Network Management
Introduction
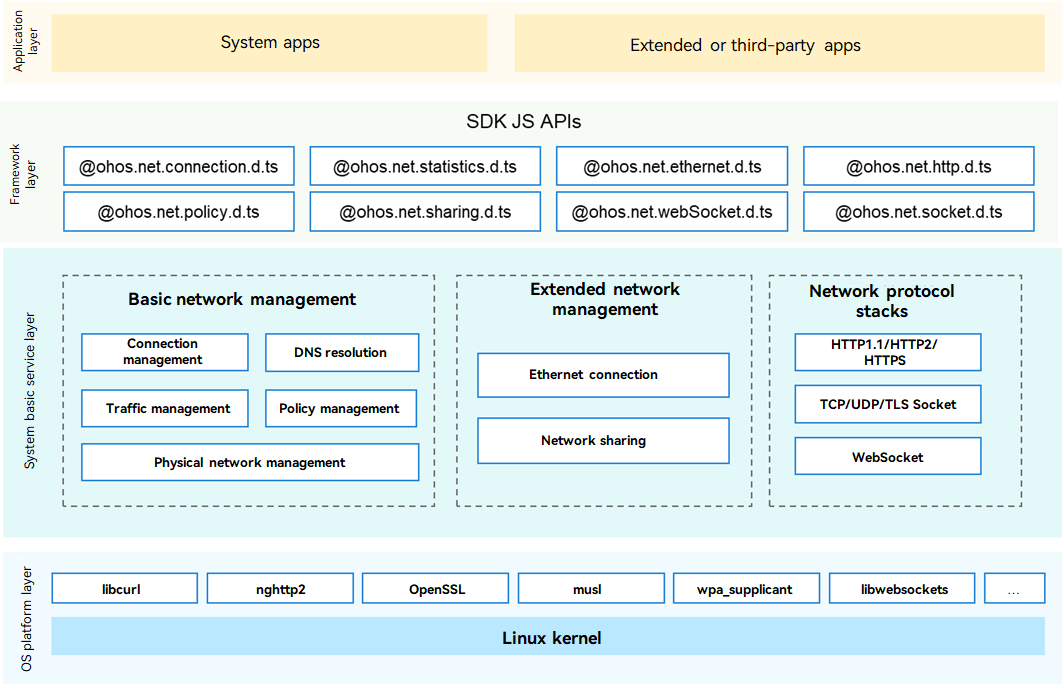
As a mandatory component for device networking, the network management subsystem implements unified connection management, traffic management, policy management, network sharing of different types of networks, and provides network protocol stack capabilities. An application can call APIs to obtain connection information of a data network, query and subscribe to connection status, network traffic data, and network policy, share the network, and transfer data using a network protocol stack.
The figure below shows the architecture of the network management subsystem. The network management subsystem consists of the following components:
- Basic network management: provides basic network connection management and related JS and native APIs, including connection priority management, connection information query, connection status observation, DNS resolution, traffic management, networking policy management, and physical network management.
- Extended network management: provides extended network management capabilities and related JS and native APIs, including Ethernet connection and hotspot sharing.
- Network protocol stacks: provides basic network protocol stacks (such as HTTP, HTTPS, WebSocket, and TCP/UDP/TLS socket) and related JS APIs.
Figure 1 Architecture of the network management subsystem
Directory Structure
foundation/communication/
├── netmanager_base # Basic network management
├── netmanager_ext # Extended network management
└── netstack # Network protocol stacks
Usage
Observing Network Status Changes
-
Import the connection namespace from @ohos.net.connection.d.ts.
-
Call createNetConnection() to create a NetConnection object. You can specify the network type, capability, and timeout interval. If you do not specify parameters, the default values will be used.
-
Call conn.on() to subscribe to the target event. You must pass in type and callback.
-
Call conn.register() to subscribe to network status changes of the specified network.
-
When the network is available, the callback will be invoked to return the netAvailable event.
-
Call conn.unregister() to unsubscribe from the network status changes if required.
