Pin
Overview
Pin
The pin, also called pin controller, manages pin resources of system on a chip (SoC) vendors and provides the pin multiplexing function.
Basic Concepts
Pin, as a software concept, provides APIs for uniformly managing the pins from different SoC vendors, providing the pin multiplexing function, and configuring the electrical features of pins.
-
SoC
An SOC is a chip that integrates microprocessors, analog IP cores, digital IP cores, and memory for specific purposes.
-
Pin multiplexing
When the number of pins of a chip cannot handle the increasing connection requests, you can set the software registers to make the pins to work in different states.
Working Principles
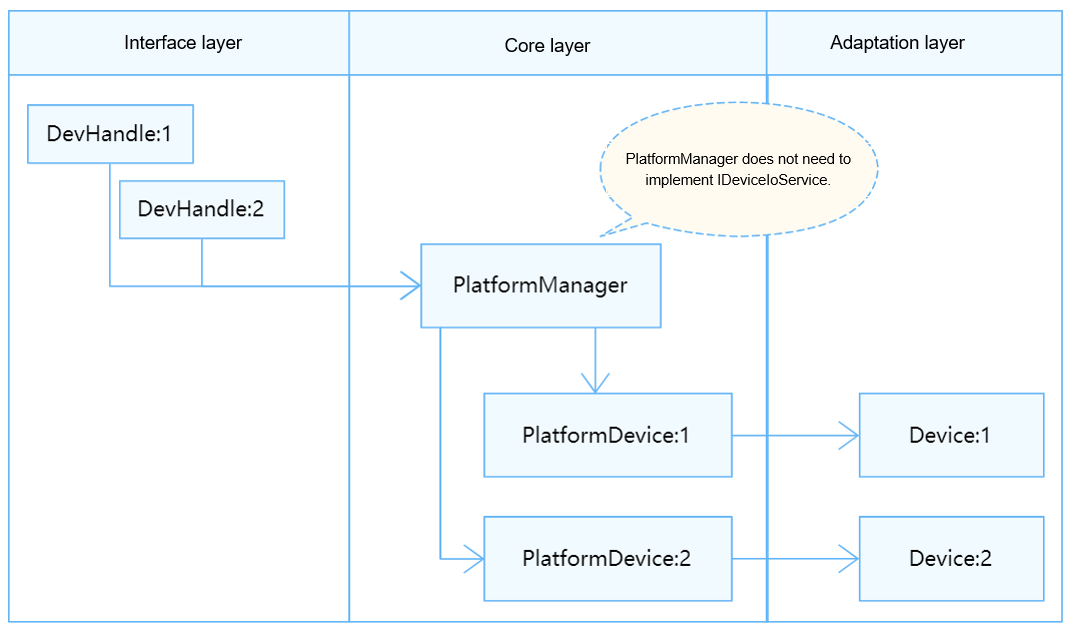
In the HDF, the pin module does not support the user mode and therefore does not need to publish services. It uses the service-free mode in interface adaptation. The service-free mode applies to the devices that do not provide user-mode APIs or the OS that does not distinguish the user mode and the kernel mode. The DevHandle, a void pointer, directly points to the kernel mode address of the device object.
The pin module is divided into the following layers:
- Interface layer: provides APIs for obtaining a pin, setting or obtaining the pull type, pull strength, and functions of a pin, and releasing a pin.
- Core layer: provides the capabilities of matching pin resources and adding, removing, and managing pin controllers. The core layer interacts with the adaptation layer by using hooks.
- Adaptation layer: instantiates hooks to implement specific functions.
Figure 1 Service-free mode
Constraints
Currently, the pin module supports only the kernels (LiteOS) of mini and small systems.
Development Guidelines
When to Use
The pin module is used to manage pin resources. When the devices from SoC vendors interconnect with the HDF, the pin driver needs to be adapted.
