Vibrator
Overview
Function
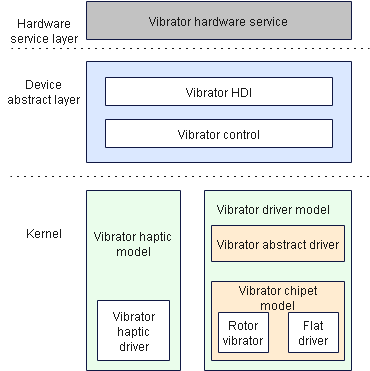
The vibrator driver model is developed based on OpenHarmony Hardware Driver Foundation (HDF) to facilitate vibrator driver development. The vibrator driver model shields the interaction between the device driver and the system, and provides unified and stable driver interface capabilities for the hardware service layer. It also provides open interfaces and interface parsing capabilities for developing vibrator drivers and deploying vibrators in different OSs.
The figure below shows the vibrator driver model.
Figure 1 Vibrator driver model
Basic Concepts
Vibrators can be classified into the following types based on vibration mechanism:
-
Rotor vibrator
The rotor vibrator uses magnetic field caused by current to drive the rotor to rotate and produce vibration. Rotor vibrators include ordinary rotor vibrators and coin rotor vibrators. The rotor vibrators cannot start or stop quickly or implement multiple vibration modes. However, they have small footprint and are cost-efficient.
-
Linear vibrator
The linear vibrator drives the spring mass for linear movement and produce vibration. Linear vibrators include longitudinal and transverse linear vibrators. The linear vibrators start and stop quickly, produce different vibration inductions, and have good sense of direction.
The system calls the vibrator driver APIs to control the vibration of the device. There are two vibration modes:
-
One-shot vibration
The vibrator vibrates once for a given duration.
-
Periodic vibration
The vibrator vibrates at preset intervals. For example, if haptic.clock.timer is set to [600, 600, 200, 600], the vibrator waits for 600 ms, vibrates for 600 ms, waits for 200 ms, and vibrates for 600 ms.
Working Principles
The figure below shows how a vibrator driver is loaded.
Figure 2 How a vibrator driver works
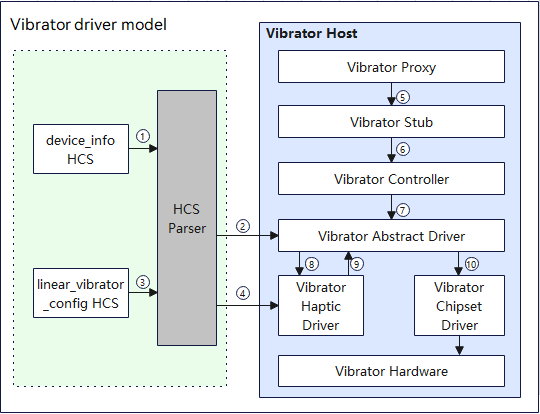
The following describes how a vibrator module driver loads and starts on a Hi3516DV300 that runs the standard system.
- The Device Manager reads the vibrator management configuration from the device_info.hcs file.
- The HDF Configuration Source (HCS) Parser parses the vibrator management configuration and loads the vibrator abstract driver.
- The Device Manager reads the Vibrator data configuration from the linear_vibrator_config.hcs file.
- The HCS Parser parses the vibrator data configuration and loads the haptic driver.
- The Vibrator Proxy obtains the vibrator HDI service instance and sends it to the Vibrator Stub over Inter-Process Communication (IPC).
- The Vibrator Stub processes IPC-related service logic and calls the Light Controller after parameter deserialization.
- The Vibrator Controller implements the HDI APIs and calls the Vibrator abstract driver APIs over IPC.
- The haptic driver starts a thread to parse the vibrator haptic module.
- The haptic driver calls Start() in the vibrator abstract driver.
- The vibrator abstract driver calls Start() in the vibrator differentiated driver to control the vibrator device to vibrate with a given effect.
