Getting Started with JavaScript in FA Model
NOTE
For best possible results, use DevEco Studio 3.1 Beta2 for your development.
Creating a JavaScript Project
-
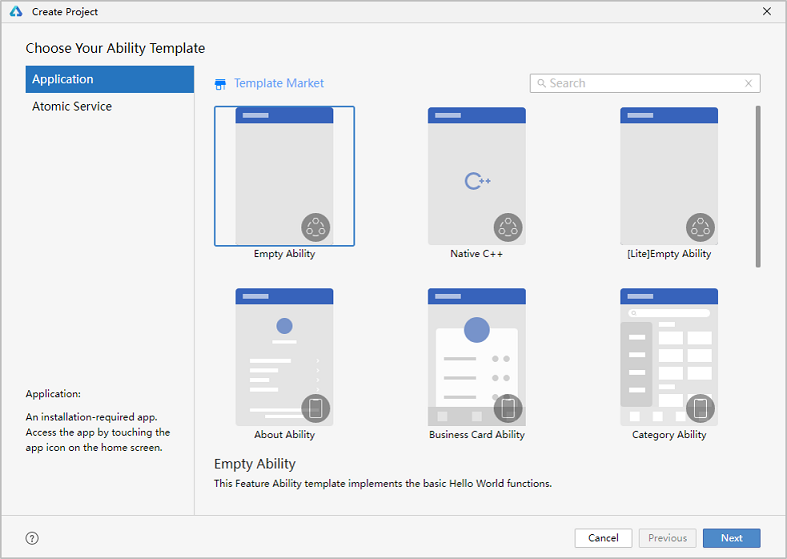
If you are opening DevEco Studio for the first time, click Create Project. If a project is already open, choose File > New > Create Project from the menu bar. On the Choose Your Ability Template page, select Application (or Atomic Service, depending on your project), select Empty Ability as the template, and click Next.
-
In the project configuration page, set Compile SDK to 8 or 9 (in the latter case, you also need to set Model to FA) and Language to JS and retain the default values for other parameters.
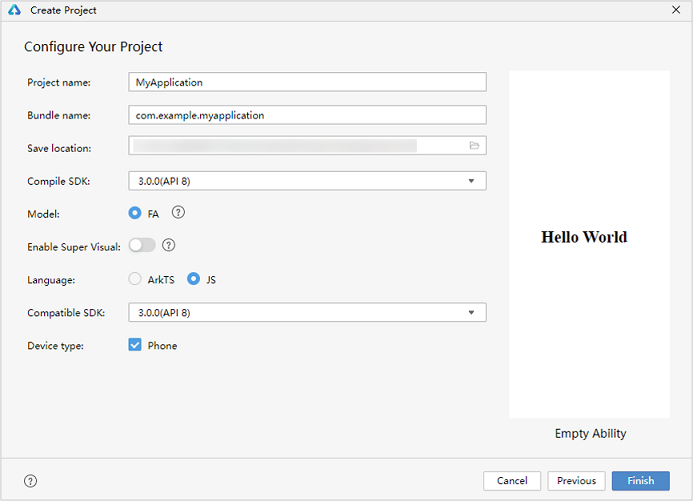
NOTE
If you are using DevEco Studio V2.2 Beta1 or later, you can use the low-code development mode apart from the traditional coding approach.
On the low-code development pages, you can design your application UI in an efficient, intuitive manner, with a wide array of UI editing features.
To use the low-code development mode, turn on Enable Super Visual on the page shown above.
-
Click Finish. DevEco Studio will automatically generate the sample code and resources that match your project type. Wait until the project is created.
-
After the project is created, in the entry > build-profile.json5 file, change runtimeOS under targets to OpenHarmony, and click Sync Now in the upper right corner to start development.
