Multimedia
Introduction
The multimedia subsystem provides a set of simple and easy-to-use APIs for you to access the system and media resources.
This subsystem offers various media services covering audio, videos, and cameras, which provide the following capabilities:
- Audio playback and recording
- Video playback and recording
- Photographing and recording (with cameras)
System Architecture
Figure 1 Architecture of the multimedia subsystem
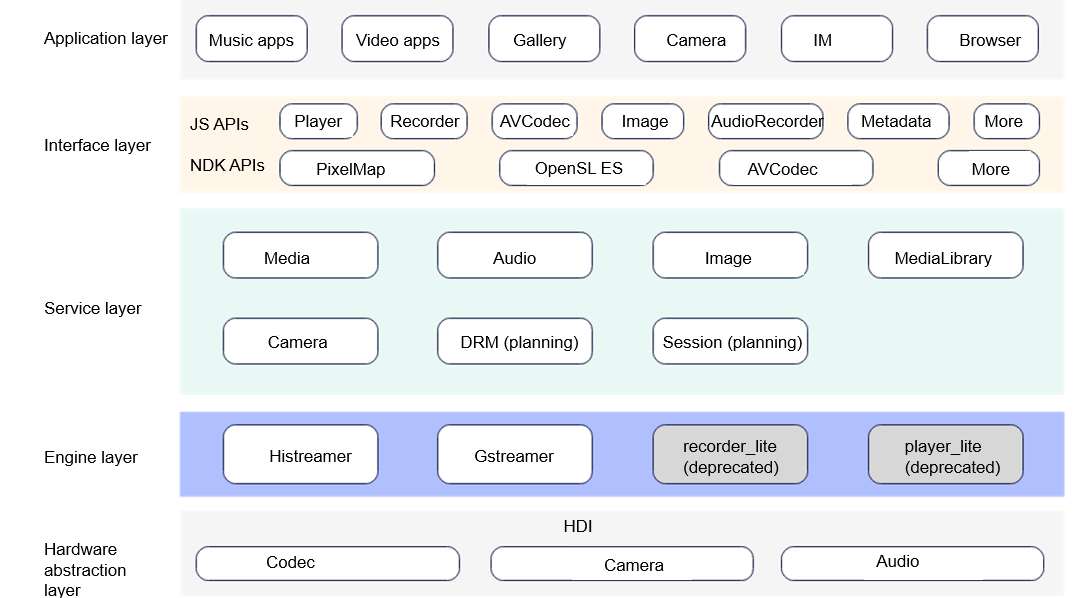
- Media: provides playback and recording APIs for applications, and invokes the Gstreamer, Histreamer, or other engines through cross-process calling or direct calling.
- For the mini system, the media component invokes Histreamer to support audio playback.
- For the small system, the media component invokes recorder_lite to support audio/video recording and invokes player_lite by default to support audio/video playback. If the system variable debug.media_service.histreamer is set to 1, the component invokes Histreamer to support audio/video playback. For details, see syspara Module or syspara_lite.
- For the standard system, the media component invokes Gstreamer to support audio/video playback and recording.
- Audio: supports audio input and output, policy management, and audio focus management.
- Camera: provides camera operation APIs for preview, photographing, and video recording.
- Image: supports encoding and decoding of common image formats.
- MediaLibrary: supports local and distributed media data access management.
- Histreamer: a lightweight media engine that supports file/network streaming media input, audio/video decoding and playback, audio/video encoding and recording, and plugin extension.
- Gstreamer: an open-source GStreamer engine that supports streaming media, audio and video playback, and recording.
Directory Structure
The structure of the repository directory is as follows:
/foundation/multimedia # Service code
├── audio_lite # Audio module for the small system
│ ├── figures # Architecture and process figures of the audio module for the small system
│ ├── frameworks # Audio framework implementation for the small system
│ └── interfaces # Audio module APIs for the small system
├── audio_standard # Audio module for the standard system
│ ├── figures # Architecture and process figures of the audio module for the standard system
│ ├── frameworks # Audio framework implementation for the standard system
│ ├── interfaces # Audio module APIs for the standard system
│ ├── sa_profile # Audio service profile for the standard system
│ └── services # Audio service implementation for the standard system
├── camera_lite # Camera module for the small system
│ ├── figures # Architecture and process figures of the camera module for the small system
│ ├── frameworks # Camera framework implementation for the small system
│ └── interfaces # Camera module APIs for the small system
├── camera_standard # Camera module for the standard system
│ ├── figures # Architecture and process figures of the camera module for the standard system
│ ├── frameworks # Camera framework implementation for the standard system
│ └── interfaces # Camera module APIs for the standard system
├── media_lite # Playback and recording module for the small system
│ ├── figures # Architecture and process figures of the playback and recording module for the small system
│ ├── frameworks # Playback and recording framework implementation for the small system
│ ├── interfaces # Playback and recording module APIs for the small system
│ └── services # Playback and recording service implementation for the small system
├── media_standard # Playback and recording module for the standard system
│ ├── figures # Architecture and process figures of the playback and recording module for the standard system
│ ├── frameworks # Playback and recording framework implementation for the standard system
│ └── interfaces # Playback and recording module APIs for the standard system
├── histreamer # Histreamer engine
│ └── engine # Media engine
│ ├── player # Encapsulated player
│ ├── foundation # Basic tools
│ ├── pipeline # Pipeline framework
│ └── plugin # Plugin framework
│ └── plugins # Platform software plugins
└── utils # Subsystem utility module
└── lite # Utility module for the small system
├── figures # Architecture and process figures of the utility module for the small system
├── hals # Hardware abstraction interfaces of the subsystem for the small system
├── interfaces # Utility module APIs for the standard system
└── src # Utility module framework implementation for the small system
Constraints
Hardware-based decoding and encoding functions of audio and video data are device-specific.
Usage Guidelines
You can use the APIs in any of the provided classes based on your development requirements.
- For details about how to call media APIs to implement the video recording, preview, and playback, see Multimedia Development Guide.
- For a simple player, use Player and Recorder classes to quickly implement the playback and recording features.
- The CameraKit class provides a group of effective methods for controlling a camera, which facilitates the camera development.
- You can create a CameraKit object and register various callbacks to respond to many events in the multimedia module. Then, create a Camera object to operate camera resources, for example, to start preview, recording, and stream capturing, and set related parameters.
Installation
Load the kernel and related drivers before installing the repository. For details, see readme files of kernel and driver subsystems.