Development Guidelines
When to Use
You can set different vibration effects as needed, for example, customizing vibration effects with different intensities and durations for buttons on the device, and customizing one-shot or periodic vibration effects with different intensities and durations for alarm clocks and incoming calls.
Available APIs
The vibrator driver model supports static HCS and dynamic parameter configuration. The vibrator hardware service calls StartOnce() to trigger continuous vibration and calls Start() to trigger vibration with a specified effect. The following table describes the APIs provided by the vibrator driver model for the hardware service layer.
Table 1 APIs of the vibrator driver model
| API | Description |
|---|---|
| int32_t (*StartOnce)([in] uint32_t duration) | Triggers a one-short vibration with a given duration. duration specifies the duration of the one-short vibration. |
| int32_t (*Start)([in] const char *effectType) | Triggers periodic vibrations with a preset effect. effectType indicates the pointer to the preset effect type. |
| int32_t (*Stop)([in] enum VibratorMode mode) | Stops vibration. mode indicates the vibration mode, which can be one-short or periodic vibration. |
| int32_t (*EnableVibratorModulation)(uint32_t duration, int32_t intensity, int32_t frequency) | Triggers a vibration with the given duration, frequency, and intensity. duration indicates the duration of the vibration. intensity indicates the vibration amplitude. frequency indicates the vibrator frequency in the vibration period. |
| int32_t (*GetVibratorInfo)([out] struct VibratorInfo **vibratorInfo) | Obtains information about all vibrators whose amplitude and frequency can be set in the system. vibratorInfo indicates the pointer to the vibrator information obtained. |
How to Develop
The vibrator driver model provides APIs for the upper-layer hardware service to trigger a one-shot vibration with a given duration, trigger vibration with a given effect, and stop vibration. This model implements functionalities such as cross-OS porting and device-specific configurations. The development procedure is as follows:
-
Develop the vibrator abstract driver based on the driver entry. Specifically, implement the Bind, Init, Release, and Dispatch functions, configure resources, and parse the HCS.
-
Call HDF_INIT to register the driver entry with the HDF. The HDF calls Bind and then Init to load the driver. If Init fails to be called, the HDF calls Release to release the driver resources and exit the vibrator driver model. The vibrator driver model uses the HCS as the configuration source code. For details about HCS fields, see Configuration Management. The driver entry function is defined as follows:
/* Register the entry structure object of the vibrator abstract driver. */ struct HdfDriverEntry g_vibratorDriverEntry = { .moduleVersion = 1, // Vibrator module version. .moduleName = "HDF_VIBRATOR", // Vibrator module name, which must be the same as moduleName in the device_info.hcs file. .Bind = BindVibratorDriver, // Bind function for the vibrator driver. .Init = InitVibratorDriver, // Ini function for the vibrator driver. .Release = ReleaseVibratorDriver, // Release function for the vibrator driver. }; /* Call HDF_INIT to register the driver entry with the HDF. */ HDF_INIT(g_vibratorDriverEntry); -
Develop the vibrator abstract driver. Specifically, implement the Bind, Init, Release, and Dispatch functions.
