Compilation and Building Guide
Overview
The OpenHarmony Compilation and Building subsystem provides a build framework based on Generate Ninja (GN) and Ninja. It abstracts the build and configuration granularity by component, and provides function enhancement for built-in modules and function extension for service modules. The OpenHarmony Compilation and Building subsystem provides the following functions:
- Allows products to be assembled and independently built by component.
- Supports version builds for mini, small, and standard systems and build of the software development kit (SDK), which facilitates application developers to use the Integrated development environment (IDE).
- Supports customization and independent build based on different chipset solutions.
Application Scope
This guide is applicable to mini, small, and standard systems. The Chipset Solution applies only to mini and small systems.
Basic Concepts
Learn the following basic concepts before you get started:
-
Platform
A platform consists of a development board and the kernel. The subsystems and components vary with the platform.
-
Product
A product is a collection of components. The product image built can run on different development boards.
-
Subsystem
OpenHarmony is designed with a layered architecture, which consists of the kernel layer, system service layer, framework layer, and application layer from bottom up. For details, see OpenHarmony Technical Architecture. System functions are built from components, subsystems, and then to the system. In a multi-device deployment, you can customize subsystems and components as required. A subsystem, as a logical concept, consists of the least required components.
-
Component
A component is a reusable software binary unit that contains source code, configuration files, resource files, and build scripts. It can be built independently, integrated in binary mode, and tested independently. The chipset solution mentioned in this guide is a special component in nature.
-
Module
A module is a target to build. A component can also be a target to build.
-
Feature
A component can provide differentiated functions through features.
-
GN
GN is used to generate Ninja files.
-
Ninja
Ninja is a small high-speed build system.
-
hb
hb is an OpenHarmony command line tool used to execute build commands.
The Compilation and Build subsystem implements compilation and packaging through configuration. The following describes the relationships between the product, subsystem, component, and module.
Figure 1 Relationships between product, subsystem, component, and module
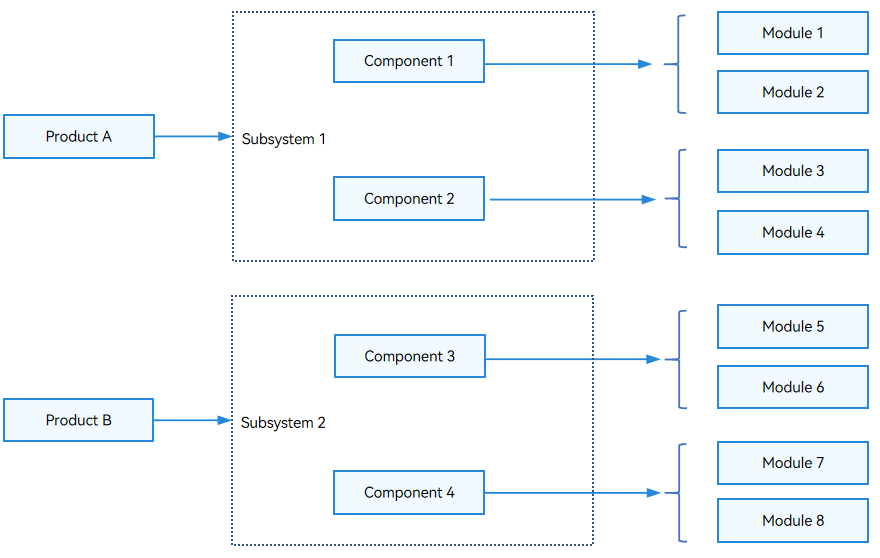
The relationships between the product, subsystem, component, and module are as follows:
- A subsystem is a collection of all components. A component can belong to only one subsystem.
- A component is a collection of modules. A module can belong to only one component.
- The product configuration file contains the configuration of all the components of the product. The component configuration can be reused.
- A component used in different products can provide differentiated functions through variants or features.
- A module is a target to build, and a component can also be a target to build.
Working Principles
A product, component, and module can be built, but a subsystem cannot. The figure below shows the build process.