// Import the connection namespace. import connection from '@ohos.net.connection' let netCap = { // Set the network type to CELLULAR. bearerTypes: [connection.NetBearType.BEARER_CELLULAR], // Set the network capability to INTERNET. networkCap: [connection.NetCap.NET_CAPABILITY_INTERNET], }; let netSpec = { netCapabilities: netCap, }; // Set the timeout interval to 10s. let timeout = 10 * 1000; // Create a NetConnection object. let conn = connection.createNetConnection(netSpec, timeout); // Subscribe to the netAvailable event. conn.on('netAvailable', (data=> { console.log("net is available, netId is " + data.netId); })); // Register an observer for network status changes. conn.register((err, data) => {}); // Unregister the observer for network status changes. conn.unregister((err, data) => {});
Sharing a Network
- Import the sharing namespace from @ohos.net.sharing.
- Set the network sharing type.
- Start network sharing.
- Stop network sharing.
// Import the connection namespace.
import sharing from '@ohos.net.sharing';
// Set the network sharing type.
this.sharingType = 0; // The value 0 indicates Wi-Fi, 1 indicates USB, and 2 indicates Bluetooth.
// Start network sharing.
sharing.startSharing(this.sharingType,(err)=>{
this.callBack(err);
})
// Stop network sharing.
sharing.stopSharing(this.sharingType,(err)=>{
this.callBack(err);
})
Initiating a Network Request
- Import the http namespace from @ohos.net.http.d.ts.
- Call createHttp() to create an HttpRequest object.
- Call httpRequest.on() to subscribe to HTTP response header events. This API returns a response earlier than the request. You can subscribe to HTTP response header events based on service requirements.
- Call httpRequest.request() to initiate a network request. You need to pass in the URL and optional parameters of the HTTP request.
- Parse the returned result based on service requirements.
- Call off() to unsubscribe from HTTP response header events.
- Call httpRequest.destroy() to release resources after the request is processed.
// Import the http namespace.
import http from '@ohos.net.http';
// Each httpRequest corresponds to an HTTP request task and cannot be reused.
let httpRequest = http.createHttp();
// This API is used to listen for the HTTP Response Header event, which is returned earlier than the result of the HTTP request. It is up to you whether to listen for HTTP Response Header events.
// on('headerReceive', AsyncCallback) is replaced by on('headersReceive', Callback) since API version 8.
httpRequest.on('headersReceive', (header) => {
console.info('header: ' + JSON.stringify(header));
});
httpRequest.request(
// Customize EXAMPLE_URL in extraData on your own. It is up to you whether to add parameters to the URL.
"EXAMPLE_URL",
{
method: http.RequestMethod.POST, // Optional. The default value is http.RequestMethod.GET.
// You can add header fields based on service requirements.
header: {
'Content-Type': 'application/json'
},
// This field is used to transfer data when the POST request is used.
extraData: {
"data": "data to send",
},
expectDataType: http.HttpDataType.STRING, // Optional. This field specifies the type of the return data.
usingCache: true, // Optional. The default value is true.
priority: 1, // Optional. The default value is 1.
connectTimeout: 60000 // Optional. The default value is 60000, in ms.
readTimeout: 60000, // Optional. The default value is 60000, in ms.
usingProtocol: http.HttpProtocol.HTTP1_1, // Optional. The default protocol type is automatically specified by the system.
usingProxy: false, // Optional. By default, network proxy is not used. This field is supported since API 10.
}, (err, data) => {
if (!err) {
// data.result carries the HTTP response. Parse the response based on service requirements.
console.info('Result:' + JSON.stringify(data.result));
console.info('code:' + JSON.stringify(data.responseCode));
// data.header carries the HTTP response header. Parse the content based on service requirements.
console.info('header:' + JSON.stringify(data.header));
console.info('cookies:' + JSON.stringify(data.cookies)); // 8+
} else {
console.info('error:' + JSON.stringify(err));
// Unsubscribe from HTTP Response Header events.
httpRequest.off('headersReceive');
// Call the destroy() method to release resources after HttpRequest is complete.
httpRequest.destroy();
}
}
);
Repositories Involved
Network Management Subsystem
communication_netmanager_base communication_netmanager_ext communication_netstack