/* External service published by the vibrator driver. */ static int32_t DispatchVibrator(struct HdfDeviceIoClient *client, int32_t cmd, struct HdfSBuf *data, struct HdfSBuf *reply) { int32_t loop; for (loop = 0; loop < sizeof(g_vibratorCmdHandle) / sizeof(g_vibratorCmdHandle[0]); ++loop) { if ((cmd == g_vibratorCmdHandle[loop].cmd) && (g_vibratorCmdHandle[loop].func != NULL)) { return g_vibratorCmdHandle[loop].func(data, reply); } } return HDF_SUCCESS; } /* Bind the external service provided by the vibrator driver to the HDF. */ int32_t BindVibratorDriver(struct HdfDeviceObject *device) { struct VibratorDriverData *drvData = NULL; CHECK_VIBRATOR_NULL_PTR_RETURN_VALUE(device, HDF_FAILURE); drvData = (struct VibratorDriverData *)OsalMemCalloc(sizeof(*drvData)); CHECK_VIBRATOR_NULL_PTR_RETURN_VALUE(drvData, HDF_ERR_MALLOC_FAIL); drvData->ioService.Dispatch = DispatchVibrator; drvData->device = device; device->service = &drvData->ioService; g_vibratorDrvData = drvData; return HDF_SUCCESS; } /* Entry function for vibrator driver initialization. */ int32_t InitVibratorDriver(struct HdfDeviceObject *device) { struct VibratorDriverData *drvData = NULL; drvData->mode = VIBRATOR_MODE_BUTT; drvData->state = VIBRATOR_STATE_IDLE; ...... if (CreateVibratorHaptic(device) != HDF_SUCCESS) { HDF_LOGE("%s: init workQueue failed!", __func__); return HDF_FAILURE; } return HDF_SUCCESS; } /* Release the resources allocated during vibrator driver initialization. */ void ReleaseVibratorDriver(struct HdfDeviceObject *device) { struct VibratorDriverData *drvData = NULL; ...... (void)DestroyVibratorHaptic(); (void)OsalMutexDestroy(&drvData->mutex); (void)OsalMemFree(drvData); g_vibratorDrvData = NULL; } -
During system startup, the HDF configuration management loads the vibrator abstract driver based on the device information HCS and publishes the vibrator driver interfaces.
/* Device information HCS. */ vibrator :: host { hostName = "vibrator_host"; device_vibrator :: device { device0 :: deviceNode { policy = 2; // Policy for the driver to publish services. priority = 100; // Priority (0–200) for starting the vibrator driver. A larger value indicates a lower priority. The recommended value is 100. If the priorities are the same, the device loading sequence is not ensured. preload = 0; // The value 0 means to load the driver by default during the startup of the system. The value 2 means the opposite. permission = 0664; // Permission for the device node created. moduleName = "HDF_VIBRATOR"; // Vibrator driver name. It must be the same as moduleName in the driver entry structure. serviceName = "hdf_misc_vibrator"; // Service published by the vibrator driver. The service name must be unique. deviceMatchAttr = "hdf_vibrator_driver"; // Keyword matching the private data of the driver. The value must be the same as that of match_attr in the private data configuration table of the driver. } } }
-
-
Create a vibrator haptic model and parse the haptic HCS.
-
Create a vibrator haptic model.
/* Create a vibrator haptic model, allocate resources, and parse the haptic HCS. */ int32_t CreateVibratorHaptic(struct HdfDeviceObject *device) { struct VibratorHapticData *hapticData = NULL; CHECK_VIBRATOR_NULL_PTR_RETURN_VALUE(device, HDF_FAILURE); hapticData = (struct VibratorHapticData *)OsalMemCalloc(sizeof(*hapticData)); CHECK_VIBRATOR_NULL_PTR_RETURN_VALUE(hapticData, HDF_ERR_MALLOC_FAIL); g_vibratorHapticData = hapticData; hapticData->supportHaptic = false; if (OsalMutexInit(&hapticData->mutex) != HDF_SUCCESS) { HDF_LOGE("%s: failed to init mutex", __func__); goto EXIT; } DListHeadInit(&hapticData->effectSeqHead); /* Parse the haptic HCS. */ if (ParserVibratorHapticConfig(device->property) != HDF_SUCCESS) { HDF_LOGE("%s: parser haptic config failed!", __func__); goto EXIT; } return HDF_SUCCESS; EXIT: OsalMemFree(hapticData); return HDF_FAILURE; } -
The vibrator haptic model uses the HCS. For details about the HCS fields, see Configuration Management.
/* Vibrator data configuration template (vibrator_config.hcs). */ root { vibratorConfig { boardConfig { match_attr = "hdf_vibrator_driver"; // The value must be the same as that of match_attr in the vibrator device configuration file. vibratorAttr { /* The value 0 means a rotor vibrator, and 1 means a linear vibrator. */ deviceType = 1; // Device type. upportPreset = 1; // Supported preset type. } vibratorHapticConfig { haptic_clock_timer { effectName = "haptic.clock.timer"; type = 1; // The value 0 indicates the built-in mode, and 1 indicates the time sequence. seq = [600, 600, 200, 600]; // Time sequence. } haptic_default_effect { effectName = "haptic.default.effect"; type = 0; seq = [0, 3, 800, 1]; } } } } }
-
-
Implement the APIs for obtaining vibrator information, triggering and stopping a vibration, and creating and destroying a timer based on the vibration mode.