Available APIs
The PinCntlrMethod APIs are used to call the functions of the pin driver. PinCntlrMethod definition:
struct PinCntlrMethod {
int32_t (*SetPinPull)(struct PinCntlr *cntlr, uint32_t index, enum PinPullType pullType);
int32_t (*GetPinPull)(struct PinCntlr *cntlr, uint32_t index, enum PinPullType *pullType);
int32_t (*SetPinStrength)(struct PinCntlr *cntlr, uint32_t index, uint32_t strength);
int32_t (*GetPinStrength)(struct PinCntlr *cntlr, uint32_t index, uint32_t *strength);
int32_t (*SetPinFunc)(struct PinCntlr *cntlr, uint32_t index, const char *funcName);
int32_t (*GetPinFunc)(struct PinCntlr *cntlr, uint32_t index, const char **funcName);
};
Table 1 APIs for the members in the PinCntlrMethod structure
| API | Input Parameter | Output Parameter | Return Value | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SetPinPull | cntlr: structure pointer to the pin controller at the core layer. index: pin index, which is a uint32_t variable. pullType: pull type of the pin. It is an enum constant. |
- | HDF_STATUS | Sets the pull type of a pin. |
| GetPinPull | cntlr: structure pointer to the pin controller at the core layer. index: pin index, which is a uint32_t variable. |
pullType: pointer to the pull type of the pin. | HDF_STATUS | Obtains the pull type of a pin. |
| SetPinStrength | cntlr: structure pointer to the pin controller at the core layer. index: pin index, which is a uint32_t variable. strength: pull strength of the pin. It is a uint32_t variable. |
- | HDF_STATUS | Sets the pull strength of a pin. |
| GetPinStrength | cntlr: structure pointer to the pin controller at the core layer. index: pin index, which is a uint32_t variable. |
strength: pointer to the pull strength of the pin. | HDF_STATUS | Obtains the pull strength of a pin. |
| SetPinFunc | cntlr: structure pointer to the pin controller at the core layer. index: pin index, which is a uint32_t variable. funcName: char pointer to the pin function. |
- | HDF_STATUS | Sets the pin function. |
| GetPinFunc | cntlr: structure pointer to the pin controller at the core layer. index: pin index, which is a uint32_t variable. |
funcName: char double pointer to the pin function. | HDF_STATUS | Obtains the pin function. |
How to Develop
The pin module adaptation procedure is as follows:
- Instantiate the driver entry.
- Configure attribute files.
- Instantiate the core layer APIs.
- Debug the driver.
-
Instantiate the driver entry.
-
Instantiate the HdfDriverEntry structure. Instantiate the driver entry. The driver entry must be a global variable of the HdfDriverEntry type (defined in hdf_device_desc.h), and the value of moduleName must be the same as that in device_info.hcs.
-
Call HDF_INIT to register the HdfDriverEntry instance with the HDF. Generally, the HDF calls the Init() function to load the driver. If Init() fails to be called, the HDF calls Release() to release driver resources and exit.
static struct HdfDriverEntry g_hi35xxPinDriverEntry = { .moduleVersion = 1, .Bind = Hi35xxPinBind, .Init = Hi35xxPinInit, .Release = Hi35xxPinRelease, .moduleName = "hi35xx_pin_driver",// (Mandatory) The value must be the same as that of moduleName in the .hcs file. }; HDF_INIT(g_hi35xxPinDriverEntry);// Call HDF_INIT to register the driver entry with the HDF.
-
-
Configure attribute files.
- Add the device node description to the vendor/hisilicon/hispark_taurus/hdf_config/device_info/device_info.hcs file.
root { device_info { platform :: host { hostName = "platform_host"; priority = 50; device_pin :: device { device0:: deviceNode { // Set an HDF device node for each pin controller. policy = 0; // 2: visible in user mode; 1: visible in kernel mode; 0: no service required. priority = 10; // Driver startup priority. permission = 0644; // Permission to create device nodes for the driver. /* (Mandatory) Driver name, which must be the same as the moduleName in the driver entry. */ moduleName = "hi35xx_pin_driver"; /* (Mandatory) Set the controller private data, which must be same as that in pin_config.hcs. */ deviceMatchAttr = "hisilicon_hi35xx_pin_0"; } device1 :: deviceNode { policy = 0; priority = 10; permission = 0644; moduleName = "hi35xx_pin_driver"; deviceMatchAttr = "hisilicon_hi35xx_pin_1"; } ...... } } } } - Add the pin_config.hcs file.
