Development Guidelines
When to Use
-
Develop Page abilities for applications that have a UI for human-machine interaction, such as news applications, video players, navigation applications, and payment applications. Most applications we use in our daily lives are such type of applications.
-
Develop Service abilities for applications so that they can run particular services in the background, such as music playing, computing, and navigation services.
-
Pack both Page and Service abilities into HarmonyOS Ability Packages (HAPs). All applications must be packed into HAP files before being published to the application market. Once published, users can then download the applications from the application market.
Available APIs
Table 1 APIs of the ability management framework
How to Develop
Creating a Service Ability
-
Create the MyServiceAbility child class from Ability in my_service_ability.h.
class MyServiceAbility: public Ability { protected: void OnStart(const Want& want); const SvcIdentity *OnConnect(const Want &want) override; void MsgHandle(uint32_t funcId, IpcIo *request, IpcIo *reply) override; }; -
Call the REGISTER_AA macro to register the ServiceAbility class with the application framework so that the framework can instantiate the MyServiceAbility class you have created.
#include "my_service_ability.h" REGISTER_AA(ServiceAbility) void MyServiceAbility::OnStart(const Want& want) { printf("ServiceAbility::OnStart\n"); Ability::OnStart(want); } const SvcIdentity *MyServiceAbility::OnConnect(const Want &want) { printf("ServiceAbility::OnConnect\n"); return Ability::OnConnect(want); } void MyServiceAbility::MsgHandle(uint32_t funcId, IpcIo *request, IpcIo *reply) { printf("ServiceAbility::MsgHandle, funcId is %u\n", funcId); int result = 0; if (funcId == 0) { result = IpcIoPopInt32(request) + IpcIoPopInt32(request); } // push data IpcIoPushInt32(reply, result); } -
Override the following lifecycle callbacks for Service abilities to implement your own logic for your Service ability. When overriding a lifecycle callback, you must call the corresponding function from the parent class.
-
OnStart()
This callback is invoked when a Service ability is being created to perform Service ability initialization operations that take a short time. This callback is invoked only once in the entire lifecycle of a Service ability.
void MyServiceAbility::OnStart(const Want& want) { printf("ServiceAbility::OnStart\n"); Ability::OnStart(want); } -
OnConnect()
This callback is invoked when another ability is connected to the Service ability. This callback returns an SvcIdentity object for the other ability to interact with the Service ability.
const SvcIdentity *MyServiceAbility::OnConnect(const Want &want) { printf("ServiceAbility::OnConnect\n"); return Ability::OnConnect(want); } -
OnDisconnect()
This callback is invoked when another ability is disconnected from the Service ability.
-
OnStop()
This callback is invoked when a Service ability is destroyed. You should override this callback for your Service ability to clear its resources, such as threads and registered listeners.
-
-
Override the message handling function.
The MsgHandle function is used by Service abilities to handle messages sent from clients. funcId indicates the type of the message sent from the client, and request indicates the pointer to the serialized request parameters sent from the client. If you want to send the result back after the message is handled, serialize the result and write it into reply.
void ServiceAbility::MsgHandle(uint32_t funcId, IpcIo *request, IpcIo *reply) { printf("ServiceAbility::MsgHandle, funcId is %d\n", funcId); int result = 0; if (funcId == PLUS) { result = IpcIoPopInt32(request) + IpcIoPopInt32(request); } // push data IpcIoPushInt32(reply, result); } -
Register a Service ability.
Declare your Service ability in the config.json file by setting its type attribute to service.
"abilities": [{ "name": "ServiceAbility", "icon": "res/drawable/phone.png", "label": "test app 2", "launchType": "standard", "type": "service", "visible": true } ] -
Start a Service ability.
-
The Ability class provides the StartAbility() function to start another ability. You can pass a Want object to this function to start a Service ability.
You can use the SetWantElement() function provided in the AbilityKit to set information about the target Service ability to start. The element parameter of the SetWantElement() function indicates the ElementName structure that contains the bundle name and target ability name required for starting an ability.
{ Want want = { nullptr }; ElementName element = { nullptr }; SetElementBundleName(&element, "com.company.appname"); SetElementAbilityName(&element, "ServiceAbility"); SetWantElement(&want, element); StartAbility(want); ClearElement(&element); ClearWant(&want); }The StartAbility() function is executed immediately. If the Service ability is not running while the function is called, the system invokes OnStart() first.
