Development Guidelines on Clock Apps
Overview
This document describes how to quickly set up a development environment (using the Hi3516D V300 development board) and develop a clock app running on OpenHarmony. You can click here to obtain the sample code.
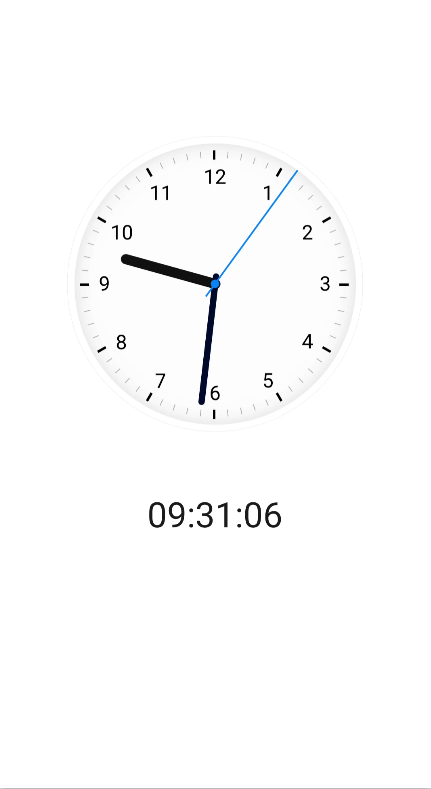
The clock app displays the current time, as shown in the following figure.
Preparations
Download and install DevEco Studio. For details, see the DevEco Studio User Guide.
How to Develop
The clock app displays the current time through a clock face and numbers.
As shown in Figure 1, the UI consists of two parts:
- Clock face area: displays a dynamic analog clock whose hands rotate accurately.
- Digital time area: displays the current time in numerals.
To build such an app, we can create a page that has a flexible layout with two rows vertically arranged. The development procedure is as follows:
-
Add a root component <div> to the .hml file. Note that each .hml file can contain only one root component. The sample code is as follows:
<div class="container"> </div>class="container" indicates the style used by the component. The container is a style class defined in the index.css file.
.container { flex-direction: column; justify-content: center; align-items: center; width: 100%; height: 100%; }The height and width of the root component <div> are set in the style class. Note that the height and width must be explicitly specified (except for some components, such as <text>). Otherwise, the component may fail to display. In the container style class, the flex-direction attribute is set to column, which means that child components of <div> are vertically arranged from top to bottom for implementing the flexible page layout.
-
Implement clock hand rotation using the <stack> component. The <stack> component provides a stack container where child components are successively stacked and the latter one overwrites the previous one.
Add a stack container to the root component. The sample code is as follows:
<div class="container"> <stack class="stack"> <image src="/common/clock_bg.png" class="clock-bg"></image> <!--Set the clock face image.--> <image src="/common/hour_hand.png" class="clock-hand" style="transform : rotate({{ hour * 30 + minute / 2 }}deg);"></image> <!--Set the hour hand image. (hour * 30) indicates that the hour hand rotates 30 degrees every hour. (minute / 2) indicates the rotation degrees per minute.--> <image src="/common/minute_hand.png" class="clock-hand" style="transform : rotate({{ minute * 6 + second / 10 }}deg);"></image> <!--Set the minute hand image. (minute * 6) indicates that the minute hand rotates 6 degrees every minute. (second / 10) indicates the rotation degrees per second.--> <image src="/common/second_hand.png" class="clock-hand" style="transform : rotate({{ second * 6 }}deg);"></image> <!--Set the second hand image. (second * 6) indicates that the second hand rotates 6 degrees per second.--> </stack> </div>style="transform: rotate({{ second * 6 }}deg) sets the rotation event of a component. transform translates, rotates, or scales an image. rotate rotates an image. You can set an image to rotate around its x-axis or y-axis.