Configure the device attributes in the device/soc/hisilicon/hi3516dv300/sdk_liteos/hdf_config/pin/pin_config.hcs file. The parameters are set as follows:
root { platform { pin_config_hi35xx { template pin_controller { // (Mandatory) Template configuration. In the template, you can configure the common parameters shared by device nodes. number = 0; // (Mandatory) Controller ID. regStartBasePhy = 0; // (Mandatory) Start physical base address of the register. regSize = 0; // (Mandatory) Register bit width. PinCount = 0; // (Mandatory) Number of pins. match_attr = ""; template pin_desc { pinName = ""; // (Mandatory) Name of the pin. init = 0; // (Mandatory) Default value of the register. F0 = ""; // (Mandatory) Function 0. F1 = ""; // Function 1. F2 = ""; // Function 2. F3 = ""; // Function 3. F4 = ""; // Function 4. F5 = ""; // Function 5. } } controller_0 :: pin_controller { number = 0; regStartBasePhy = 0x10FF0000; regSize = 0x48; pinCount = 18; match_attr = "hisilicon_hi35xx_pin_0"; T1 :: pin_desc { pinName = "T1"; init = 0x0600; F0 = "EMMC_CLK"; F1 = "SFC_CLK"; F2 = "SFC_BOOT_MODE"; } ...... // Correspond to the pins of the pin controller. Add pins according to actual situation. } ...// Each pin controller corresponds to a controller node. If there are multiple pin controllers, add the corresponding controller nodes one by one. } } }
- Add the device node description to the vendor/hisilicon/hispark_taurus/hdf_config/device_info/device_info.hcs file.
-
Instantiate the pin controller object.
-
Initialize the PinCntlr object. Call Hi35xxPinCntlrInit to initialize the PinCntlr members.
struct Hi35xxPinDesc { // Pin name. const char *pinName; // Initial value. uint32_t init; // Index of the pin. uint32_t index; // Pull type of the pin. int32_t pullType; // Pull strength of the pin. int32_t strength; // Array of pin function names. const char *func[HI35XX_PIN_FUNC_MAX]; }; struct Hi35xxPinCntlr { // Pin controller. struct PinCntlr cntlr; // Pointer to the pin description structure. struct Hi35xxPinDesc *desc; // Register mapping address. volatile unsigned char *regBase; // ID of the pin controller. uint16_t number; // Start address of the register physical base addresses. uint32_t regStartBasePhy; // Register bit width. uint32_t regSize; // Number of pins. uint32_t pinCount; }; // PinCntlr is the controller structure at the core layer. Its members are assigned with values by using the Init() function. struct PinCntlr { struct IDeviceIoService service; struct HdfDeviceObject *device; struct PinCntlrMethod *method; struct DListHead node; // Node in the linked list. OsalSpinlock spin; // Spinlock. uint16_t number; // ID of the pin controller. uint16_t pinCount; // Number of pins. struct PinDesc *pins; void *priv; // Private data. }; // Initialize PinCntlr. static int32_t Hi35xxPinCntlrInit(struct HdfDeviceObject *device, struct Hi35xxPinCntlr *hi35xx) { struct DeviceResourceIface *drsOps = NULL; int32_t ret; // Read the pin controller attributes from the .hcs file. drsOps = DeviceResourceGetIfaceInstance(HDF_CONFIG_SOURCE); if (drsOps == NULL || drsOps->GetUint32 == NULL || drsOps->GetUint16 == NULL) { HDF_LOGE("%s: invalid drs ops fail!", __func__); return HDF_FAILURE; } ret = drsOps->GetUint16(device->property, "number", &hi35xx->number, 0); if (ret != HDF_SUCCESS) { HDF_LOGE("%s: read number failed", __func__); return ret; } ret = drsOps->GetUint32(device->property, "regStartBasePhy", &hi35xx->regStartBasePhy, 0); if (ret != HDF_SUCCESS) { HDF_LOGE("%s: read regStartBasePhy failed", __func__); return ret; } ret = drsOps->GetUint32(device->property, "regSize", &hi35xx->regSize, 0); if (ret != HDF_SUCCESS) { HDF_LOGE("%s: read regSize failed", __func__); return ret; } ret = drsOps->GetUint32(device->property, "pinCount", &hi35xx->pinCount, 0); if (ret != HDF_SUCCESS) { HDF_LOGE("%s: read pinCount failed", __func__); return ret; } // Assign the values read to the members of the pin controller to initialize the pin controller. hi35xx->cntlr.pinCount = hi35xx->pinCount; hi35xx->cntlr.number = hi35xx->number; hi35xx->regBase = OsalIoRemap(hi35xx->regStartBasePhy, hi35xx->regSize); // Pin controller mapping. if (hi35xx->regBase == NULL) { HDF_LOGE("%s: remap Pin base failed", __func__); return HDF_ERR_IO; } hi35xx->desc = (struct Hi35xxPinDesc *)OsalMemCalloc(sizeof(struct Hi35xxPinDesc) * hi35xx->pinCount); hi35xx->cntlr.pins = (struct PinDesc *)OsalMemCalloc(sizeof(struct PinDesc) * hi35xx->pinCount); return HDF_SUCCESS; } -
Instantiate the callback structure PinCntlrMethod in PinCntlr. Other members are initialized by using the Init() function.
// The members of the PinCntlrMethod structure are all callbacks. Vendors need to implement the corresponding functions according to Table 1. static struct PinCntlrMethod g_method = { .SetPinPull = Hi35xxPinSetPull, // Set the pull type. .GetPinPull = Hi35xxPinGetPull, // Obtains the pull type. .SetPinStrength = Hi35xxPinSetStrength, // Set the pull strength. .GetPinStrength = Hi35xxPinGetStrength, // Obtains the pull strength. .SetPinFunc = Hi35xxPinSetFunc, // Set the pin functions. .GetPinFunc = Hi35xxPinGetFunc, // Obtain the pin functions. }; -
Init() function
Input parameters: HdfDeviceObject, an interface parameter exposed by the driver, contains the .hcs information.
Return value: HDF_STATUS (The following table lists some states. For more details, see HDF_STATUS in /drivers/framework/include/utils/hdf_base.h.)
-
| State | Description |
|---|---|
| HDF_ERR_INVALID_OBJECT | Invalid controller object. |
| HDF_ERR_MALLOC_FAIL | Failed to allocate memory. |
| HDF_ERR_INVALID_PARAM | Invalid parameter. |
| HDF_ERR_IO | I/O error. |
| HDF_SUCCESS | Initialization successful. |
| HDF_FAILURE | Initialization failed. |
Function description:
Initializes the custom structure object and **PinCntlr** members, and connects to the pin controller by calling the **PinCntlrAdd()** function.
```c
static int32_t Hi35xxPinReadFunc(struct Hi35xxPinDesc *desc, const struct DeviceResourceNode *node, struct DeviceResourceIface *drsOps)
{
int32_t ret;
uint32_t funcNum = 0;
// Read the pin function names of the pin controller child nodes from the .hcs file.
ret = drsOps->GetString(node, "F0", &desc->func[funcNum], "NULL");
if (ret != HDF_SUCCESS) {
HDF_LOGE("%s: read F0 failed", __func__);
return ret;
}
funcNum++;
ret = drsOps->GetString(node, "F1", &desc->func[funcNum], "NULL");
if (ret != HDF_SUCCESS) {
HDF_LOGE("%s: read F1 failed", __func__);
return ret;
}
funcNum++;
......