The vibrator hardware service calls StartOnce to start a one-shot vibration with a given duration and calls StartEffect to start vibration with a specified effect.
/* Trigger a one-short vibration with a given duration. */ static int32_t StartOnce(struct HdfSBuf *data, struct HdfSBuf *reply) { uint32_t duration; int32_t ret; struct VibratorEffectCfg config; struct VibratorDriverData *drvData = GetVibratorDrvData(); (void)reply; ...... config.cfgMode = VIBRATOR_MODE_ONCE; config.duration = duration; config.effect = NULL; /* Create a timer based on the vibration effect. */ ret = StartHaptic(&config); if (ret != HDF_SUCCESS) { HDF_LOGE("%s: start haptic failed!", __func__); return ret; } return HDF_SUCCESS; } /* Trigger a vibration with a given effect. */ static int32_t StartEffect(struct HdfSBuf *data, struct HdfSBuf *reply) { int32_t ret; const char *effect = NULL; struct VibratorEffectCfg config; struct VibratorDriverData *drvData = GetVibratorDrvData(); (void)reply; ...... config.cfgMode = VIBRATOR_MODE_PRESET; config.duration = 0; config.effect = effect; ret = StartHaptic(&config); if (ret != HDF_SUCCESS) { HDF_LOGE("%s: start haptic failed!", __func__); return ret; } return HDF_SUCCESS; } /* Stop vibration based on the specified vibration mode. */ static int32_t Stop(struct HdfSBuf *data, struct HdfSBuf *reply) { int32_t ret; int32_t mode; struct VibratorDriverData *drvData = GetVibratorDrvData(); (void)reply; ...... /* Stop vibration and destroy the timer. */ ret = StopHaptic(); if (ret != HDF_SUCCESS) { HDF_LOGE("%s: stop haptic failed!", __func__); return ret; } (void)OsalMutexLock(&drvData->mutex); drvData->mode = VIBRATOR_MODE_BUTT; (void)OsalMutexUnlock(&drvData->mutex); return HDF_SUCCESS; } /* Trigger vibration with the given duration, frequency, and intensity. */ static int32_t EnableModulationParameter(struct HdfSBuf *data, struct HdfSBuf *reply) { (void)reply; struct VibratorEffectCfg config; struct VibratorDriverData *drvData; uint32_t duration; int32_t intensity; int32_t frequency; int32_t ret; ..... (void)OsalMutexLock(&drvData->mutex); drvData->mode = VIBRATOR_MODE_ONCE; (void)OsalMutexUnlock(&drvData->mutex); /* Set the vibration intensity and frequency. */ ret = drvData->ops.SetParameter(intensity, frequency); if (ret != HDF_SUCCESS) { HDF_LOGE("%s: set parameter failed", __func__); return HDF_FAILURE; } config.cfgMode = VIBRATOR_MODE_ONCE; config.duration = duration; config.effect = NULL; ret = StartHaptic(&config); if (ret != HDF_SUCCESS) { HDF_LOGE("%s: start haptic failed", __func__); return HDF_FAILURE; } return HDF_SUCCESS; } /* Obtain vibrator information, including whether the intensity and frequency can be set and the intensity and frequency range. */ static int32_t GetVibratorInfo(struct HdfSBuf *data, struct HdfSBuf *reply) { (void)data; struct VibratorDriverData *drvData; drvData = GetVibratorDrvData(); CHECK_VIBRATOR_NULL_PTR_RETURN_VALUE(drvData, HDF_ERR_INVALID_PARAM); CHECK_VIBRATOR_NULL_PTR_RETURN_VALUE(reply, HDF_ERR_INVALID_PARAM); if (!HdfSbufWriteBuffer(reply, &drvData->vibratorInfo, sizeof(drvData->vibratorInfo))) { HDF_LOGE("%s: write sbuf failed", __func__); return HDF_FAILURE; } return HDF_SUCCESS; } -
Implement the interfaces for the vibrator chipset driver.
