UIAbility Component Launch Type
The launch type of the UIAbility component refers to the state of the UIAbility instance at startup. The system provides three launch types:
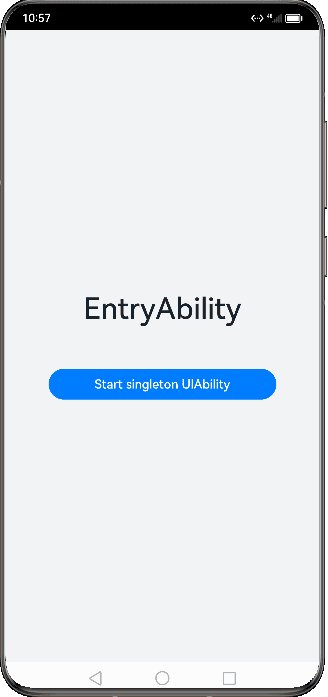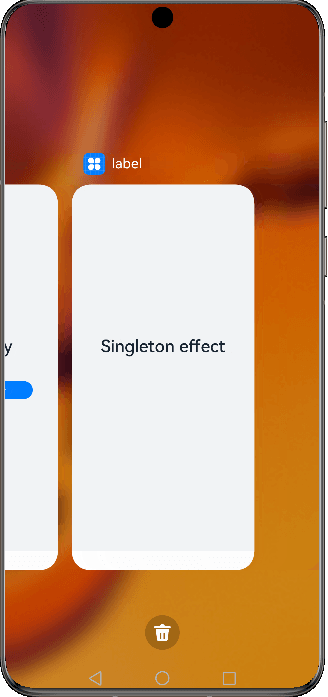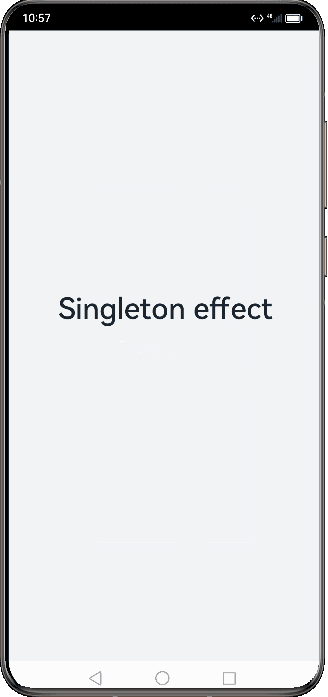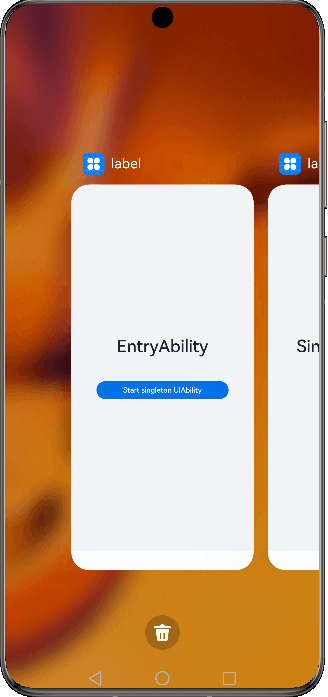
Singleton
singleton is the default launch type.
Each time startAbility() is called, if a UIAbility instance of this type already exists in the application process, the instance is reused. Therefore, only one UIAbility instance of this type exists in the system, that is, displayed in Recents.
Figure 1 Demonstration effect in singleton mode
NOTE
Assume that the application already has a UIAbility instance created, and the launch type of the UIAbility instance is set to singleton. If startAbility() is called again to start the UIAbility instance, the original UIAbility instance is started, and no new UIAbility instance is created. In this case, the onNewWant() callback is invoked, but the onCreate() and onWindowStageCreate() callbacks are not.
To use the singleton mode, set launchType in the module.json5 configuration file to singleton.
{
"module": {
// ...
"abilities": [
{
"launchType": "singleton",
// ...
}
]
}
}
Multiton
In multiton mode, each time startAbility() is called, a new UIAbility instance of this type is created in the application process. Multiple UIAbility instances of this type are displayed in Recents.