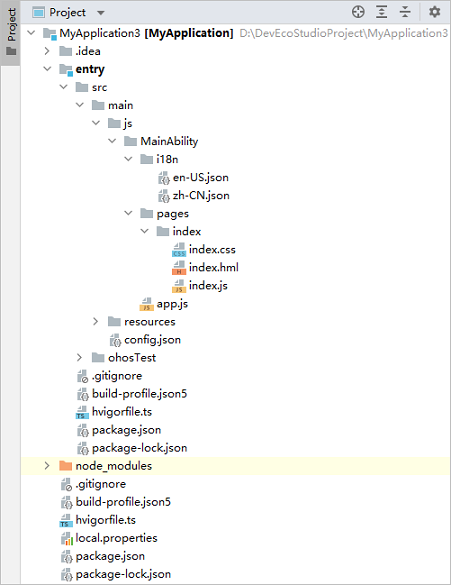
JavaScript Project Directory Structure
-
entry: OpenHarmony project module, which can be built into an OpenHarmony Ability Package (HAP).
-
src > main > js: a collection of JavaScript source code.
-
src > main > js > MainAbility: entry to your application/service.
-
src > main > js > MainAbility > i18n: resources in different languages, for example, UI strings and image paths.
-
src > main > js > MainAbility > pages: pages contained in MainAbility.
-
src > main > js > MainAbility > app.js: ability lifecycle file.
-
src > main > resources: a collection of resource files used by your application/service, such as graphics, multimedia, character strings, and layout files. For details about resource files, see Resource Limitations and Access.
-
src > main > config.json: module configuration file. This file describes the global configuration information of the application/service, the device-specific configuration information, and the configuration information of the HAP file. For details, see Application Configuration File Overview (FA Model).
-
build-profile.json5: current module information and build configuration options, including buildOption and targets. Under targets, you can set runtimeOS to HarmonyOS (default) or OpenHarmony, depending on the OS of your application.
-
hvigorfile.ts: module-level build script. You can customize related tasks and code implementation.
-
-
build-profile.json5: application-level configuration information, including the signature and product configuration.
-
hvigorfile.ts: application-level build script.
Building the First Page
-
Use the <Text> component.
After the project synchronization is complete, choose entry > src > main > js > MainAbility > pages > index in the Project window and open the index.hml file. You can see that the file contains a
component. The sample code in the index.hml file is shown below: <!-- index.hml --> <div class="container"> <text class="title"> Hello World </text> </div> -
Add a button and bind the onclick method to this button.
On the default page, add a <Button> component to respond to user clicks and implement redirection to another page. The sample code in the index.hml file is shown below:
<!-- index.hml --> <div class="container"> <text class="title"> Hello World </text> <!-- Add a button, set its value to Next, and bind the onclick method to the button. --> <input class="btn" type="button" value="Next" onclick="onclick"></input> </div> -
Set the page style in the index.css file.
From the Project window, choose entry > src > main > js > MainAbility > pages > index, open the index.css file, and set the page styles, such as the width, height, font size, and spacing. The sample code in the index.css file is shown below:
/* index.css */ .container { display: flex; flex-direction: column; justify-content: center; align-items: center; left: 0px; top: 0px; width: 100%; height: 100%; } .title { font-size: 100px; font-weight: bold; text-align: center; width: 100%; margin: 10px; } .btn { font-size: 60px; font-weight: bold; text-align: center; width: 40%; height: 5%; margin-top: 20px; } -
On the toolbar in the upper right corner of the editing window, click Previewer. Below is how the first page looks in the Previewer.

Building the Second Page
-
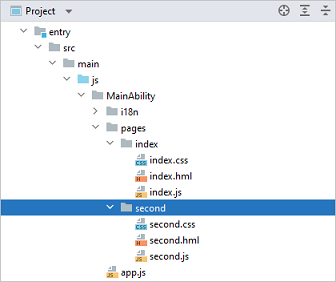
Create the second page.
In the Project window, choose entry > src > main > js > MainAbility, right-click the pages folder, choose New > Page, name the page second, and click Finish. Below is the structure of the second folder.
-
Add <Text> and <Button> components.
