Trace
Basic Concepts
Trace helps you learn about the kernel running process and the execution sequence of modules and tasks. With the traced information, you can better understand the code running process of the kernel and locate time sequence problems.
Working Principles
The kernel provides a hook framework to embed hooks in the main process of each module. In the initial startup phase of the kernel, the trace function is initialized and the trace handlers are registered with the hooks.
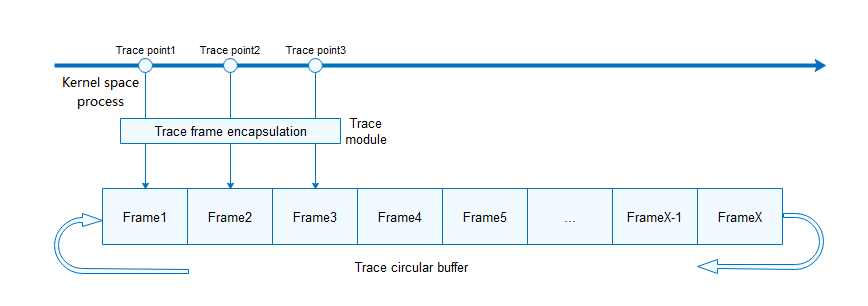
When a hook is triggered, the trace module encapsulates the input information and adds the trace frame header information, including the event type, ID of the running CPU, ID of the running task, and relative timestamp.
The trace module provides two working modes: offline mode and online mode.
In offline mode, trace frames are stored in a circular buffer. If too many frames are stored in the circular buffer, earlier frames will be overwritten to ensure that the information in the buffer is always the latest. Data in the circular buffer can be exported by running the shell command for further analysis. The exported information is sorted by timestamp.
The online mode must be used with the integrated development environment (IDE). Trace frames are sent to the IDE in real time. The IDE parses the records and displays them in a visualized manner.
Available APIs
The trace module of the OpenHarmony LiteOS-M kernel provides the following APIs. For more details about the APIs, see the API reference.
Table 1 APIs of the trace module
| Category | API |
|---|---|
| Starting/Stopping trace | - LOS_TraceStart: starts a trace. - LOS_TraceStop: stops the trace. |
| Managing trace records | - LOS_TraceRecordDump: dumps data from the trace buffer. - LOS_TraceRecordGet: obtains the start address of the trace buffer. - LOS_TraceReset: clears events in the trace buffer. |
| Filtering trace records | LOS_TraceEventMaskSet: sets the event mask to trace only events of the specified modules. |
| Masking events of specified interrupt IDs | LOS_TraceHwiFilterHookReg: registers a hook to filter out events of specified interrupt IDs. |
| Performing function instrumentation | - LOS_TRACE_EASY: performs simple instrumentation. - LOS_TRACE: performs standard instrumentation. |
-
You can perform function instrumentation in the source code to trace specific events. The system provides the following APIs for instrumentation:
- LOS_TRACE_EASY(TYPE, IDENTITY, params...) for simple instrumentation
-
You only need to insert this API into the source code.
-
TYPE specifies the event type. The value range is 0 to 0xF. The meaning of each value is user-defined.
-
IDENTITY specifies the object of the event operation. The value is of the UIntPtr type.
-
Params specifies the event parameters. The value is of the UIntPtr type.
-
Example of simple instrumentation for reading and writing data based on the file FDs:
/* Set TYPE to 1 for read operation and 2 for write operations. */ LOS_TRACE_EASY(1, fd, flag, size); /* Add it to a proper position. */ LOS_TRACE_EASY(2, fd, flag, size); /* Add it to a proper position. */
-
- LOS_TRACE(TYPE, IDENTITY, params...) for standard instrumentation.
-
Compared with simple instrumentation, standard instrumentation supports dynamic event filtering and parameter tailoring. However, you need to extend the functions based on rules.
-
TYPE specifies the event type. You can define the event type in enum LOS_TRACE_TYPE in the header file los_trace.h. For details about methods and rules for defining events, see other event types.
-
The IDENTITY and Params are the same as those of simple instrumentation.
-
Example:
- Define the type of the FS module (event mask of the FS module) in enum LOS_TRACE_MASK.
/* Define the event mask in the format of TRACE_#MOD#_FLAG, where #MOD# indicates the module name. */ TRACE_FS_FLAG = 0x4000- Define the event types of the FS module.
/* Define the event type in the format: #TYPE# = TRACE_#MOD#_FLAG | NUMBER */ FS_READ = TRACE_FS_FLAG | 0; /* Read data. */ FS_WRITE = TRACE_FS_FLAG | 1; /* Write data. */- Define event parameters.