Figure 2 Build process
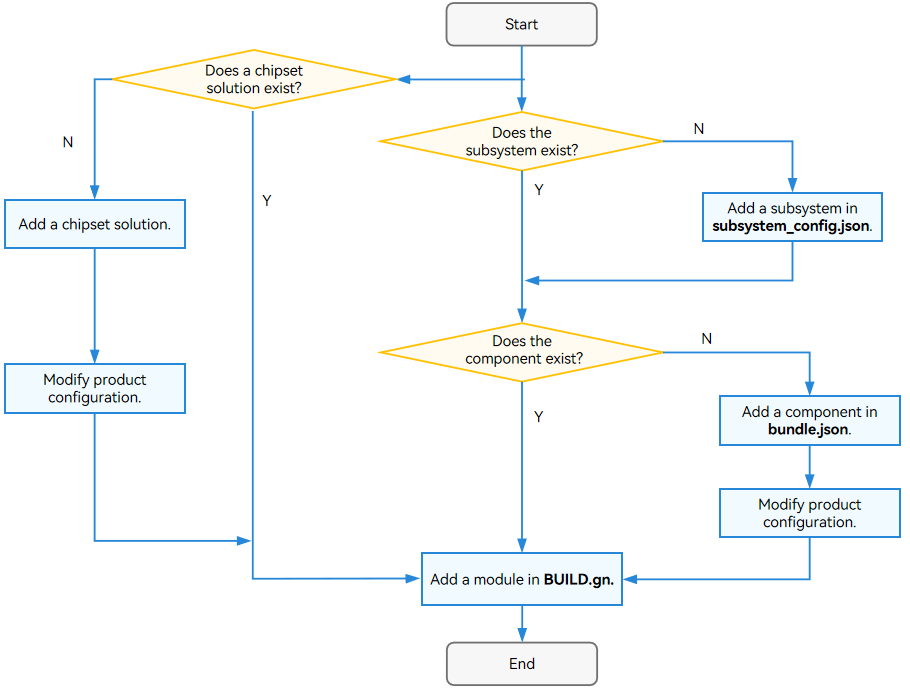
-
Run hb set to set the product to build.
-
Use hb build to build a product, development board, or component.
The procedure is as follows:
- Read the config.gni file of the development board selected. The file contains the build toolchain, linking commands, and build options.
- Run the gn gen command to read the product configuration and generate the out directory and ninja files for the product solution.
- Run ninja -C out/board/product to start the build.
- Package the files built, set the file attributes and permissions, and create a file system image.
Constraints
Currently, only Ubuntu18.04 and Ubuntu20.04 are supported. Ubuntu22.04 is not supported.
Environment Configuration
You must install the software packages required for build. The command is as follows:
-
Method 1: Run the script in the project directory.
./build/build_scripts/env_setup.sh -
Method 2: Run the apt-get install and pip3 install commands.
apt-get update -y apt-get install -y # Install Python 3.9 for Ubuntu 20.04, and install Python 3.8 for Ubuntu 18.04. apt-get install -y apt-utils binutils bison flex bc build-essential make mtd-utils gcc-arm-linux-gnueabi u-boot-tools python3.9 python3-pip git zip unzip curl wget gcc g++ ruby dosfstools mtools default-jre default-jdk scons python3-distutils perl openssl libssl-dev cpio git-lfs m4 ccache zlib1g-dev tar rsync liblz4-tool genext2fs binutils-dev device-tree-compiler e2fsprogs git-core gnupg gnutls-bin gperf lib32ncurses5-dev libffi-dev zlib* libelf-dev libx11-dev libgl1-mesa-dev lib32z1-dev xsltproc x11proto-core-dev libc6-dev-i386 libxml2-dev lib32z-dev libdwarf-dev apt-get install -y grsync xxd libglib2.0-dev libpixman-1-dev kmod jfsutils reiserfsprogs xfsprogs squashfs-tools pcmciautils quota ppp libtinfo-dev libtinfo5 libncurses5 libncurses5-dev libncursesw5 libstdc++6 gcc-arm-none-eabi vim ssh locales doxygen apt-get install -y libxinerama-dev libxcursor-dev libxrandr-dev libxi-dev # The following modules must be installed for Python. You can obtain the repo file from the source code of the build environment you use. chmod +x /usr/bin/repo pip3 install --trusted-host https://repo.huaweicloud.com -i https://repo.huaweicloud.com/repository/pypi/simple requests setuptools pymongo kconfiglib pycryptodome ecdsa ohos-build pyyaml prompt_toolkit==1.0.14 redis json2html yagmail python-jenkins pip3 install esdk-obs-python --trusted-host pypi.org pip3 install six --upgrade --ignore-installed six #Install LLVM, hc-gen, gcc_riscv32, Ninja, node-v14.15.4-linux-x64, and GN. If the shell in use is not bash or zsh, configure the following environment variables: # export PATH=/home/tools/llvm/bin:$PATH # export PATH=/home/tools/hc-gen:$PATH # export PATH=/home/tools/gcc_riscv32/bin:$PATH # export PATH=/home/tools/ninja:$PATH # export PATH=/home/tools/node-v12.20.0-linux-x64/bin:$PATH # export PATH=/home/tools/gn:$PATH # export PATH=~/.local/bin:$PATH NOTE
NOTE
The hb tool will be installed during the installation of ohos-build. If hb tool fails to be installed, install hb again.