-
Stops a Service ability.
Once created, the Service ability keeps running in the background. You can call StopAbility() to stop the Service ability.
-
-
Connect to a Service ability.
-
If you need to connect a Service ability to a Page ability or to a Service ability in another application, you should first create a Service ability for connection. A Service ability allows other abilities to connect to it through ConnectAbility() by passing a Want object that contains information about the target Service ability to the function. You can implement callbacks in IAbilityConnection to be invoked when a Service ability is connected or disconnected. The OnAbilityConnectDone() callback is invoked when an ability is connected, and OnAbilityDisconnectDone() is invoked when an ability is disconnected.
{ // Create an IAbilityConnection object and implement the two callbacks. IAbilityConnection abilityConnection = new IAbilityConnection(); abilityConnection->OnAbilityConnectDone = OnAbilityConnectDone; abilityConnection->OnAbilityDisconnectDone = OnAbilityDisconnectDone; void OnAbilityConnectDone(ElementName *elementName, SvcIdentity *serviceSid, int resultCode, void *data) { if (resultCode != 0) { return; } // Push data. IpcIo request; char dataBuffer[IPC_IO_DATA_MAX]; IpcIoInit(&request, dataBuffer, IPC_IO_DATA_MAX, 0); IpcIoPushInt32(&request, 10); IpcIoPushInt32(&request, 6); // Send and receive the reply. IpcIo reply; uintptr_t ptr = 0; if (Transact(nullptr, *serviceSid, 0, &request, &reply, LITEIPC_FLAG_DEFAULT, &ptr) != LITEIPC_OK) { printf("transact error\n"); return; } int result = IpcIoPopInt32(&reply); printf("execute add method, result is %d\n", result); if (ptr != 0) { FreeBuffer(nullptr, reinterpret_cast<void *>(ptr)); } } void OnAbilityDisconnectDone(ElementName *elementName, int resultCode, void *data) { printf("elementName is %s, %s\n", elementName->bundleName, elementName->abilityName); } } -
The following sample code snippet shows how to initiate ability connection and disconnection:
{ // Connect an ability to a specified Service ability. Want want = { nullptr }; ElementName element = { nullptr }; SetElementBundleName(&element, "com.company.appname"); SetElementAbilityName(&element, "ServiceAbility"); SetWantElement(&want, element); ConnectAbility(want, *abilityConnection, this); // Disconnect from a Service ability. DisconnectAbility(*abilityConnection); }
-
Development Guidelines on Bundle Management
Installing an Application
The installation API can only be used by built-in system applications. Applications can be installed in either of the following paths:
- Default installation directory /storage/app/ in the system
- Particular directory on the external storage, for example, a microSD card
You can specify the installation path when creating an InstallParam instance. To install the application in the /storage/app/ directory, set the installLocation member variable in the InstallParam instance to INSTALL_LOCATION_INTERNAL_ONLY. To install the application in the /sdcard/app/ directory of the external storage, set installLocation to INSTALL_LOCATION_PREFER_EXTERNAL. The application installation process is asynchronous, and a semaphore-like mechanism is required to ensure that the installation callback can be executed.
The procedure for installing an application is as follows (the system directory is used as an example):
-
Place the signed HAP file in a specified directory.
-
Create an InstallParam instance and define the semaphore.
InstallParam installParam = { .installLocation = INSTALL_LOCATION_INTERNAL_ONLY, // Install the application in the system directory. .keepData = false }; static sem_t g_sem; -
Define the callback function.
static void InstallCallback(const uint8_t resultCode, const void *resultMessage) { std::string strMessage = reinterpret_cast<const char *>(resultMessage); if (!strMessage.empty()) { printf("install resultMessage is %s, %d\n", strMessage.c_str(),resultCode); } sem_post(&g_sem); } -
Call the Install function.
const uint32_t WAIT_TIMEOUT = 30; sem_init(&g_sem, 0, 0); std::string installPath = "/storage/bundle/demo.hap"; // Specify the path where the HAP file is stored. bool result = Install(installPath.c_str(), &installParam, InstallCallback); struct timespec ts = {}; clock_gettime(CLOCK_REALTIME, &ts); ts.tv_sec += WAIT_TIMEOUT; // Release the semaphore upon timeout. sem_timedwait(&g_sem, &ts);
Uninstalling an Application
When uninstalling an application, you can specify whether to retain application data using the keepData member variable in the created InstallParam instance. If keepData is set to true, the application data will be retained after the application is uninstalled. If the variable is set to false, the application data will be removed during application installation.
