Continuation Overview
When to Use
As the all-scenario, multi-device lifestyle becomes popular, users have an increasing number of devices. Each device provides users with what they need in a certain scenario. For example, watches allow users to view information in a timely manner, and smart TVs bring them an immersive watching experience. However, each device has its limitation, for example, typing text on a smart TV is frustrating as it is much more difficult than on a mobile device. If multiple devices can sense each other through a distributed OS and together form a super device, the strengths of each device can be fully exerted to provide a more natural and smoother distributed experience for users.
In OpenHarmony, distributed operations across devices are called continuation (previously named hopping), which is further classified into cross-device migration and multi-device collaboration. To implement continuation, cross-device interaction capabilities of application components are required. Currently, these capabilities are open only to system applications.
Basic Concepts
-
Continuation
Continuation refers to distributed operations across devices. It breaks device boundaries and makes applications modular. For example, a user can edit the same email, carry out fitness, or play a game across devices. Continuation provides broad application scenarios, innovative product perspectives, enhanced product advantages, and superior experience.
-
Cross-device migration
When the environment changes, for example, when a user goes outdoors or when a more appropriate device is detected, the user can migrate an ongoing task to another device for better experience. The original device exits the task. A typical cross-device migration scenario is as follows: You migrate a video playback task from your tablet to a smart TV. The video application on the tablet exits. From the perspective of application development, cross-device migration migrates the UIAbility component running on device A to device B. After the migration is complete, the UIAbility component on device B continues the task, whereas that on device A exits.
-
Multi-device collaboration
Multi-device collaboration enables collaboration between multiple devices, providing users with more efficient and immersive experience than with a single device. A typical multi-device collaboration scenario is as follows: Application A on the tablet is used as the answer board, and application B on the smart TV is used for live broadcast, delivering a better online class experience. From the perspective of application development, multi-device collaboration enables different UIAbility or ServiceExtensionAbility components to run simultaneously or alternately on multiple devices to provide a complete service, or enables the same UIAbility and ServiceExtensionAbility component to run simultaneously on multiple devices to provide a complete service.
Continuation Architecture
OpenHarmony provides a set of APIs for you to implement continuation in your applications. The continuation architecture has the following advantages:
-
Capabilities such as remote service invocation to facilitate service design
-
Simultaneous continuation of multiple applications
-
Different device forms supported, such as tablets, smart TVs, and watches
The following figure shows the continuation architecture.
Figure 1 Continuation architecture
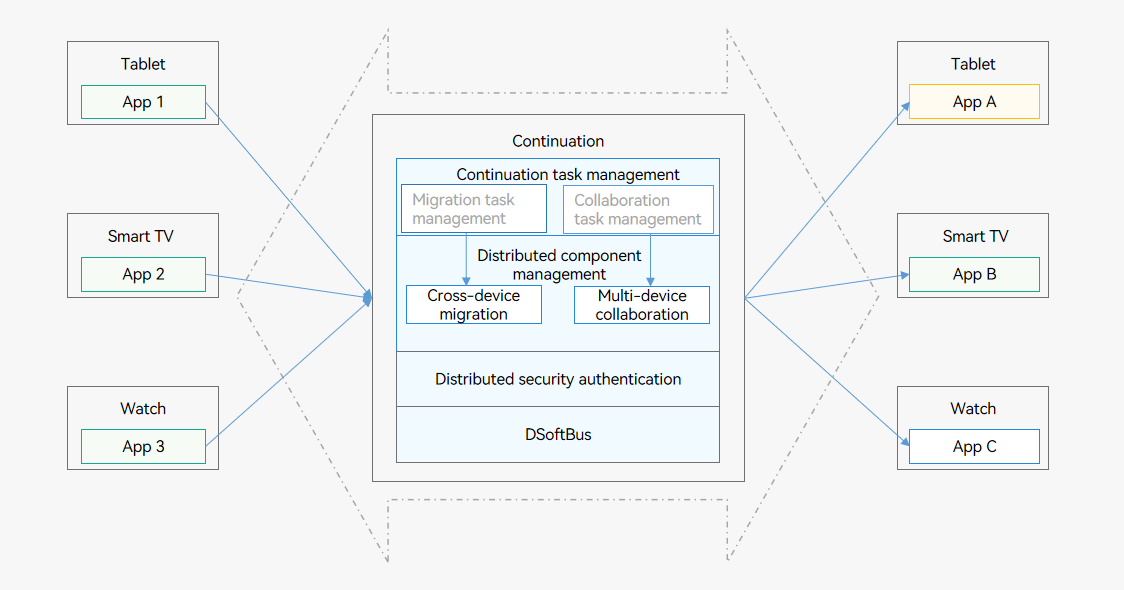
-
Cross-device migration task management: The initiator accepts a migration request from the user, provides a migration entry, and displays the migration result. (This capability is unavailable yet.)
-
Multi-device collaboration task management: The initiator accepts an application registration request and provides management capabilities such as starting or stopping collaboration and status display. (This capability is unavailable yet.)
-
Distributed component management: provides capabilities such as remote service startup, remote service connection, and remote migration, and enables cross-device migration or multi-device collaboration of applications based on a combination of these capabilities.
-
Distributed security authentication: provides an E2E encrypted channel for cross-device transmission between applications to ensure that the right person uses the right data through the right device.
-
DSoftBus: functions as a unified communication base for a wide range of devices such as tablets, wearables, and smart TVs, and enables unified distributed communication between these devices.