Configuration Rules
To ensure that chipset and product solutions are decoupled from OpenHarmony, you need to follow certain rules during the configuration.
- Product Configuration Rules
- Subsystem Configuration Rules
- Component Configuration Rules
- Module Configuration Rules
- Chipset Solution Configuration Rules
- Feature Configuration Rules
- System Capability Configuration Rules
Guidelines
Directory Structure
/build # Directory for build
├── __pycache__
├── build_scripts/ # Python scripts for build
├── common/
├── config/ # Build-related configuration
├── core
│ └── gn/ # BUILD.gn configuration
└── build_scripts/
├── docs
gn_helpers.py*
lite/ # hb and preloader entry
misc/
├── ohos # Configuration of OpenHarmony build and packaging
│ ├── kits # Kits build and packaging templates and processing
│ ├── ndk # NDK templates and processing
│ ├── notice # Notice templates and processing
│ ├── packages # Distribution packaging templates and processing
│ ├── sa_profile # SA profiles and processing
│ ├── sdk # SDK templates and processing, which contains the module configuration in the SDK
│ └── testfwk # Testing-related processing
├── ohos.gni* # Common .gni files (facilitating one-time import of each module)
├── ohos_system.prop
├── ohos_var.gni*
├── prebuilts_download.sh*
├── print_python_deps.py*
├── scripts/
├── subsystem_config.json
├── subsystem_config_example.json
├── templates/ # C/C++ build templates
├── test.gni*
├── toolchain # Build toolchain configuration
├── tools # Common tools
├── version.gni
├── zip.py*
Build Commands
Run the prebuilts script in the root directory of the source code to perform precompilation and install the compiler and binary tool.
bash build/prebuilts_download.sh
Then, run the build commands in command line (CLI) mode or hb mode.
- Using the CLI
-
Run the following command in the root directory of the source code to build a full distribution:
Release version:
./build.sh --product-name {product_name}Debug version:
./build.sh --product-name {product_name} --gn-args is_debug=true CAUTION
CAUTION
Due to the limitation of the image size, the full build for the debug version may fail to be burnt. You are advised to build the binary file for each module separately. Run the following command to build a module separately:./build.sh --product-name {product_name} --gn-args is_debug=true --build-target {target_name}{product_name} specifies the product platform supported by the current distribution, for example, hispark_taurus_standard.
The image generated is stored in the out/{device_name}/packages/phone/images/ directory.
-
The ./build.sh command supports the following options:
-h, --help # Display help information and exit. --source-root-dir=SOURCE_ROOT_DIR # Specify the path. --product-name=PRODUCT_NAME # Specify the product name. --device-name=DEVICE_NAME # Specify the device name. --target-cpu=TARGET_CPU # Specify the CPU. --target-os=TARGET_OS # Specify the operating system. -T BUILD_TARGET, --build-target=BUILD_TARGET # Specify one or more targets to build. --gn-args=GN_ARGS # Specify GN parameters. --ninja-args=NINJA_ARGS # Specify Ninja parameters. -v, --verbose # Display all commands used. --keep-ninja-going # Keep Ninja going until 1,000,000 jobs fail. --jobs=JOBS --export-para=EXPORT_PARA --build-only-gn # Perform GN parsing and do not run Ninja. --ccache # (Optional) Use ccache for build. You need to install ccache locally. --fast-rebuild # Specify whether to allow fast rebuild. The default value is False. --log-level=LOG_LEVEL # Specify the log level used in the build process. The options are debug, info, and error. The default value is info. --device-type=DEVICE_TYPE # Specify the device type. The default value is default. --build-variant=BUILD_VARIANT # Specify the device operation mode. The default value is user.
