File Management Overview
The data in an operating system (OS) can be classified into the following types based on the data structure:
-
Structured data: data that can be defined in a unified data model. The structured data is generally stored in a database. In application development, the management of structured data is implemented by the data management module.
-
Unstructured data: data that does not conform to any predefined data structure or model and cannot be easily presented in two-dimensional database tables. Unstructured data includes files in a variety of formats, such as documents, images, videos, and audio clips. In application development, the management of unstructured data is implemented by the file management module, which will be elaborated in this document.
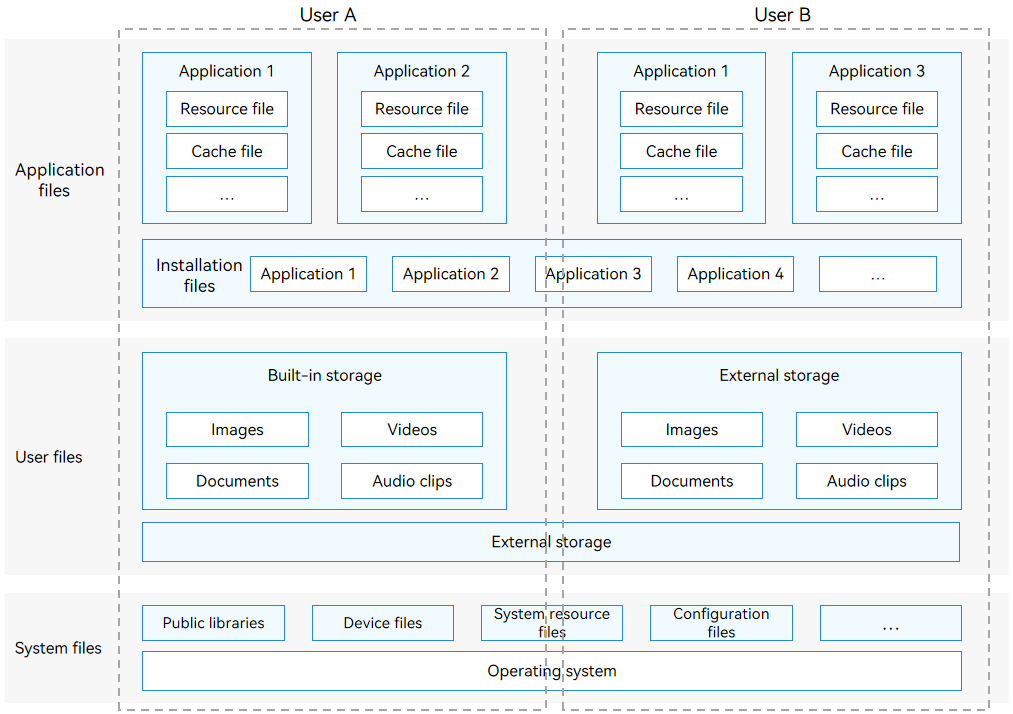
In the file management module, the files can be classified into the following types based on the file owner:
-
Application files: files of an application, including the application's installation files, resource files, and cached files.
-
User files: files of a user who logs in to the device, including the user's images, video and audio clips, and documents.
-
System files: files irrelevant to applications and users, including public libraries, device files, and system resource files. System files do not need to be managed by developers and are not described in this document.
The file systems can be classified into the following types based on the file storage location (data source location):
-
Local file system: provides capabilities for accessing the files stored on a local device or its external storage devices (such as USB flash drives and removable hard drives). The local file system is the most basic file system and is not described in this document.
-
Distributed file system: provides capabilities for accessing files across devices, which are connected through a computer network.
Figure 1 Files in an OS