Using AudioRenderer for Audio Playback (ArkTS)
The AudioRenderer is used to play Pulse Code Modulation (PCM) audio data. Unlike the AVPlayer, the AudioRenderer can perform data preprocessing before audio input. Therefore, the AudioRenderer is more suitable if you have extensive audio development experience and want to implement more flexible playback features.
Development Guidelines
The full rendering process involves creating an AudioRenderer instance, configuring audio rendering parameters, starting and stopping rendering, and releasing the instance. In this topic, you will learn how to use the AudioRenderer to render audio data. Before the development, you are advised to read AudioRenderer for the API reference.
The figure below shows the state changes of the AudioRenderer. After an AudioRenderer instance is created, different APIs can be called to switch the AudioRenderer to different states and trigger the required behavior. If an API is called when the AudioRenderer is not in the given state, the system may throw an exception or generate other undefined behavior. Therefore, you are advised to check the AudioRenderer state before triggering state transition.
To prevent the UI thread from being blocked, most AudioRenderer calls are asynchronous. Each API provides the callback and promise functions. The following examples use the callback functions.
Figure 1 AudioRenderer state transition
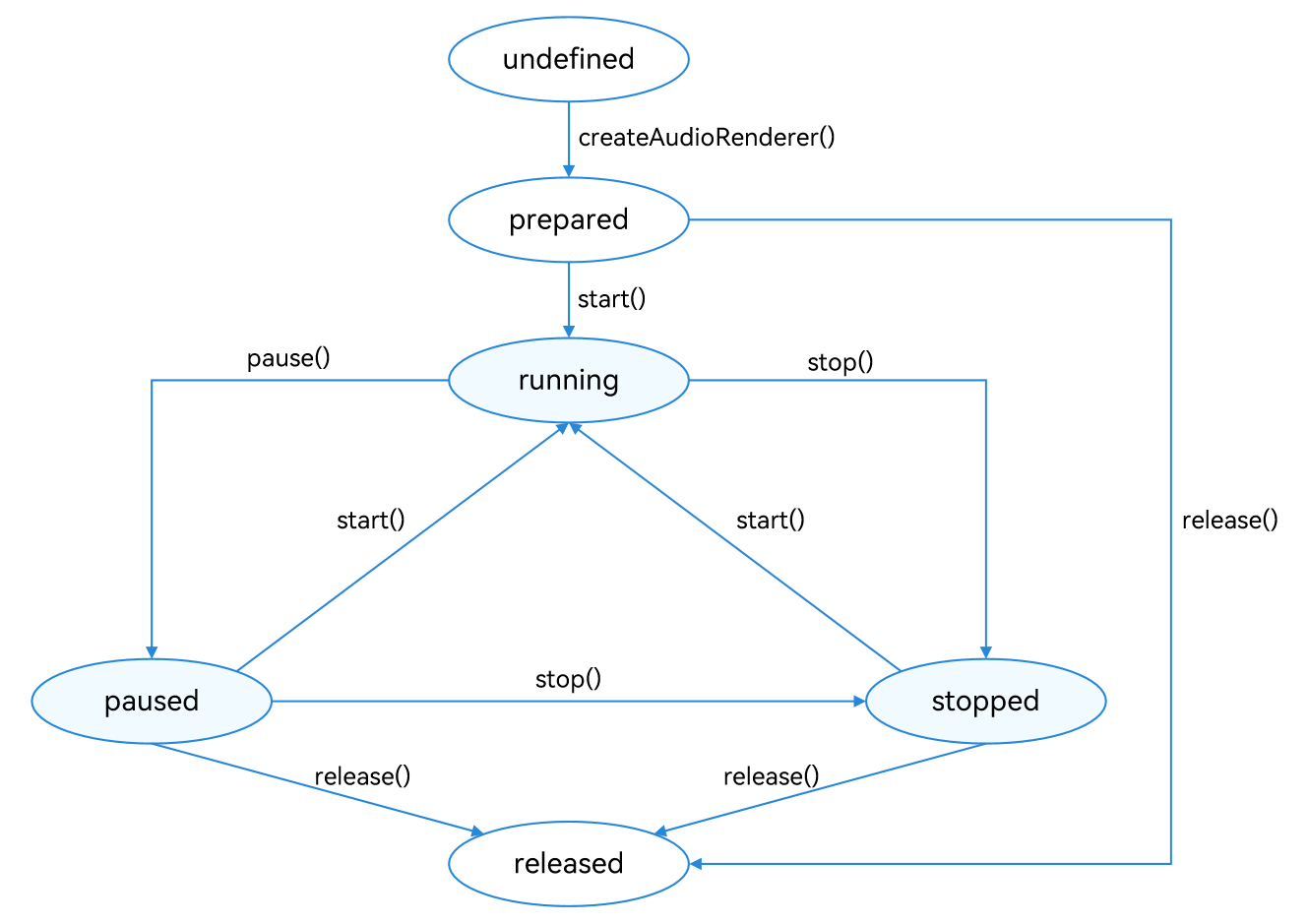
During application development, you are advised to use on('stateChange') to subscribe to state changes of the AudioRenderer. This is because some operations can be performed only when the AudioRenderer is in a given state. If the application performs an operation when the AudioRenderer is not in the given state, the system may throw an exception or generate other undefined behavior.