/* Define the parameters in the format: #TYPE#_PARAMS(IDENTITY, parma1...) IDENTITY, ... */ #define FS_READ_PARAMS(fp, fd, flag, size) fp, fd, flag, size /* The parameters defined by the macro correspond to the event parameters recorded in the trace buffer. You can tailor the parameters as required. */ #define FS_READ_PARAMS(fp, fd, flag, size) /* If no parameters are defined, events of this type are not traced. */- Add the code stubs in the code.
/* Format: LOS_TRACE(#TYPE#, #TYPE#_PARAMS(IDENTITY, parma1...)) */ LOS_TRACE(FS_READ, fp, fd, flag, size); /* Code stub for reading data. */NOTE
You can modify the traced event types and parameters as required. For details about the parameters, see kernel\include\los_trace.h.
-
- LOS_TRACE_EASY(TYPE, IDENTITY, params...) for simple instrumentation
-
For LOS_TraceEventMaskSet(UINT32 mask), only the most significant 28 bits (corresponding to the enable bit of the module in LOS_TRACE_MASK) of the mask take effect and are used only for module-based tracing. Currently, fine-grained event-based tracing is not supported. For example, in LOS_TraceEventMaskSet(0x202), the effective mask is 0x200 (TRACE_QUE_FLAG) and all events of the QUE module are collected. The recommended method is LOS_TraceEventMaskSet(TRACE_EVENT_FLAG | TRACE_MUX_FLAG | TRACE_SEM_FLAG | TRACE_QUE_FLAG);.
-
To enable trace of only simple instrumentation events, set Trace Mask to TRACE_MAX_FLAG.
-
The trace buffer has limited capacity. When the trace buffer is full, events will be overwritten. You can use LOS_TraceRecordDump to export data from the trace buffer and locate the latest records by CurEvtIndex.
-
The typical trace operation process includes LOS_TraceStart, LOS_TraceStop, and LOS_TraceRecordDump.
-
You can filter out interrupt events by interrupt ID to prevent other events from being overwritten due to frequent triggering of a specific interrupt in some scenarios. You can customize interrupt filtering rules.
The sample code is as follows:BOOL Example_HwiNumFilter(UINT32 hwiNum) { if ((hwiNum == TIMER_INT) || (hwiNum == DMA_INT)) { return TRUE; } return FALSE; } LOS_TraceHwiFilterHookReg(Example_HwiNumFilter);The interrupt events with interrupt ID of TIMER_INT or DMA_INT are not traced.
Development Guidelines
How to Develop
The typical development process is as follows:
- Configure the macros related to the trace module in the target_config.h file.
| Configuration Item | Description | Value |
|---|---|---|
| LOSCFG_KERNEL_TRACE | Whether to enable the trace feature. | YES/NO |
| LOSCFG_RECORDER_MODE_OFFLINE | Whether to enable the online trace mode. | YES/NO |
| LOSCFG_RECORDER_MODE_ONLINE | Whether to enable the offline trace mode. | YES/NO |
| LOSCFG_TRACE_CLIENT_INTERACT | Whether to enable interaction with Trace IDE (dev tools), including data visualization and process control. | YES/NO |
| LOSCFG_TRACE_FRAME_CORE_MSG | Whether to enable trace of the CPU ID, interruption state, and lock task state. | YES/NO |
| LOSCFG_TRACE_FRAME_EVENT_COUNT | Whether to enable trace of the event sequence number. | YES/NO |
| LOSCFG_TRACE_FRAME_MAX_PARAMS | Specifies the maximum number of parameters for event tracing. | INT |
| LOSCFG_TRACE_BUFFER_SIZE | Specifies the trace buffer size. | INT |
-
(Optional) Preset event parameters and stubs (or use the default event parameter settings and event stubs).
-
(Optional) Call LOS_TraceStop to stop trace and LOS_TraceReset to clear the trace buffer. (Trace is started by default.)
-
(Optional) Call LOS_TraceEventMaskSet to set the event mask for trace (only the interrupts and task events are enabled by default). For details about the event mask, see LOS_TRACE_MASK in los_trace.h.
-
Call LOS_TraceStart at the start of the code where the event needs to be traced.
-
Call LOS_TraceStop at the end of the code where the event needs to be traced.
-
Call LOS_TraceRecordDump to output the data in the buffer. (The input parameter of the function is of the Boolean type. The value FALSE means to output data in the specified format, and the value TRUE means to output data to a Windows client.)
The methods in steps 3 to 7 are encapsulated with shell commands. After the shell is enabled, the corresponding commands can be executed. The mapping is as follows:
-
LOS_TraceReset —— trace_reset
-
LOS_TraceEventMaskSet —— trace_mask
-
LOS_TraceStart —— trace_start
-
LOS_TraceStop —— trace_stop
-
LOS_TraceRecordDump —— trace_dump
Development Example
This example implements the following:
-
Create a trace task.