Set attributes, such as the height, width, and position, of the stack component in the CSS file. The sample code is as follows:
.stack { flex-direction: column; justify-content: center; align-items: center; width: 100%; height: 50%; }Set attributes, such as the height and width, of the clock-bg component in the CSS file. The sample code is as follows:
.clock-bg { width: 80%; height: 80%; object-fit: scale-down; }Set attributes, such as the height and width of the hour, minute, and second hands, of the clock-hand component in the CSS file. The sample code is as follows:
.clock-hand { width: 25%; height: 65%; object-fit: contain; }Add a timer in the index.js file to update the hour, minute, and second variables in real time so that the time can be automatically updated on the app UI. The sample code is as follows:
export default { timer: undefined, // Define parameters. data: { hour: 0, // Define hours. minute: 0, // Define minutes. second: 0 // Define seconds. }, onInit () { this.updateTime(); this.timer = setInterval(this.updateTime, 1000)// Set the timer to 1 second. }, updateTime: function () { var nowTime = new Date() this.hour = nowTime.getHours() this.minute = nowTime.getMinutes() this.second = nowTime.getSeconds() if (this.hour < 10) { this.hour = '0' + this.hour } if (this.minute < 10) { this.minute = '0' + this.minute } if (this.second < 10) { this.second = '0' + this.second } }, } -
Display the current time in numerals under the analog clock. Add the text component at the end of the root layout. The following example shows the UI structure:
<text class="digit-clock"> {{ hour }}:{{ minute }}:{{ second }}</text>class="digit-clock" sets the height, width, and font size of the component. The sample code is as follows:
.digit-clock { font-size: 58px; width: 100%; margin-top: 0px; text-align: center; } -
Set the style, animation effect, and dynamic data binding for all components. The complete sample code is as follows:
-
index.hml
<div class="container"> <stack class="stack"> <image src="/common/clock_bg.png" class="clock-bg"></image> <image src="/common/hour_hand.png" class="clock-hand" style="transform : rotate({{ hour * 30 + minute / 2 }}deg);"></image> <image src="/common/minute_hand.png" class="clock-hand" style="transform : rotate({{ minute * 6 + second / 10 }}deg);"></image> <image src="/common/second_hand.png" class="clock-hand" style="transform : rotate({{ second * 6 }}deg);"></image> </stack> <text class="digit-clock">{{ hour }}:{{ minute }}:{{ second }}</text> </div> -
index.css
.container { flex-direction: column; justify-content: center; align-items: center; width: 100%; height: 100%; } .stack { flex-direction: column; justify-content: center; align-items: center; width: 100%; height: 50%; } .digit-clock { font-size: 58px; width: 100%; margin-top: 0px; text-align: center; } .clock-bg { width: 80%; height: 80%; object-fit: scale-down; } .clock-hand { width: 25%; height: 65%; object-fit: contain; } -
index.js
A .js file is used to implement logic interactions of the clock app. The following .js file implements the function of periodically obtaining the system time.
export default { timer: undefined, data: { hour: 0, minute: 0, second: 0 }, onInit() { this.updateTime() this.timer = setInterval(this.updateTime, 1000) }, updateTime: function () { var nowTime = new Date() this.hour = nowTime.getHours() this.minute = nowTime.getMinutes() this.second = nowTime.getSeconds() if (this.hour < 10) { this.hour = '0' + this.hour } if (this.minute < 10) { this.minute = '0' + this.minute } if (this.second < 10) { this.second = '0' + this.second } }, onDestroy() { clearInterval(this.timer); } }
-
Signing and Packaging
After finishing writing the app code, you need to sign and package the app before running it on a real device. For details, see Signing and Packaging Guide.
Running on the Real Device
Before you install the app and run it on the development board, install the DevEco Device Tool by following operations provided in DevEco Device Tool User Guide. Burn OpenHarmony into the development board and run it. For details about how to build, burn, and run an image, see Getting Started with the Standard System with Hi3516 (IDE Mode). After the image is running normally and the system is started properly, perform the following steps to install or uninstall the app:
-
Obtain the HDC client from the following path:
developtools/hdc_standard/prebuilt/windows/hdc_std.exeChange the HDC client name to hdc.exe and add the path above to the system environment variable path.
-
Open the cmd window, and run the following commands to push the HAP file to the device directory, and install it:
hdc install clock.hap -
Run the following command to start the app. ohos.samples.clock indicates the app package name, and MainAbility indicates the ability started by the app.
hdc shell aa start -d 123 -a ohos.samples.clock.MainAbility -b ohos.samples.clock -
(Optional) Run the following command to uninstall the app. ohos.samples.clock indicates the app package name.
hdc shell bm uninstall -n ohos.samples.clock
FAQs
hdc_std Fails to Connect to a Device
-
Symptom
[Empty] is displayed in the output after the hdc_std list targets command is run.
-
Possible Causes and Solutions
-
The device fails to be identified.
Check whether HDC Device exists in the universal serial bus device of the device manager. If HDC Device does not exist, the device cannot be connected. In this case, remove and then insert the device or burn the latest image for the device.
-
hdc_std works improperly.
Run the hdc kill or hdc start -r command to kill or restart the HDC service, and then run the hdc list targets command to check whether device information is obtained.
-
hdc_std does not match the device.
If the latest image is burnt for the device, hdc_std must also be of the latest version. As hdc_std is updated continuously, obtain hdc_std of the latest version from the developtools_hdc_standard repository in the prebuilt directory.
-
hdc_std Fails to Run
-
Symptom
The hdc_std.exe file does not run after being clicked.
-
Possible Causes and Solutions
hdc_std.exe requires no installation and can be directly used on a disk. It can also be added to environment variables. Open the cmd window and run the hdc_std command to use hdc_std.exe.