Light
Overview
Light
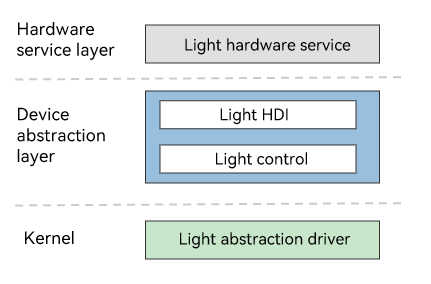
The light driver model provides APIs for the upper-layer light hardware service layer to control lights, including obtaining the light type, setting the lighting mode and blinking effect, and turning on or off a light. This model implements cross-OS porting and differentiated configurations based on the Hardware Driver Foundation (HDF) to achieve the goal of "one-time development for cross-system deployment" of the light driver.
The figure below shows the light driver model.
Figure 1 Light driver model
Working Principles
The figure below shows how the light driver works.
Figure 2 How light driver works
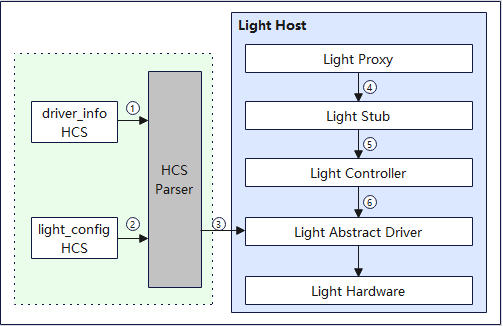
The following describes how the light module driver loads and starts on a Hi3516D V300 board that runs the standard system.
- The Device Manager reads the Light device management configuration from the device_info.hcs file.
- The Device Manager reads the light data configuration from the light_config.hcs file.
- The HCS Parser parses the light device management configuration, loads the Light Host, and controls the Host to load the driver.
- The Light Proxy obtains the light HDI service instance and calls the Light Stub over Inter-Process Communication (IPC).
- The Light Stub processes IPC-related service logic and calls the Light Controller after parameter deserialization.
- The Light Controller implements the HDI APIs and calls the Light Abstract Driver APIs to operate the light devices.
Development Guidelines
When to Use
Light control is widely used in daily life. For example, a light is blinking when a mobile phone receives an SMS message or has low battery level, and a light changes its colors based on the device charging status. These actions are implemented by calling the APIs provided by the light driver model.
Available APIs
The light driver model provides APIs for obtaining information about all the lights in the system and dynamically setting the blinking mode and duration. The light hardware service calls GetLightInfo() to obtain the basic light information, calls TurnOnLight() to set the blinking effect, and calls TurnOffLight() to turn off lights. The following table describes the APIs of the light driver model.
Table 1 APIs of the light driver model
| API | Description |
|---|---|
| int32_t (*GetLightInfo)([out] struct LightInfo **lightInfo, [out] uint32_t *count) | Obtains information about all types of lights in the system. lightInfo indicates the double pointer to the light information obtained. count indicates the pointer to the number of lights. |
| int32_t (*TurnOnLight)([in] uint32_t lightId, [in] struct LightEffect *effect) | Turns on available lights in the list based on the specified light type. lightId indicates the light type, and effect indicates the pointer to the light effect. |
| int32_t (*TurnOffLight)([in] uint32_t lightId) | Turns off available lights in the list based on the specified light type. |
Development Procedure
-
Based on the HDF and the driver entry, complete the light abstract driver development (using the Bind, Init, Release, and Dispatch functions), resource configuration, and HCS parsing.
-
Call HDF_INIT to register the driver entry with the HDF. Generally, the HDF calls the Bind function and then the Init function to load the driver. If Init fails to be called, the HDF calls Release to release driver resources and exit.
-
The light driver model uses HDF configuration source (HCS). For details about HCS fields, see Configuration Management. The light driver entry is defined as follows:
/* Register the light entry data structure object. */ struct HdfDriverEntry g_lightDriverEntry = { .moduleVersion = 1, // Version of the light module. .moduleName = "HDF_LIGHT", // Light module name, which must be the same as the value of moduleName in the device_info.hcs file. .Bind = BindLightDriver, // Bind() of the light driver. .Init = InitLightDriver, // Init() of the light driver. .Release = ReleaseLightDriver, // Release() of the light driver. }; /* Call HDF_INIT to register the driver entry with the HDF. */ HDF_INIT(g_lightDriverEntry); -
Develop the light abstract driver. Specifically, implement the Bind, Init, Release, and Dispatch functions.