-
Create an InstallParam instance and define the semaphore.
static sem_t g_sem; InstallParam installParam = { .installLocation = 1, .keepData = false // Remove application data. }; -
Define the callback function.
static void UninstallCallback(const uint8_t resultCode, const void *resultMessage) { std::string strMessage = reinterpret_cast<const char *>(resultMessage); if (!strMessage.empty()) { printf("uninstall resultMessage is %s\n", strMessage.c_str()); g_resultMessage = strMessage; } g_resultCode = resultCode; sem_post(&g_sem); } -
Call the Uninstall function.
sem_init(&g_sem, 0, 0); const uint32_t WAIT_TIMEOUT = 30; std::string BUNDLE_NAME = "com.example.demo"; // Bundle name of the application to be uninstalled Uninstall(BUNDLE_NAME.c_str(), &installParam, UninstallCallback); struct timespec ts = {}; clock_gettime(CLOCK_REALTIME, &ts); ts.tv_sec += WAIT_TIMEOUT; sem_timedwait(&g_sem, &ts);
Querying Bundle Information About an Installed Application
You can use the GetBundleInfo function provided by BundleManager to query the bundle information about installed applications in the system.
-
Create and initialize a BundleInfo object.
BundleInfo bundleInfo; (void) memset_s(&bundleInfo, sizeof(BundleInfo), 0, sizeof(BundleInfo)); -
Call GetBundleInfo to obtain bundle information about a specified application. The bundleName parameter indicates the pointer to the application bundle name, and the flags parameter specifies whether the obtained BundleInfo object can contain AbilityInfo.
std::string BUNDLE_NAME = "com.example.demo"; uint8_t ret = GetBundleInfo(BUNDLE_NAME.c_str(), 1, &bundleInfo); // When flags is set to 1, the obtained BundleInfo object contains AbilityInfo. -
After you finish using the obtained BundleInfo object, clear the memory space occupied by the object in a timely manner to prevent memory leakage.
ClearBundleInfo(&bundleInfo);
Packing a HAP File
The packing tool is generally integrated into the development tool or IDE, and you rarely have the occasion to use it directly. This section is provided for you to have a general knowledge of the packing tool. The JAR file of the packing tool is stored in the developtools/packing_tool/jar directory of the open-source code.
-
CLI command parameters for packing a HAP file
Table 2 Description of resource files required for packing
-
Example HAP File Structure
-
Development view
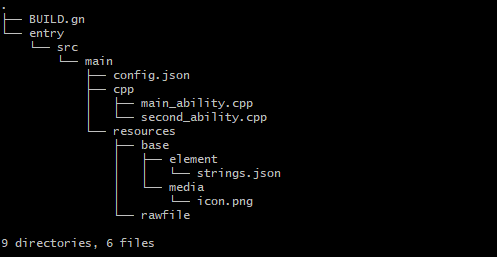
-
Compilation view
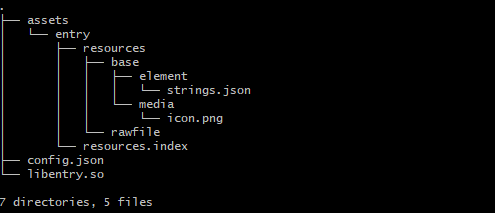
-
Run the following commands to pack a HAP file using the packing tool.
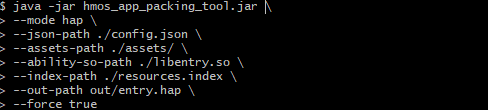
$ java -jar hmos_app_packing_tool.jar --mode hap --json-path ./config.json --assets-path ./assets/ --ability-so-path ./libentry.so --index-path ./resources.index --out-path out/entry.hap --force true
-