return HDF_SUCCESS;
}
static int32_t Hi35xxPinParsePinNode(const struct DeviceResourceNode *node, struct Hi35xxPinCntlr *hi35xx, int32_t index)
{
int32_t ret;
struct DeviceResourceIface *drsOps = NULL;
// Read the pin attributes of the pin controller child nodes from the .hcs file.
drsOps = DeviceResourceGetIfaceInstance(HDF_CONFIG_SOURCE);
if (drsOps == NULL || drsOps->GetUint32 == NULL || drsOps->GetString == NULL) {
HDF_LOGE("%s: invalid drs ops fail!", __func__);
return HDF_FAILURE;
}
ret = drsOps->GetString(node, "pinName", &hi35xx->desc[index].pinName, "NULL");
if (ret != HDF_SUCCESS) {
HDF_LOGE("%s: read pinName failed", __func__);
return ret;
}
......
ret = Hi35xxPinReadFunc(&hi35xx->desc[index], node, drsOps);
if (ret != HDF_SUCCESS) {
HDF_LOGE("%s:Pin read Func failed", __func__);
return ret;
}
hi35xx->cntlr.pins[index].pinName = hi35xx->desc[index].pinName;
hi35xx->cntlr.pins[index].priv = (void *)node;
......
return HDF_SUCCESS;
}
static int32_t Hi35xxPinInit(struct HdfDeviceObject *device)
{
......
struct Hi35xxPinCntlr *hi35xx = NULL;
......
ret = Hi35xxPinCntlrInit(device, hi35xx); // Initialize the pin controller.
......
DEV_RES_NODE_FOR_EACH_CHILD_NODE(device->property, childNode) { // Traverses each child node of the pin controller.
ret = Hi35xxPinParsePinNode(childNode, hi35xx, index); // Parsing the child nodes.
......
}
hi35xx->cntlr.method = &g_method; // Instantiate method.
ret = PinCntlrAdd(&hi35xx->cntlr); // Connect to the controller.
if (ret != HDF_SUCCESS) {
HDF_LOGE("%s: add Pin cntlr: failed", __func__);
ret = HDF_FAILURE;
}
return HDF_SUCCESS;
}
```
-
Release() function
Input parameters:
HdfDeviceObject, an interface parameter exposed by the driver, contains the .hcs information.
Return value:
–
Function description:
Releases memory and deletes the controller. This function assigns a value to the Release API in the driver entry structure. If the HDF fails to call the Init() function to initialize the driver, the Release() function can be called to release driver resources.
static void Hi35xxPinRelease(struct HdfDeviceObject *device) { int32_t ret; uint16_t number; struct PinCntlr *cntlr = NULL; struct Hi35xxPinCntlr *hi35xx = NULL; struct DeviceResourceIface *drsOps = NULL; if (device == NULL || device->property == NULL) { HDF_LOGE("%s: device or property is null", __func__); return; } // Read the pin controller ID from the .hcs file. drsOps = DeviceResourceGetIfaceInstance(HDF_CONFIG_SOURCE); if (drsOps == NULL || drsOps->GetUint32 == NULL || drsOps->GetString == NULL) { HDF_LOGE("%s: invalid drs ops", __func__); return; } ret = drsOps->GetUint16(device->property, "number", &number, 0); if (ret != HDF_SUCCESS) { HDF_LOGE("%s: read cntlr number failed", __func__); return; } cntlr = PinCntlrGetByNumber(number); // Obtain the pin controller based on the controller ID. PinCntlrRemove(cntlr); hi35xx = (struct Hi35xxPinCntlr *)cntlr; if (hi35xx != NULL) { if (hi35xx->regBase != NULL) { OsalIoUnmap((void *)hi35xx->regBase); } OsalMemFree(hi35xx); } }
- Debug the driver. (Optional) Verify basic functionalities of new drivers. For example, verify the information returned when the driver is loaded and whether data is successfully transmitted.