmc_config.hcs file. The deviceNode information is related to registration of the driver entry. The device attribute values are closely related to the default values or value ranges of the MmcCntlr members at the core layer.
If there are multiple devices, you need to add the deviceNode information to the device_info file and add the corresponding device attributes to the mmc_config file.
-
device_info.hcs configuration reference
root { device_info { match_attr = "hdf_manager"; platform :: host { hostName = "platform_host"; priority = 50; device_mmc:: device { device0 :: deviceNode { policy = 2; priority = 10; permission = 0644; moduleName = "hi3516_mmc_driver"; // (Mandatory) Driver name, which must be the same as the moduleName in the driver entry. serviceName = "HDF_PLATFORM_MMC_0"; // (Mandatory) Unique name of the service published by the driver deviceMatchAttr = "hi3516_mmc_emmc";// (Mandatory) Used to configure the private data of the controller. The value must be the same as the controller in mmc_config.hcs. } device1 :: deviceNode { policy = 1; priority = 20; permission = 0644; moduleName = "hi3516_mmc_driver"; serviceName = "HDF_PLATFORM_MMC_1"; deviceMatchAttr = "hi3516_mmc_sd"; // Indicates an SD. } device2 :: deviceNode { policy = 1; priority = 30; permission = 0644; moduleName = "hi3516_mmc_driver"; serviceName = "HDF_PLATFORM_MMC_2"; deviceMatchAttr = "hi3516_mmc_sdio";// Indicates an SDIO. } } } } } -
mmc_config.hcs configuration reference
root { platform { mmc_config { template mmc_controller {// Template configuration. In the template, you can configure the common parameters shared by service nodes. match_attr = ""; voltDef = 0; // 3.3V freqMin = 50000; // (Mandatory) Minimum frequency freqMax = 100000000; // (Mandatory) Maximum frequency freqDef = 400000; // (Mandatory) Default frequency maxBlkNum = 2048; // (Mandatory) Maximum block number maxBlkSize = 512; // (Mandatory) Maximum number of blocks ocrDef = 0x300000; // (Mandatory) Working voltage. caps2 = 0; // (Mandatory) Attribute register. For details, see MmcCaps2 in mmc_caps.h. regSize = 0x118; // (Mandatory) Register bit width hostId = 0; // (Mandatory) Host ID regBasePhy = 0x10020000;// (Mandatory) Physical base address of the register irqNum = 63; // (Mandatory) Interrupt number devType = 2; // (Mandatory) Device mode, which can be eMMC, SD, SDIO, or COMBO caps = 0x0001e045; // (Mandatory) Attribute register. For details, see MmcCaps in mmc_caps.h. } controller_0x10100000 :: mmc_controller { match_attr = "hi3516_mmc_emmc";// (Mandatory) The value must be the same as that of deviceMatchAttr in device_info.hcs. hostId = 0; regBasePhy = 0x10100000; irqNum = 96; devType = 0; // The value 0 indicates an eMMC. caps = 0xd001e045; caps2 = 0x60; } controller_0x100f0000 :: mmc_controller { match_attr = "hi3516_mmc_sd"; hostId = 1; regBasePhy = 0x100f0000; irqNum = 62; devType = 1; // The value 1 indicates an SD card. caps = 0xd001e005; } controller_0x10020000 :: mmc_controller { match_attr = "hi3516_mmc_sdio"; hostId = 2; regBasePhy = 0x10020000; irqNum = 63; devType = 2; // The value 2 indicates an SDIO device. caps = 0x0001e04d; } } } }
-
-
Initialize the MmcCntlr object at the core layer, including initializing the vendor custom structure (transferring parameters and data), instantiating MmcCntlrOps (used to call underlying functions of the driver) in MmcCntlr, and implementing the HdfDriverEntry member functions (Bind, Init, and Release).
-
Custom structure reference
To the driver, the custom structure carries parameters and data. The values in the mmc_config.hcs file are read by the HDF, and the structure members are initialized through DeviceResourceIface. Some important values are also transferred to the objects at the core layer.
struct HimciHost { struct MmcCntlr *mmc;// (Mandatory) Core layer structure struct MmcCmd *cmd; // (Mandatory) Core layer structure used to transfer commands. For details about related commands, see MmcCmdCode. //(Optional) Set parameters based on the vendor's requirements. void *base; enum HimciPowerStatus powerStatus; uint8_t *alignedBuff; uint32_t buffLen; struct scatterlist dmaSg; struct scatterlist *sg; uint32_t dmaSgNum; DMA_ADDR_T dmaPaddr; uint32_t *dmaVaddr; uint32_t irqNum; bool isTuning; uint32_t id; struct OsalMutex mutex; bool waitForEvent; HIMCI_EVENT himciEvent; }; // MmcCntlr is the core layer controller structure. Its members are assigned with values by using the bind function. struct MmcCntlr { struct IDeviceIoService service; struct HdfDeviceObject *hdfDevObj; struct PlatformDevice device; struct OsalMutex mutex; struct OsalSem released; uint32_t devType; struct MmcDevice *curDev; struct MmcCntlrOps *ops; struct PlatformQueue *msgQueue; uint16_t index; uint16_t voltDef; uint32_t vddBit; uint32_t freqMin; uint32_t freqMax; uint32_t freqDef; union MmcOcr ocrDef; union MmcCaps caps; union MmcCaps2 caps2; uint32_t maxBlkNum; uint32_t maxBlkSize; uint32_t maxReqSize; bool devPluged; bool detecting; void *priv; }; -
Instantiate the callback function structure MmcCntlrOps in MmcCntlr. Other members are initialized by using the Bind function.