Figure 2 Demonstration effect in multiton mode
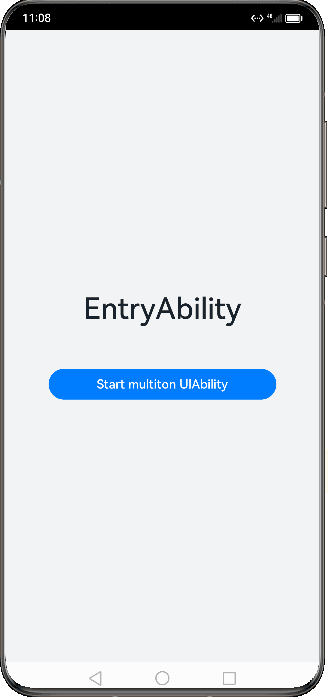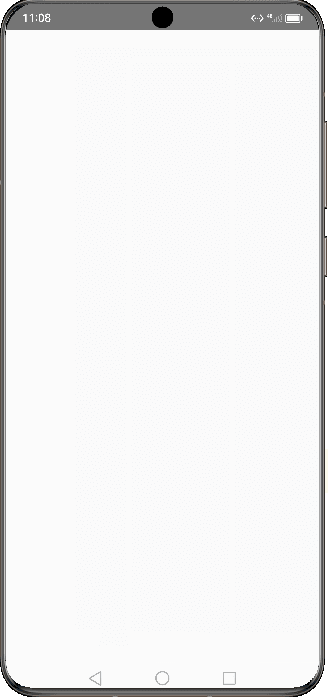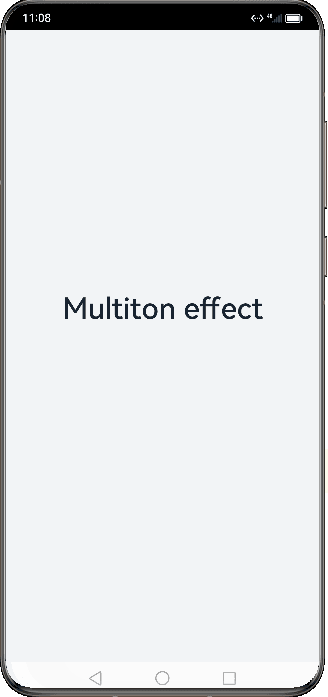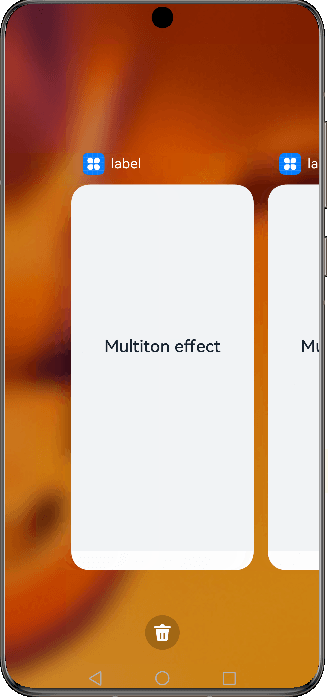
To use the multiton mode, set launchType in the module.json5 file to multiton.
{
"module": {
// ...
"abilities": [
{
"launchType": "multiton",
// ...
}
]
}
}
Specified
The specified mode is used in some special scenarios. For example, in a document application, you want a document instance to be created each time you create a document, but you want to use the same document instance when you repeatedly open an existing document.
Figure 3 Demonstration effect in specified mode
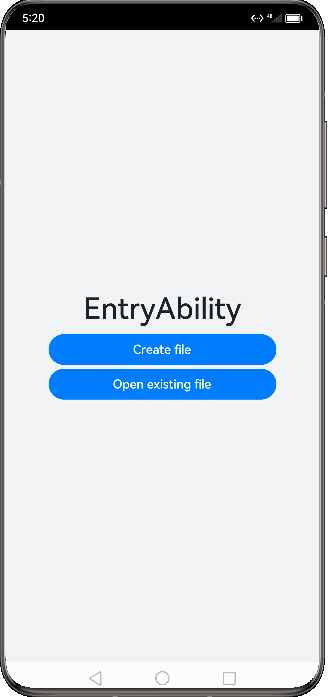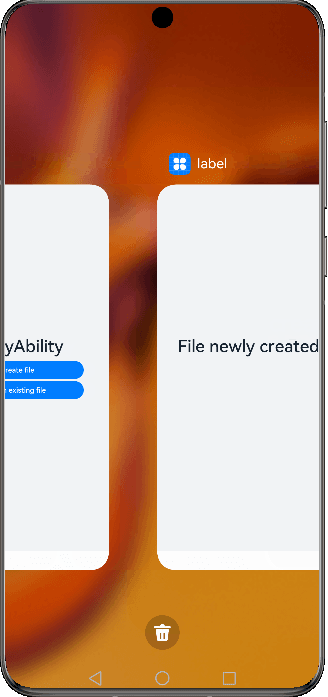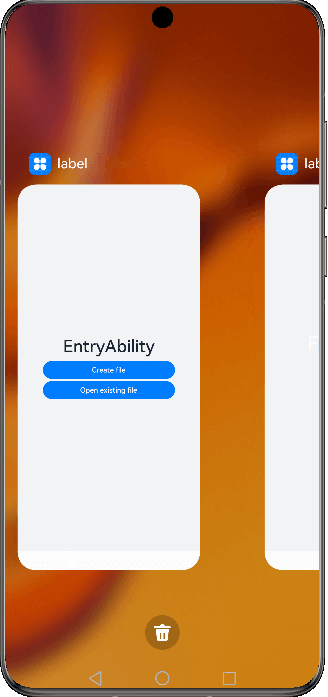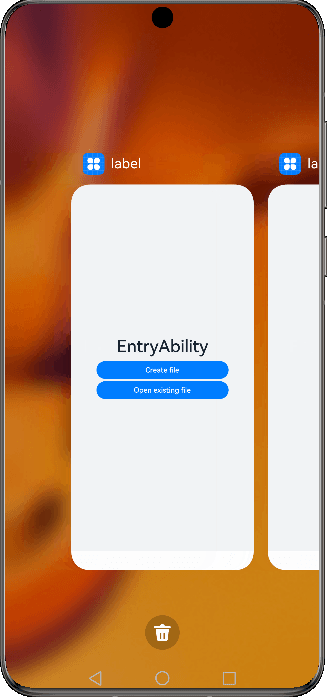
For example, there are two UIAbility components: EntryAbility and SpecifiedAbility (with the launch type specified). You are required to start SpecifiedAbility from EntryAbility.