/* Dispatch the light driver. */ static int32_t DispatchLight(struct HdfDeviceIoClient *client, int32_t cmd, struct HdfSBuf *data, struct HdfSBuf *reply) { ..... if (cmd == LIGHT_IO_CMD_GET_INFO_LIST) { CHECK_LIGHT_NULL_PTR_RETURN_VALUE(reply, HDF_ERR_INVALID_PARAM); return GetAllLightInfo(data, reply); } CHECK_LIGHT_NULL_PTR_RETURN_VALUE(data, HDF_ERR_INVALID_PARAM); (void)OsalMutexLock(&drvData->mutex); if (!HdfSbufReadInt32(data, &lightId)) { HDF_LOGE("%s: sbuf read lightId fail", __func__); (void)OsalMutexUnlock(&drvData->mutex); return HDF_ERR_INVALID_PARAM; } ..... ret = DispatchCmdHandle(lightId, data, reply); (void)OsalMutexUnlock(&drvData->mutex); return ret; } /* Bind the external service provided by the light driver to the HDF. */ int32_t BindLightDriver(struct HdfDeviceObject *device) { struct LightDriverData *drvData = NULL; CHECK_LIGHT_NULL_PTR_RETURN_VALUE(device, HDF_FAILURE); /* Allocate resources for private interfaces. */ drvData = (struct LightDriverData *)OsalMemCalloc(sizeof(*drvData)); CHECK_LIGHT_NULL_PTR_RETURN_VALUE(drvData, HDF_ERR_MALLOC_FAIL); /* Functions to be dispatched. */ drvData->ioService.Dispatch = DispatchLight; drvData->device = device; device->service = &drvData->ioService; g_lightDrvData = drvData; return HDF_SUCCESS; } /* Initialize the light driver. */ int32_t InitLightDriver(struct HdfDeviceObject *device) { ..... /* Initialize the workqueue. */ if (HdfWorkQueueInit(&drvData->workQueue, LIGHT_WORK_QUEUE_NAME) != HDF_SUCCESS) { HDF_LOGE("%s: init workQueue fail!", __func__); return HDF_FAILURE; } /* Initialize work items. */ if (HdfWorkInit(&drvData->work, LightWorkEntry, (void*)drvData) != HDF_SUCCESS) { HDF_LOGE("%s: init work fail!", __func__); return HDF_FAILURE; } /* Parse the HCS. */ if (GetLightConfigData(device->property) != HDF_SUCCESS) { HDF_LOGE("%s: get light config fail!", __func__); return HDF_FAILURE; } /* Set the GPIO pin direction. */ if (SetLightGpioDir(drvData) != HDF_SUCCESS) { HDF_LOGE("%s: set light gpio dir fail!", __func__); return HDF_FAILURE; } return HDF_SUCCESS; } /* Release the resources allocated for driver initialization. */ void ReleaseLightDriver(struct HdfDeviceObject *device) { ..... /* Release the allocated resources. */ for (i = LIGHT_TYPE_NONE; i < LIGHT_TYPE_BUTT; ++i) { if (drvData->info[i] != NULL) { OsalMemFree(drvData->info[i]); drvData->info[i] = NULL; } } /* Destroy workqueue resources. */ HdfWorkDestroy(&drvData->work); HdfWorkQueueDestroy(&drvData->workQueue); (void)OsalMutexDestroy(&drvData->mutex); OsalMemFree(drvData); g_lightDrvData = NULL; } -
The light device management module is responsible for publishing light device APIs in the system. During the system startup process, the HDF loads the device management driver based on Light Host in the HCS.
/* HCS of the light device. */ light :: host { hostName = "light_host"; device_light :: device { device0 :: deviceNode { policy = 2; // Policy for the driver to publish services. If the value is 0, the driver does not publish services. If the value is 1, the driver publishes services to the kernel space. If the value is 2, the driver publishes services to both the kernel space and user space. priority = 100; // Priority (0–200) for starting the light driver. A larger value indicates a lower priority. The recommended value is 100. If the priorities are the same, the device loading sequence is not ensured. preload = 0; // The value 0 means to load the driver by default during the startup of the system. The value 2 means the opposite. permission = 0664; // Permission for the device node created. moduleName = "HDF_LIGHT"; // Light driver name. The value must be the same as the value of moduleName in the driver entry structure. serviceName = "hdf_light"; // Service published by the light driver. The service name must be unique. deviceMatchAttr = "hdf_light_driver"; // Keyword for matching the private data of the driver. The value must be the same as that of match_attr in the private data configuration table of the driver. } } }
-
-
Parse the device attribute information and registers, and register them with the light device management module.