-
prepared: The AudioRenderer enters this state by calling createAudioRenderer().
-
running: The AudioRenderer enters this state by calling start() when it is in the prepared, paused, or stopped state.
-
paused: The AudioRenderer enters this state by calling pause() when it is in the running state. When the audio playback is paused, it can call start() to resume the playback.
-
stopped: The AudioRenderer enters this state by calling stop() when it is in the paused or running state.
-
released: The AudioRenderer enters this state by calling release() when it is in the prepared, paused, or stopped state. In this state, the AudioRenderer releases all occupied hardware and software resources and will not transit to any other state.
How to Develop
-
Set audio rendering parameters and create an AudioRenderer instance. For details about the parameters, see AudioRendererOptions.
import audio from '@ohos.multimedia.audio'; let audioStreamInfo: audio.AudioStreamInfo = { samplingRate: audio.AudioSamplingRate.SAMPLE_RATE_44100, channels: audio.AudioChannel.CHANNEL_1, sampleFormat: audio.AudioSampleFormat.SAMPLE_FORMAT_S16LE, encodingType: audio.AudioEncodingType.ENCODING_TYPE_RAW }; let audioRendererInfo: audio.AudioRendererInfo = { usage: audio.StreamUsage.STREAM_USAGE_VOICE_COMMUNICATION, rendererFlags: 0 }; let audioRendererOptions: audio.AudioRendererOptions = { streamInfo: audioStreamInfo, rendererInfo: audioRendererInfo }; audio.createAudioRenderer(audioRendererOptions, (err, data) => { if (err) { console.error(`Invoke createAudioRenderer failed, code is ${err.code}, message is ${err.message}`); return; } else { console.info('Invoke createAudioRenderer succeeded.'); let audioRenderer = data; } }); -
Call start() to switch the AudioRenderer to the running state and start rendering.
import { BusinessError } from '@ohos.base'; audioRenderer.start((err: BusinessError) => { if (err) { console.error(`Renderer start failed, code is ${err.code}, message is ${err.message}`); } else { console.info('Renderer start success.'); } }); -
Specify the address of the file to render. Open the file and call write() to continuously write audio data to the buffer for rendering and playing. To implement personalized playback, process the audio data before writing it.
import fs from '@ohos.file.fs'; let context = getContext(this); async function read() { const bufferSize: number = await audioRenderer.getBufferSize(); let path = context.filesDir; const filePath = path + '/voice_call_data.wav'; let file: fs.File = fs.openSync(filePath, fs.OpenMode.READ_ONLY); let buf = new ArrayBuffer(bufferSize); let readsize: number = await fs.read(file.fd, buf); let writeSize: number = await audioRenderer.write(buf); } -
Call stop() to stop rendering.
import { BusinessError } from '@ohos.base'; audioRenderer.stop((err: BusinessError) => { if (err) { console.error(`Renderer stop failed, code is ${err.code}, message is ${err.message}`); } else { console.info('Renderer stopped.'); } }); -
Call release() to release the instance.
import { BusinessError } from '@ohos.base'; audioRenderer.release((err: BusinessError) => { if (err) { console.error(`Renderer release failed, code is ${err.code}, message is ${err.message}`); } else { console.info('Renderer released.'); } });
Sample Code
Refer to the sample code below to render an audio file using AudioRenderer.
import audio from '@ohos.multimedia.audio';
import fs from '@ohos.file.fs';
const TAG = 'AudioRendererDemo';
let context = getContext(this);
let renderModel: audio.AudioRenderer | undefined = undefined;
let audioStreamInfo: audio.AudioStreamInfo = {
samplingRate: audio.AudioSamplingRate.SAMPLE_RATE_48000, // Sampling rate.
channels: audio.AudioChannel.CHANNEL_2, // Channel.
sampleFormat: audio.AudioSampleFormat.SAMPLE_FORMAT_S16LE, // Sampling format.
encodingType: audio.AudioEncodingType.ENCODING_TYPE_RAW // Encoding format.
}
let audioRendererInfo: audio.AudioRendererInfo = {
usage: audio.StreamUsage.STREAM_USAGE_MUSIC, // Audio stream usage type.
rendererFlags: 0 // AudioRenderer flag.