-
Register the vibrator chipset driver interfaces when the vibrator chipset driver is initialized successfully.
/* Register the vibrator chipset driver interfaces. */ int32_t RegisterVibrator(struct VibratorOps *ops) { struct VibratorDriverData *drvData = GetVibratorDrvData(); CHECK_VIBRATOR_NULL_PTR_RETURN_VALUE(ops, HDF_FAILURE); CHECK_VIBRATOR_NULL_PTR_RETURN_VALUE(drvData, HDF_FAILURE); (void)OsalMutexLock(&drvData->mutex); drvData->ops.Start = ops->Start; drvData->ops.StartEffect = ops->StartEffect; drvData->ops.Stop = ops->Stop; drvData->ops.SetParameter = ops->SetParameter; (void)OsalMutexUnlock(&drvData->mutex); return HDF_SUCCESS; } /* Register vibrator information. */ int32_t RegisterVibratorInfo(struct VibratorInfo *vibratorInfo) { struct VibratorDriverData *drvData = GetVibratorDrvData(); CHECK_VIBRATOR_NULL_PTR_RETURN_VALUE(vibratorInfo, HDF_FAILURE); CHECK_VIBRATOR_NULL_PTR_RETURN_VALUE(drvData, HDF_FAILURE); (void)OsalMutexLock(&drvData->mutex); if (memcpy_s(&drvData->vibratorInfo, sizeof(drvData->vibratorInfo), vibratorInfo, sizeof(*vibratorInfo)) != EOK) { HDF_LOGE("%s: Memcpy vibrator config failed", __func__); return HDF_FAILURE; } (void)OsalMutexUnlock(&drvData->mutex); return HDF_SUCCESS; } -
The vibrator driver model provides vibrator chipset driver interfaces. Implement these interfaces as follows:
/* Stop vibration based on the specified vibration mode. */ static int32_t StopModulationParameter() { uint8_t value[DRV2605L_VALUE_BUTT]; struct Drv2605lDriverData *drvData = NULL; drvData = GetDrv2605lDrvData(); CHECK_VIBRATOR_NULL_PTR_RETURN_VALUE(drvData, HDF_FAILURE); CHECK_VIBRATOR_NULL_PTR_RETURN_VALUE(drvData->drv2605lCfgData, HDF_FAILURE); value[DRV2605L_ADDR_INDEX] = (uint8_t)DRV2605_REG_MODE; value[DRV2605L_VALUE_INDEX] = (uint8_t)DRV2605_MODE_STANDBY; if (WriteDrv2605l(&drvData->drv2605lCfgData->vibratorBus.i2cCfg, value, sizeof(value)) != HDF_SUCCESS) { HDF_LOGE("%s: i2c addr [%0X] write failed", __func__, value[DRV2605L_ADDR_INDEX]); return HDF_FAILURE; } value[DRV2605L_ADDR_INDEX] = (uint8_t)DRV2605_REG_RTPIN; value[DRV2605L_VALUE_INDEX] = (uint8_t)&drvData->drv2605lCfgData->vibratorAttr.defaultIntensity; if (WriteDrv2605l(&drvData->drv2605lCfgData->vibratorBus.i2cCfg, value, sizeof(value)) != HDF_SUCCESS) { HDF_LOGE("%s: i2c addr [%0X] write failed", __func__, value[DRV2605L_ADDR_INDEX]); } value[DRV2605L_ADDR_INDEX] = (uint8_t)DRV2605_REG_LRARESON; value[DRV2605L_VALUE_INDEX] = (uint8_t)&drvData->drv2605lCfgData->vibratorAttr.defaultFrequency; if (WriteDrv2605l(&drvData->drv2605lCfgData->vibratorBus.i2cCfg, value, sizeof(value)) != HDF_SUCCESS) { HDF_LOGE("%s: i2c addr [%0X] write failed", __func__, value[DRV2605L_ADDR_INDEX]); } return HDF_SUCCESS; } /* Set the vibration intensity and frequency. */ static void