/* Allocate resources and parse the HCS. */ static int32_t ParseLightInfo(const struct DeviceResourceNode *node, const struct DeviceResourceIface *parser) { ..... /* Obtain the number of supported light types from the HCS. */ drvData->lightNum = parser->GetElemNum(light, "lightId"); .... for (i = 0; i < drvData->lightNum; ++i) { /* Obtain the light type. */ ret = parser->GetUint32ArrayElem(light, "lightId", i, &temp, 0); CHECK_LIGHT_PARSER_RESULT_RETURN_VALUE(ret, "lightId"); } for (i = 0; i < drvData->lightNum; ++i) { ..... /* Types are used as subscripts to create space. */ drvData->info[temp] = (struct LightDeviceInfo *)OsalMemCalloc(sizeof(struct LightDeviceInfo)); ..... /* Fill in the light device information. */ ret = parser->GetUint32(node, "busRNum", (uint32_t *)&drvData->info[temp]->busRNum, 0); if (ret != HDF_SUCCESS) { /* If busNum fails to be obtained, the color of the light corresponding to busNum cannot be set. */ drvData->info[temp]->busRNum = LIGHT_INVALID_GPIO; } ret = parser->GetUint32(node, "busGNum", (uint32_t *)&drvData->info[temp]->busGNum, 0); if (ret != HDF_SUCCESS) { drvData->info[temp]->busGNum = LIGHT_INVALID_GPIO; } ret = parser->GetUint32(node, "busBNum", (uint32_t *)&drvData->info[temp]->busBNum, 0); if (ret != HDF_SUCCESS) { drvData->info[temp]->busBNum = LIGHT_INVALID_GPIO; } } ..... return HDF_SUCCESS; } -
Implement the APIs for obtaining the light type, setting the blinking mode, turning on and off lights, and creating and destroying a timer based on the blinking mode.
/* Call GetAllLightInfo() to obtain the light types, call TurnOnLight() to turn on lights, and call TurnOffLight() to turn off lights. */ static int32_t GetAllLightInfo(struct HdfSBuf *data, struct HdfSBuf *reply) { ..... /* Obtain the number of light types. */ if (!HdfSbufWriteUint32(reply, drvData->lightNum)) { HDF_LOGE("%s: write sbuf fail", __func__); return HDF_FAILURE; } for (i = 0; i < LIGHT_TYPE_BUTT; ++i) { if (drvData->info[i] == NULL) { continue; } lightInfo.lightId = i; lightInfo.reserved = NULL; /* Fill the light device information into the reply. */ if (!HdfSbufWriteBuffer(reply, &lightInfo, sizeof(lightInfo))) { HDF_LOGE("%s: write sbuf fail", __func__); return HDF_FAILURE; } } return HDF_SUCCESS; } /* Update the status of the lights of the specified type. */ static int32_t UpdateLight(uint32_t lightId, uint32_t lightOn) { ..... /* If the lightBrightness value passed in is invalid, use the default value. */ if (drvData->info[lightId]->lightBrightness == 0) { lightBrightness = drvData->info[lightId]->defaultBrightness; } else { lightBrightness = drvData->info[lightId]->lightBrightness; } /* If bits 0 to 7 are not 0, output the GPIO pins corresponding to blue based on the status of lightOn. */ if ((lightBrightness & LIGHT_MAKE_B_BIT) != 0) { ret = WriteGpio(drvData->info[lightId]->busBNum, lightOn); if (ret != HDF_SUCCESS) { HDF_LOGE("%s: write blue gpio fail", __func__); return HDF_FAILURE; } } /* If bits 8 to 15 are not 0, output the GPIO pins corresponding to green based on the status of lightOn. */ if ((lightBrightness & LIGHT_MAKE_G_BIT) != 0) { ret = WriteGpio(drvData->info[lightId]->busGNum, lightOn); if (ret != HDF_SUCCESS) { HDF_LOGE("%s: write green gpio fail", __func__); return HDF_FAILURE; } } /* If bits 16 to 23 are not 0, output the GPIO pins corresponding to red based on the status of lightOn. */ if ((lightBrightness & LIGHT_MAKE_R_BIT) != 0) { ret = WriteGpio(drvData->info[lightId]->busRNum, lightOn); if (ret != HDF_SUCCESS) { HDF_LOGE("%s: write red gpio fail", __func__); return HDF_FAILURE; } } ..... } /* Enable lights based on the specified light type and input parameters. */ static int32_t TurnOnLight(uint32_t lightId, struct HdfSBuf *data, struct HdfSBuf *reply) { ..... /* Receive the lightBrightness value passed in. Bits 24 to 31 are extension bits, bits 16 to 23 indicate red, bits 8 to 15 indicate green, and bits 0 to 7 indicate blue. If lightBrightness is not 0, turn on the light in the specified color. Set