-
Set the event mask.
-
Start trace.
-
Stop trace.
-
Output trace data in the specified format.
Sample Code
The sample code is as follows:
The sample code can be compiled and verified in ./kernel/liteos_m/testsuites/src/osTest.c. The ExampleTraceTest function is called in TestTaskEntry.
#include "los_trace.h"
UINT32 g_traceTestTaskId;
VOID Example_Trace(VOID)
{
UINT32 ret;
LOS_TaskDelay(10);
/* Start trace. */
ret = LOS_TraceStart();
if (ret != LOS_OK) {
dprintf("trace start error\n");
return;
}
/* Trigger a task switching event. */
LOS_TaskDelay(1);
LOS_TaskDelay(1);
LOS_TaskDelay(1);
/* Stop trace. */
LOS_TraceStop();
LOS_TraceRecordDump(FALSE);
}
UINT32 ExampleTraceTest(VOID){
UINT32 ret;
TSK_INIT_PARAM_S traceTestTask = { 0 };
/* Create a trace task. */
memset(&traceTestTask, 0, sizeof(TSK_INIT_PARAM_S));
traceTestTask.pfnTaskEntry = (TSK_ENTRY_FUNC)Example_Trace;
traceTestTask.pcName = "TestTraceTsk"; /* Trace task name. */
traceTestTask.uwStackSize = 0x800;
traceTestTask.usTaskPrio = 5;
traceTestTask.uwResved = LOS_TASK_STATUS_DETACHED;
ret = LOS_TaskCreate(&g_traceTestTaskId, &traceTestTask);
if(ret != LOS_OK){
dprintf("TraceTestTask create failed .\n");
return LOS_NOK;
}
/* Trace is started by default. You can stop trace, clear the buffer, and restart trace. */
LOS_TraceStop();
LOS_TraceReset();
/* Enable trace of the Task module events. */
LOS_TraceEventMaskSet(TRACE_TASK_FLAG);
return LOS_OK;
}
Verification
The output is as follows:
***TraceInfo begin***
clockFreq = 50000000
CurEvtIndex = 7
Index Time(cycles) EventType CurTask Identity params
0 0x366d5e88 0x45 0x1 0x0 0x1f 0x4 0x0
1 0x366d74ae 0x45 0x0 0x1 0x0 0x8 0x1f
2 0x36940da6 0x45 0x1 0xc 0x1f 0x4 0x9
3 0x3694337c 0x45 0xc 0x1 0x9 0x8 0x1f
4 0x36eea56e 0x45 0x1 0xc 0x1f 0x4 0x9
5 0x36eec810 0x45 0xc 0x1 0x9 0x8 0x1f
6 0x3706f804 0x45 0x1 0x0 0x1f 0x4 0x0
7 0x37070e59 0x45 0x0 0x1 0x0 0x8 0x1f
***TraceInfo end***
The preceding data may vary depending on the running environment.
The output event information includes the occurrence time, event type, task in which the event occurs, object of the event operation, and other parameters of the event.
-
EventType: event type. For details, see enum LOS_TRACE_TYPE in the header file los_trace.h.
-
CurrentTask: ID of the running task.
-
Identity: object of the event operation. For details, see #TYPE#_PARAMS in the header file los_trace.h.
-
params: event parameters. For details, see #TYPE#_PARAMS in the header file los_trace.h.
The following uses output No. 0 as an example.
Index Time(cycles) EventType CurTask Identity params
0 0x366d5e88 0x45 0x1 0x0 0x1f 0x4
-
Time (cycles) can be converted into time (in seconds) by dividing the cycles by clockFreq.
-
0x45 indicates the task switching event. 0x1 is the ID of the task in running.
-
For details about the meanings of Identity and params, see the TASK_SWITCH_PARAMS macro.
#define TASK_SWITCH_PARAMS(taskId, oldPriority, oldTaskStatus, newPriority, newTaskStatus) \
taskId, oldPriority, oldTaskStatus, newPriority, newTaskStatus
Identity is taskId (0x0), and the first parameter is oldPriority (0x1f).
NOTE
The number of parameters in params is specified by LOSCFG_TRACE_FRAME_MAX_PARAMS. The default value is 3. Excess parameters are not recorded. Set LOSCFG_TRACE_FRAME_MAX_PARAMS based on service requirements.
Task 0x1 is switched to Task 0x0. The priority of task 0x1 is 0x1f, and the state is 0x4. The priority of task 0x0 is 0x0.