}
let audioRendererOptions: audio.AudioRendererOptions = {
streamInfo: audioStreamInfo,
rendererInfo: audioRendererInfo
}
// Create an AudioRenderer instance, and set the events to listen for.
async function init() {
audio.createAudioRenderer(audioRendererOptions, (err, renderer) => { // Create an AudioRenderer instance.
if (!err) {
console.info(`${TAG}: creating AudioRenderer success`);
renderModel = renderer;
if (renderModel !== undefined) {
(renderModel as audio.AudioRenderer).on('stateChange', (state: audio.AudioState) => { // Set the events to listen for. A callback is invoked when the AudioRenderer is switched to the specified state.
if (state == 2) {
console.info('audio renderer state is: STATE_RUNNING');
}
});
(renderModel as audio.AudioRenderer).on('markReach', 1000, (position: number) => { // Subscribe to the markReach event. A callback is triggered when the number of rendered frames reaches 1000.
if (position == 1000) {
console.info('ON Triggered successfully');
}
});
}
} else {
console.info(`${TAG}: creating AudioRenderer failed, error: ${err.message}`);
}
});
}
// Start audio rendering.
async function start() {
if (renderModel !== undefined) {
let stateGroup = [audio.AudioState.STATE_PREPARED, audio.AudioState.STATE_PAUSED, audio.AudioState.STATE_STOPPED];
if (stateGroup.indexOf((renderModel as audio.AudioRenderer).state.valueOf()) === -1) { // Rendering can be started only when the AudioRenderer is in the prepared, paused, or stopped state.
console.error(TAG + 'start failed');
return;
}
await (renderModel as audio.AudioRenderer).start(); // Start rendering.
const bufferSize = await (renderModel as audio.AudioRenderer).getBufferSize();
let path = context.filesDir;
const filePath = path + '/test.wav'; // Use the sandbox path to obtain the file. The actual file path is /data/storage/el2/base/haps/entry/files/test.wav.
let file = fs.openSync(filePath, fs.OpenMode.READ_ONLY);
let stat = await fs.stat(filePath);
let buf = new ArrayBuffer(bufferSize);
let len = stat.size % bufferSize === 0 ? Math.floor(stat.size / bufferSize) : Math.floor(stat.size / bufferSize + 1);
class Options {
offset: number = 0;
length: number = 0
}
for (let i = 0; i < len; i++) {
let options: Options = {
offset: i * bufferSize,
length: bufferSize
};
let readsize = await fs.read(file.fd, buf, options);
// buf indicates the audio data to be written to the buffer. Before calling AudioRenderer.write(), you can preprocess the audio data for personalized playback. The AudioRenderer reads the audio data written to the buffer for rendering.
let writeSize: number = await (renderModel as audio.AudioRenderer).write(buf);
if ((renderModel as audio.AudioRenderer).state.valueOf() === audio.AudioState.STATE_RELEASED) { // Release the instance if the AudioRenderer is in the released state.
fs.close(file);
}
if ((renderModel as audio.AudioRenderer).state.valueOf() === audio.AudioState.STATE_RUNNING) {
if (i === len - 1) { // The rendering stops if the file finishes reading.
fs.close(file);
await (renderModel as audio.AudioRenderer).stop();
}
}
}
}
}
// Pause the rendering.
async function pause() {
if (renderModel !== undefined) {
// Rendering can be paused only when the AudioRenderer is in the running state.
if ((renderModel as audio.AudioRenderer).state.valueOf() !== audio.AudioState.STATE_RUNNING) {
console.info('Renderer is not running');
return;
}
await (renderModel as audio.AudioRenderer).pause(); // Pause rendering.
if ((renderModel as audio.AudioRenderer).state.valueOf() === audio.AudioState.STATE_PAUSED) {
console.info('Renderer is paused.');
} else {
console.error('Pausing renderer failed.');
}
}
}
// Stop rendering.
async function stop() {
if (renderModel !== undefined) {
// Rendering can be stopped only when the AudioRenderer is in the running or paused state.
if ((renderModel as audio.AudioRenderer).state.valueOf() !== audio.AudioState.STATE_RUNNING && (renderModel as audio.AudioRenderer).state.valueOf() !== audio.AudioState.STATE_PAUSED) {
console.info('Renderer is not running or paused.');
return;
}
await (renderModel as audio.AudioRenderer).stop(); // Stop rendering.
if ((renderModel as audio.AudioRenderer).state.valueOf() === audio.AudioState.STATE_STOPPED) {
console.info('Renderer stopped.');
} else {
console.error('Stopping renderer failed.');
}
}
}
// Release the instance.
async function release() {
if (renderModel !== undefined) {
// The AudioRenderer can be released only when it is not in the released state.
if (renderModel.state.valueOf() === audio.AudioState.STATE_RELEASED) {
console.info('Renderer already released');
return;
}
await renderModel.release(); // Release the instance.
if (renderModel.state.valueOf() === audio.AudioState.STATE_RELEASED) {
console.info('Renderer released');
} else {
console.error('Renderer release failed.');
}
}
}
When audio streams with the same or higher priority need to use the output device, the current audio playback will be interrupted. The application can respond to and handle the interruption event. For details about how to process concurrent audio playback, see Audio Playback Concurrency Policies.