Watchdog
Overview
A watchdog, also called a watchdog timer, is a hardware timing device. If an error occurs in the main program of the system and fails to reset the watchdog timer, the watchdog timer sends a reset signal to restore the system to a normal state.
Available APIs
Table 1 Watchdog APIs
NOTE
All watchdog functions provided in this document can be called only in kernel mode.
Usage Guidelines
How to Use
The figure below illustrates how to use the APIs.
Figure 1 Using watchdog driver APIs
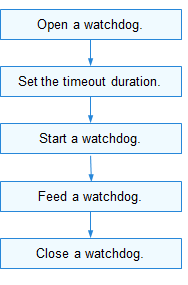
Opening a Watchdog
Use WatchdogOpen to open a watchdog. A system may have multiple watchdogs. You can open the specified watchdog by using the ID.
int32_t WatchdogOpen(int16_t wdtId);
Table 2 Description of WatchdogOpen
DevHandle handle = NULL;
handle = WatchdogOpen(0); /* Open watchdog 0.*/
if (handle == NULL) {
HDF_LOGE("WatchdogOpen: failed, ret %d\n", ret);
return;
}
Obtaining the Watchdog Status
int32_t WatchdogGetStatus(DevHandle handle, int32_t *status);
Table 3 Description of WatchdogGetStatus
int32_t ret;
int32_t status;
/* Obtain the watchdog status. */
ret = WatchdogGetStatus(handle, &status);
if (ret != 0) {
HDF_LOGE("WatchdogGetStatus: failed, ret %d\n", ret);
return;
}
Setting the Timeout Duration
int32_t WatchdogSetTimeout(PalHandle *handle, uint32_t seconds);
Table 4 Description of WatchdogSetTimeout
int32_t ret;
uint32_t timeOut = 60;
/* Set the timeout duration, in seconds. */
ret = WatchdogSetTimeout(handle, timeOut);
if (ret != 0) {
HDF_LOGE("WatchdogSetTimeout: failed, ret %d\n", ret);
return;
}
Obtaining the Timeout Duration
int32_t WatchdogGetTimeout(PalHandle *handle, uint32_t *seconds);
Table 5 Description of WatchdogGetTimeout
int32_t ret;
uint32_t timeOut;
/* Obtain the timeout duration, in seconds. */
ret = WatchdogGetTimeout(handle, &timeOut);
if (ret != 0) {
HDF_LOGE("WatchdogGetTimeout: failed, ret %d\n", ret);
return;
}
Starting a Watchdog
int32_t WatchdogStart(DevHandle handle);
Table 6 Description of WatchdogStart
int32_t ret;
/* Start the watchdog. */
ret = WatchdogStart(handle);
if (ret != 0) {
HDF_LOGE("WatchdogStart: failed, ret %d\n", ret);
return;
}
Feeding a Watchdog
int32_t WatchdogFeed(DevHandle handle);
Table 7 Description of WatchdogFeed
int32_t ret;
/* Feed the watchdog. */
ret = WatchdogFeed(handle);
if (ret != 0) {
HDF_LOGE("WatchdogFeed: failed, ret %d\n", ret);
return;
}
Stopping a Watchdog
int32_t WatchdogStop(DevHandle handle);
Table 8 Description of WatchdogStop
int32_t ret;
/* Stop the watchdog. */
ret = WatchdogStop(handle);
if (ret != 0) {
HDF_LOGE("WatchdogStop: failed, ret %d\n", ret);
return;
}
Closing a Watchdog
If the watchdog is no longer required, call WatchdogClose to close the watchdog handle.
void WatchdogClose(DevHandle handle);
Table 9 Description of WatchdogClose
/* Close the watchdog. */
ret = WatchdogClose(handle);
Usage Example
This example provides a complete process for using a watchdog.
In this example, open a watchdog, set the timeout duration, and start the watchdog.
- Feed the watchdog periodically to ensure that the system is not reset due to timer expiry.
- Stop feeding the watchdog and check whether the system is reset after the timer expires.
Example:
#include "watchdog_if.h"
#include "hdf_log.h"
#include "osal_irq.h"
#include "osal_time.h"
#define WATCHDOG_TEST_TIMEOUT 2
#define WATCHDOG_TEST_FEED_TIME 6
static int32_t TestCaseWatchdog(void)
{
int32_t i;
int32_t ret;
uint32_t timeout;
DevHandle handle = NULL;
/* Open watchdog 0. */
handle = WatchdogOpen(0);
if (handle == NULL) {
HDF_LOGE("Open watchdog fail!");
return -1;
}
/* Set the timeout duration. */
ret = WatchdogSetTimeout(handle, WATCHDOG_TEST_TIMEOUT);
if (ret != HDF_SUCCESS) {
HDF_LOGE("%s: set timeout fail! ret:%d\n", __func__, ret);
WatchdogClose(handle);
return ret;
}
/* Obtain the configured timeout duration. */
ret = WatchdogGetTimeout(handle, &timeout);
if (ret != HDF_SUCCESS) {
HDF_LOGE("%s: get timeout fail! ret:%d\n", __func__, ret);
WatchdogClose(handle);
return ret;
}
HDF_LOGI("%s: read timeout back:%u\n", __func__, timeout);
/* Start the watchdog. The timer starts. */
ret = WatchdogStart(handle);
if (ret != HDF_SUCCESS) {
HDF_LOGE("%s: satrt fail! ret:%d\n", __func__, ret);
WatchdogClose(handle);
return ret;
}
/* Feed the watchdog every 1s. */
for (i = 0; i < WATCHDOG_TEST_FEED_TIME; i++) {
HDF_LOGE("%s: feeding watchdog %d times... \n", __func__, i);
ret = WatchdogFeed(handle);
if (ret != HDF_SUCCESS) {
HDF_LOGE("%s: feed dog fail! ret:%d\n", __func__, ret);
WatchdogClose(handle);
return ret;
}
OsalSleep(1);
}
/* Because the interval for feeding the watchdog is shorter than the timeout duration, the system does not reset, and logs can be printed normally. */
HDF_LOGE("%s: no reset ... feeding test OK!!!\n", __func__);
/* Enable the timer to expire by stopping feeding the watchdog. */
for (i = 0; i < WATCHDOG_TEST_FEED_TIME; i++) {
HDF_LOGE("%s: watiting dog buck %d times... \n", __func__, i);
OsalSleep(1);
}
/* The system resets when the timer expires. If the code is correct, the log below is not displayed. */
HDF_LOGE("%s: dog has't buck!!! \n", __func__, i);
WatchdogClose(handle);
return -1;
}