static struct MmcCntlrOps g_himciHostOps = { .request = HimciDoRequest, .setClock = HimciSetClock, .setPowerMode = HimciSetPowerMode, .setBusWidth = HimciSetBusWidth, .setBusTiming = HimciSetBusTiming, .setSdioIrq = HimciSetSdioIrq, .hardwareReset = HimciHardwareReset, .systemInit = HimciSystemInit, .setEnhanceSrobe= HimciSetEnhanceSrobe, .switchVoltage = HimciSwitchVoltage, .devReadOnly = HimciDevReadOnly, .devPluged = HimciCardPluged, .devBusy = HimciDevBusy, .tune = HimciTune, .rescanSdioDev = HimciRescanSdioDev, }; -
Bind function
Input parameters:
HdfDeviceObject, an interface parameter exposed by the driver, contains the .hcs configuration file information.
Return values:
HDF_STATUS (The following table lists some status. For details about other status, see HDF_STATUS in the //drivers/framework/include/utils/hdf_base.h file.)
Function description:
Initializes the custom structure HimciHost object and MmcCntlr, and calls the MmcCntlrAdd function at the core layer. MmcCntlr, HimciHost, and HdfDeviceObject assign values with each other so that other functions can be converted successfully.
static int32_t HimciMmcBind(struct HdfDeviceObject *obj) { struct MmcCntlr *cntlr = NULL; struct HimciHost *host = NULL; int32_t ret; cntlr = (struct MmcCntlr *)OsalMemCalloc(sizeof(struct MmcCntlr)); host = (struct HimciHost *)OsalMemCalloc(sizeof(struct HimciHost)); host->mmc = cntlr; // (Mandatory) Enable conversion between HimciHost and MmcCntlr. cntlr->priv = (void *)host; // (Mandatory) Enable conversion between HimciHost and MmcCntlr. cntlr->ops = &g_himciHostOps; // (Mandatory) Connect to the MmcCntlrOps instance. cntlr->hdfDevObj = obj; // (Mandatory) Enable conversion between HdfDeviceObject and MmcCntlr. obj->service = &cntlr->service; // (Mandatory) Enable conversion between HdfDeviceObject and MmcCntlr. ret = MmcCntlrParse(cntlr, obj); // (Mandatory) Initialize cntlr. If the initialization fails, execute goto _ERR. ... ret = HimciHostParse(host, obj); // (Mandatory) Initialize the attributes of the host. If the initialization fails, execute goto _ERR. ... ret = HimciHostInit(host, cntlr);// Initialization defined by the vendor. If the initialization fails, execute goto _ERR. ... ret = MmcCntlrAdd(cntlr); // Call the function at the core layer. If the function fails to be called, execute goto _ERR. ... (void)MmcCntlrAddDetectMsgToQueue(cntlr);// Add the card detection message to the queue. HDF_LOGD("HimciMmcBind: success."); return HDF_SUCCESS; _ERR: HimciDeleteHost(host); HDF_LOGD("HimciMmcBind: fail, err = %d.", ret); return ret; } -
Init function
Input parameters:
HdfDeviceObject, an interface parameter exposed by the driver, contains the .hcs configuration file information.
Return values:
HDF_STATUS
Function description:
Implements ProcMciInit.
static int32_t HimciMmcInit(struct HdfDeviceObject *obj) { static bool procInit = false; (void)obj; if (procInit == false) { if (ProcMciInit() == HDF_SUCCESS) { procInit = true; HDF_LOGD("HimciMmcInit: proc init success."); } } HDF_LOGD("HimciMmcInit: success."); return HDF_SUCCESS; } -
Release function
Input parameters:
HdfDeviceObject, an interface parameter exposed by the driver, contains the .hcs configuration file information.
Return values:
–
Function description:
Releases the memory and deletes the controller. This function assigns a value to the Release API in the driver entry structure. When the HDF framework fails to call the Init function to initialize the driver, the Release function can be called to release driver resources. All forced conversion operations for obtaining the corresponding object can be successful only when the Init function has the corresponding value assignment operations.
static void HimciMmcRelease(struct HdfDeviceObject *obj) { struct MmcCntlr *cntlr = NULL; ... cntlr = (struct MmcCntlr *)obj->service;// Forcibly convert HdfDeviceObject to MmcCntlr by using service. For details about the value assignment, see the Bind function. ... HimciDeleteHost((struct HimciHost *)cntlr->priv);// Memory release function customized by the vendor. A forced conversion from MmcCntlr to HimciHost is involved in the process. }
-