Add <Text> and <Button> components and set their styles, as you do for the first page. The sample code in the second.hml file is shown below:
<!-- second.hml --> <div class="container"> <text class="title"> Hi there </text> <!-- Add a button, set the value to Back, and bind the back method to the button.--> <input class="btn" type="button" value="Back" onclick="back"></input> </div> -
Set the page style. The sample code in the second.css file is shown below:
/* second.css */ .container { display: flex; flex-direction: column; justify-content: center; align-items: center; left: 0px; top: 0px; width: 100%; height: 100%; } .title { font-size: 100px; font-weight: bold; text-align: center; width: 100%; margin: 10px; } .btn { font-size: 60px; font-weight: bold; text-align: center; width: 40%; height: 5%; margin-top: 20px; }
Implementing Page Redirection
You can implement page redirection through the page router, which finds the target page based on the page URL. Import the router module and then perform the steps below:
-
Implement redirection from the first page to the second page.
In the index.js file of the first page, bind the onclick method to the button so that clicking the button redirects the user to the second page. The sample code in the index.js file is shown below:
// index.js // Import the router module. import router from '@ohos.router'; export default { onclick: function () { router.push({ url: "pages/second/second" }) } } -
Implement redirection from the second page to the first page.
In the second.ets file of the second page, bind the back method to the Back button so that clicking the button redirects the user back to the first page. The sample code in the second.js file is shown below:
// second.js // Import the router module. import router from '@ohos.router'; export default { back: function () { router.back() } } -
Open any file in the index folder and click
 in the Previewer to refresh the file. The display effect is shown in the figure below.
in the Previewer to refresh the file. The display effect is shown in the figure below.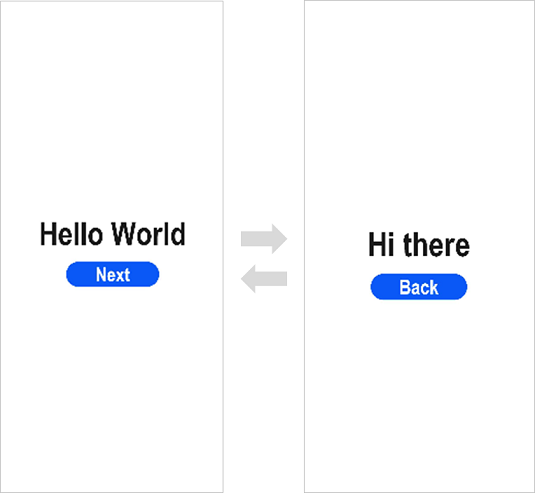
Running the Application on a Real Device
-
Connect the development board running the OpenHarmony standard system to the computer.
-
Choose File > Project Structure... > Project > Signing Configs, and select Automatically generate signature. Wait until the automatic signing is complete, and click OK. See the following figure.
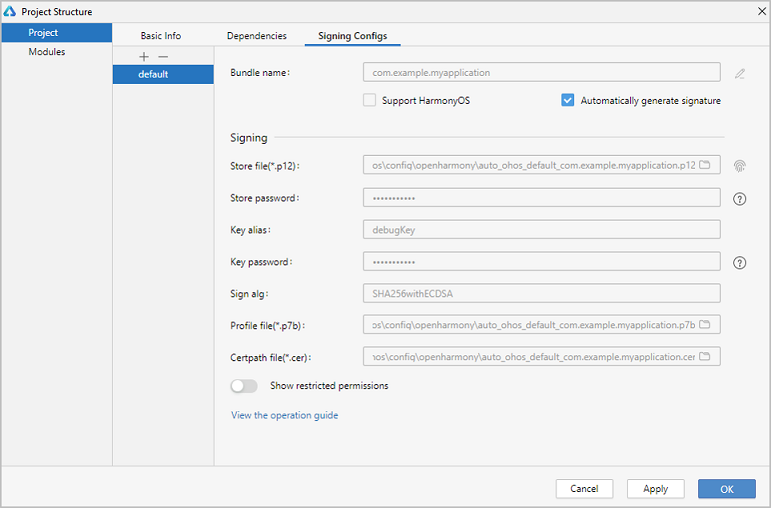
-
On the toolbar in the upper right corner of the editing window, click
 . The display effect is shown in the figure below.
. The display effect is shown in the figure below.
Congratulations! You have finished developing your OpenHarmony application in JavaScript in the FA model. To learn more about OpenHarmony application development, see Application Development Overview.