-
In SpecifiedAbility, set the launchType field in the module.json5 file to specified.
{ "module": { // ... "abilities": [ { "launchType": "specified", // ... } ] } } -
Create a unique string key for the instance. Each time startAbility() is called, the application, based on the key, identifies the UIAbility instance used to respond to the request. In EntryAbility, add a custom parameter, for example, instanceKey, to the want parameter in startAbility() to distinguish the UIAbility instance.
// Configure an independent key for each UIAbility instance. // For example, in the document usage scenario, use the document path as the key. function getInstance() { // ... } let want = { deviceId: '', // An empty deviceId indicates the local device. bundleName: 'com.example.myapplication', abilityName: 'SpecifiedAbility', moduleName: 'module1', // moduleName is optional. parameters: {// Custom information. instanceKey: getInstance(), }, } // context is the UIAbilityContext of the initiator UIAbility. this.context.startAbility(want).then(() => { // ... }).catch((err) => { // ... }) -
Before SpecifiedAbility is started, the onAcceptWant() callback of the corresponding AbilityStage instance is invoked to obtain the key of the UIAbility, because the launch type of SpecifiedAbility is set to specified. If a UIAbility instance matching the key exists, the system starts the UIAbility instance and invokes its onNewWant() callback. Otherwise, the system creates a new UIAbility instance and invokes its onCreate() and onWindowStageCreate() callbacks.
In the sample code, the onAcceptWant() callback parses the want parameter to obtain the custom parameter instanceKey. The service logic returns a key string based on instanceKey parameter to identify the UIAbility instance. If the returned key maps to a started UIAbility instance, the system pulls the UIAbility instance back to the foreground and obtains the focus. If the returned key does not map to a started UIAbility instance, the system creates a new UIAbility instance and starts it.
import AbilityStage from '@ohos.app.ability.AbilityStage'; export default class MyAbilityStage extends AbilityStage { onAcceptWant(want): string { // In the AbilityStage instance of the callee, a key value corresponding to a UIAbility instance is returned for UIAbility whose launch type is specified. // In this example, SpecifiedAbility of module1 is returned. if (want.abilityName === 'SpecifiedAbility') { // The returned key string is a custom string. return `SpecifiedAbilityInstance_${want.parameters.instanceKey}`; } return ''; } }NOTE
- Assume that the application already has a UIAbility instance created, and the launch type of the UIAbility instance is set to specified. If startAbility() is called again to start the UIAbility instance, and the onAcceptWant() callback of AbilityStage matches a created UIAbility instance, the original UIAbility instance is started, and no new UIAbility instance is created. In this case, the onNewWant() callback is invoked, but the onCreate() and onWindowStageCreate() callbacks are not.
- AbilityStage is not automatically generated in the default project of DevEco Studio. For details about how to create an AbilityStage file, see AbilityStage Component Container.
For example, in the document application, different keys are bound to different document instances. Each time a document is created, a new key (for example, file path) is passed, and a new UIAbility instance is created when UIAbility is started in AbilityStage. However, when you open an existing document, the same UIAbility instance is started again in AbilityStage.
The following steps are used as an example.
- Open file A. A UIAbility instance, for example, UIAbility instance 1, is started.
- Close the process of file A in Recents. UIAbility instance 1 is destroyed. Return to the home screen and open file A again. A new UIAbility instance is started, for example, UIAbility instance 2.
- Return to the home screen and open file B. A new UIAbility instance is started, for example, UIAbility instance 3.
- Return to the home screen and open file A again. UIAbility instance 2 is started. This is because the system automatically matches the key of the UIAbility instance and starts the UIAbility instance that has a matching key. In this example, UIAbility instance 2 has the same key as file A. Therefore, the system pulls back UIAbility instance 2 and focuses it without creating a new instance.