the light brightness to a value ranging from 0 to 255 if supported. */ drvData->info[lightId]->lightBrightness = buf->lightBrightness; /* The light is steady on. */ if (buf->flashEffect.flashMode == LIGHT_FLASH_NONE) { return UpdateLight(lightId, LIGHT_STATE_START); } /* The light is blinking. */ if (buf->flashEffect.flashMode == LIGHT_FLASH_TIMED) { drvData->info[lightId]->lightState = LIGHT_STATE_START; /* If the specified blinking duration is less than the minimum time period supported by the system, the time configured by the system (in HCS) is used. */ drvData->info[lightId]->onTime = buf->flashEffect.onTime < drvData->info[lightId]->onTime ? drvData->info[lightId]->onTime : buf->flashEffect.onTime; drvData->info[lightId]->offTime = buf->flashEffect.offTime < drvData->info[lightId]->offTime ? drvData->info[lightId]->offTime : buf->flashEffect.offTime; /* Create a timer. */ if (OsalTimerCreate(&drvData->timer, drvData->info[lightId]->onTime, LightTimerEntry, (uintptr_t)lightId) != HDF_SUCCESS) { HDF_LOGE("%s: create light timer fail!", __func__); return HDF_FAILURE; } /* Start the periodic timer. */ if (OsalTimerStartLoop(&drvData->timer) != HDF_SUCCESS) { HDF_LOGE("%s: start light timer fail!", __func__); return HDF_FAILURE; } } return HDF_SUCCESS; } /* Turn off lights based on the specified light type. */ static int32_t TurnOffLight(uint32_t lightId, struct HdfSBuf *data, struct HdfSBuf *reply) { /* Delete the timer. */ if (drvData->timer.realTimer != NULL) { if (OsalTimerDelete(&drvData->timer) != HDF_SUCCESS) { HDF_LOGE("%s: delete haptic timer fail!", __func__); } } if (UpdateLight(lightId, LIGHT_STATE_STOP) != HDF_SUCCESS) { HDF_LOGE("%s: gpio write fail", __func__); return HDF_FAILURE; } return HDF_SUCCESS; }
Verification
After the driver is developed, develop auto-test cases in the light unit test to verify the basic functionalities of the driver. Use the developer self-test platform as the test environment.
/* Initialize the LightInterfaceInstance before executing the test case. */
void HdfLightTest::SetUpTestCase()
{
g_lightDev = NewLightInterfaceInstance();
if (g_lightDev == nullptr) {
printf("test light get Module instance fail\n\r");
}
int32_t ret = g_lightDev->GetLightInfo(&g_lightInfo, &g_count);
if (ret == -1) {
printf("get light informations fail\n\r");
}
}
/* After the test case is executed, release the resources used by the test case. */
void HdfLightTest::TearDownTestCase()
{
if(g_lightDev != nullptr){
FreeLightInterfaceInstance();
g_lightDev = nullptr;
}
}
/* Obtain the test light type. */
HWTEST_F(HdfLightTest, GetLightList001, TestSize.Level1)
{
struct LightInfo *info = nullptr;
if (g_lightInfo == nullptr) {
EXPECT_NE(nullptr, g_lightInfo);
return;
}
printf("get light list num[%d]\n\r", g_count);
info = g_lightInfo;
for (int i = 0; i < g_count; ++i) {
printf("get lightId[%d]\n\r", info->lightId);
EXPECT_GE(info->lightId, g_minLightId);
EXPECT_LE(info->lightId, g_maxLightId);
info++;
}
}
/* Verify the steady on state of the light. */
HWTEST_F(HdfLightTest, EnableLight001, TestSize.Level1)
{
int32_t i;
int32_t ret;
struct LightEffect effect;
effect->lightBrightness = 0x00800000;
effect->flashEffect.flashMode = LIGHT_FLASH_NONE;
effect->flashEffect.onTime = 0;
effect->flashEffect.offTime = 0;
for (i = 0; i < g_count; ++i) {
ret = g_lightDev->TurnOnLight(g_lightInfo[i]->lightId, effect);
EXPECT_EQ(0, ret);
OsalSleep(LIGHT_WAIT_TIME);
ret = g_lightDev->TurnOffLight(type);
EXPECT_EQ(0, ret);
}
}
/* Verify the blinking mode of the light. */
HWTEST_F(HdfLightTest, EnableLight002, TestSize.Level1)
{
int32_t i;
int32_t ret;
struct LightEffect effect;
effect->lightBrightness = 0x00800000;
effect->flashEffect.flashMode = LIGHT_FLASH_TIMED;
effect->flashEffect.onTime = g_onTime;
effect->flashEffect.offTime = g_offTime;
for (i = 0; i < g_count; ++i) {
ret = g_lightDev->TurnOnLight(g_lightInfo[i]->lightId, effect);
EXPECT_EQ(0, ret);
OsalSleep(LIGHT_WAIT_TIME);
ret = g_lightDev->TurnOffLight(type);
EXPECT_EQ(0, ret);
}
}