- Using the hb tool
hb is an OpenHarmony command line tool for executing build commands. Common hb commands are described as follows:
hb set
Sets the product to build.
hb set -h
usage: hb set [-h] [-root [ROOT_PATH]] [-p]
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-root [ROOT_PATH], --root_path [ROOT_PATH]
Set OHOS root path
-p, --product Set OHOS board and kernel
-
If you run hb set with no argument, the default setting process starts.
-
You can run hb set -root dir to set the root directory of the source code.
-
You can run hb set -p to set the product to build.
hb env
Displays current settings.
hb env
[OHOS INFO] root path: xxx
[OHOS INFO] board: hispark_taurus
[OHOS INFO] kernel: liteos
[OHOS INFO] product: ipcamera
[OHOS INFO] product path: xxx/vendor/hisilicon/ipcamera
[OHOS INFO] device path: xxx/device/hisilicon/hispark_taurus/sdk_linux_4.19
hb build
Builds a product, component, module, or chipset solution.
hb build -h
usage: hb build [-h] [-b BUILD_TYPE] [-c COMPILER] [-t [TEST [TEST ...]]] [-cpu TARGET_CPU] [--dmverity] [--tee]
[-p PRODUCT] [-f] [-n] [-T [TARGET [TARGET ...]]] [-v] [-shs] [--patch] [--compact-mode]
[--gn-args GN_ARGS] [--keep-ninja-going] [--build-only-gn] [--log-level LOG_LEVEL] [--fast-rebuild]
[--device-type DEVICE_TYPE] [--build-variant BUILD_VARIANT]
[component [component ...]]
positional arguments:
component name of the component, mini/small only
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-b BUILD_TYPE, --build_type BUILD_TYPE
release or debug version, mini/small only
-c COMPILER, --compiler COMPILER
specify compiler, mini/small only
-t [TEST [TEST ...]], --test [TEST [TEST ...]]
compile test suit
-cpu TARGET_CPU, --target-cpu TARGET_CPU
select cpu
--dmverity enable dmverity
--tee Enable tee
-p PRODUCT, --product PRODUCT
build a specified product with {product_name}@{company}
-f, --full full code compilation
-n, --ndk compile ndk
-T [TARGET [TARGET ...]], --target [TARGET [TARGET ...]]
compile single target
-v, --verbose show all command lines while building
-shs, --sign_haps_by_server
sign haps by server
--patch apply product patch before compiling
--compact-mode compatible with standard build system set to false if we use build.sh as build entrance
--gn-args GN_ARGS specifies gn build arguments, eg: --gn-args="foo="bar" enable=true blah=7"
--keep-ninja-going keeps ninja going until 1000000 jobs fail
--build-only-gn only do gn parse, do not run ninja
--log-level LOG_LEVEL
specifies the log level during compilationyou can select three levels: debug, info and error
--fast-rebuild it will skip prepare, preloader, gn_gen steps so we can enable it only when there is no change
for gn related script
--device-type DEVICE_TYPE
specifies device type
--build-variant BUILD_VARIANT
specifies device operating mode
-
If you run hb build with no argument, the previously configured code directory, product, and options are used for the build. The -f option deletes all products to be built. It is equivalent to running hb clean and hb build.
-
You can run hb build {component_name} to build product components separately based on the development board and kernel set for the product, for example, hb build kv_store.
-
You can run hb build -p ipcamera@hisilicon to skip the setting step and build the product directly.
-
You can run hb build in device/board/device_company to select the kernel and build an image that contains the kernel and drivers only based on the current development board and the selected kernel.
hb clean
Deletes all the files except args.gn and build.log in the out directory (default). To clear files in a specified directory, add the directory parameter to the command, for example, hb clean out/board/product.
hb clean
usage: hb clean [-h] [out_path]
positional arguments:
out_path clean a specified path.
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
NOTE
- For details about how to set up the build environment and perform the build, see the related topics in Getting Started
- OpenHarmony also provides the Docker environment, which spares the installation of the build tool. For details, see Docker Environment
Building Procedures
You can add and build a product, component, chipset solution, and module. For details, see:
- Adding and Building a Product
- Adding and Building a Component
- Adding and Building a Module
- Adding and Building a Chipset Solution