User IAM
Introduction
The user identity and access management (IAM) subsystem provides a unified framework for user credential management and user identity authentication in OpenHarmony. It allows multiple users to set their own authentication credential information and authenticates their identities based on the information set.
This subsystem is widely used in security-sensitive scenarios such as screen lock. It also provides APIs for developers to call the identity authentication capabilities to control user access.
Figure 1 Subsystem architecture
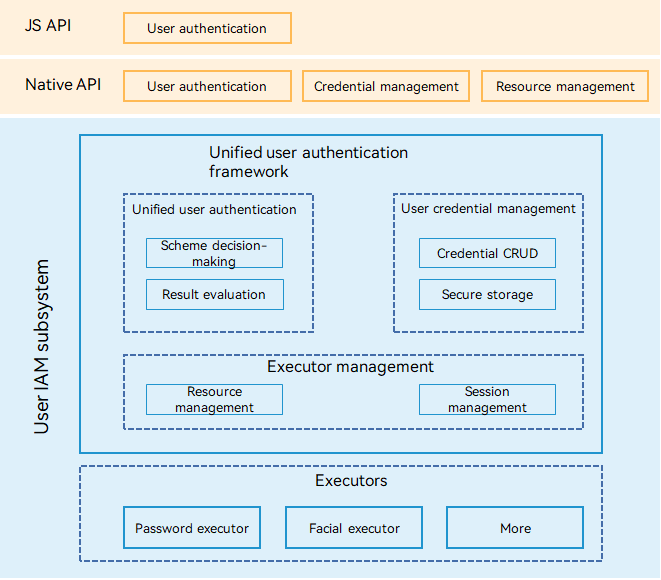 The user IAM subsystem consists of the unified user authentication framework and authentication executor. The unified user authentication framework consists of the following parts:
The user IAM subsystem consists of the unified user authentication framework and authentication executor. The unified user authentication framework consists of the following parts:
- Unified user authentication: provides unified user identity authentication externally and provides open biometric authentication capabilities for third-party applications to invoke.
- User credential management: provides a unified user credential information management interface for the upper layer and invokes authentication resources in the system through the authentication executor management part to implement lifecycle management and secure storage of user credentials.
- Authentication executor management: provides authentication resource management and authentication session management, and supports unified management, scheduling, and connection of various authentication executors in the system.
Based on the unified user authentication framework, the system can be extended to support multiple authentication capabilities. Currently, the authentication executors supported by OpenHarmony are password and facial authentication. To implement a new authentication executor, you only need to implement authentication capabilities in a new part and connect the new part to the unified user authentication framework based on the interfaces defined by the authentication executor management part.
NOTE
In the user IAM subsystem, an authentication executor is the minimum execution unit of a user identity authentication operation. For example, a password authentication module is responsible for password collection, password processing and comparison, and secure storage, and therefore it can be abstracted as a password authentication executor.
Directory Structure
//base/user_iam
├── user_auth_framework # User authentication framework, including user authentication, credential management, and executor management
├── face_auth # Facial authentication module, which connects to the authentication executor management part and supports facial information recording, deletion, and verification
├── pin_auth # Password authentication module, which connects to the authentication executor management part and supports password recording, deletion, and verification
Constraints
- User credential management is a key operation in the system, and the interfaces used for user credential management can be invoked only by basic system applications.
- The authentication executors process user authentication credentials, and their capabilities can only be implemented by system services for interconnection with the authentication executor management part.
Usage
How to Use
- The unified user authentication framework must work with an authentication executor.
- The first default authentication executor in the system must be a password authentication executor.