SetModulationParameter(int32_t intensity, int32_t frequency) { uint8_t value[DRV2605L_VALUE_BUTT]; struct Drv2605lDriverData *drvData = NULL; drvData = GetDrv2605lDrvData(); CHECK_VIBRATOR_NULL_PTR_RETURN_VALUE(drvData, HDF_FAILURE); if (intensity != 0) { value[DRV2605L_ADDR_INDEX] = (uint8_t)DRV2605_REG_RTPIN; value[DRV2605L_VALUE_INDEX] = (uint8_t)INTENSITY_MAPPING_VALUE(intensity); if (WriteDrv2605l(&drvData->drv2605lCfgData->vibratorBus.i2cCfg, value, sizeof(value)) != HDF_SUCCESS) { HDF_LOGE("%s: i2c addr [%0X] write failed", __func__, value[DRV2605L_ADDR_INDEX]); return; } } else { HDF_LOGD("%s: the setting of intensity 0 is not supported and \ will be set as the system default intensity", __func__); } if (frequency != 0) { value[DRV2605L_ADDR_INDEX] = (uint8_t)DRV2605_REG_LRARESON; value[DRV2605L_VALUE_INDEX] = (uint8_t)FREQUENCY_MAPPING_VALUE(frequency); if (WriteDrv2605l(&drvData->drv2605lCfgData->vibratorBus.i2cCfg, value, sizeof(value)) != HDF_SUCCESS) { HDF_LOGE("%s: i2c addr [%0X] write failed", __func__, value[DRV2605L_ADDR_INDEX]); return; } } else { HDF_LOGD("%s: the setting of frequency 0 is not supported and \ will be set as the system default frequency", __func__); } }
-
Verification
After the driver is developed, develop test cases in the vibrator unit test to verify the basic functionalities of the driver. Use your own platform as the test environment.
/* Initialize the vibrator interface instance before executing test cases. */
void HdfVibratorTest::SetUpTestCase()
{
g_vibratorDev = NewVibratorInterfaceInstance();
}
/* Release test case resources. */
void HdfVibratorTest::TearDownTestCase()
{
if(g_vibratorDev != nullptr){
FreeVibratorInterfaceInstance();
g_vibratorDev = nullptr;
}
}
/* Verify one-short vibration. */
HWTEST_F(HdfVibratorTest, PerformOneShotVibratorDuration_001, TestSize.Level1)
{
ASSERT_NE(nullptr, g_vibratorDev);
int32_t startRet = g_vibratorDev->StartOnce(g_duration);
EXPECT_EQ(startRet, HDF_SUCCESS);
OsalMSleep(g_sleepTime1);
int32_t endRet = g_vibratorDev->Stop(VIBRATOR_MODE_ONCE);
EXPECT_EQ(endRet, HDF_SUCCESS);
}
/* Verify vibration with the preset effect. */
HWTEST_F(HdfVibratorTest, ExecuteVibratorEffect_002, TestSize.Level1)
{
ASSERT_NE(nullptr, g_vibratorDev);
int32_t startRet = g_vibratorDev->Start(g_builtIn);
EXPECT_EQ(startRet, HDF_SUCCESS);
OsalMSleep(g_sleepTime1);
int32_t endRet = g_vibratorDev->Stop(VIBRATOR_MODE_PRESET);
EXPECT_EQ(endRet, HDF_SUCCESS);
}
/* Obtain vibrator information, including whether the intensity and frequency can be set and the intensity and frequency range. */
HWTEST_F(HdfVibratorTest, GetVibratorInfo_001, TestSize.Level1)
{
ASSERT_NE(nullptr, g_vibratorDev);
int32_t startRet = g_vibratorDev->GetVibratorInfo(&g_vibratorInfo);
EXPECT_EQ(startRet, HDF_SUCCESS);
EXPECT_NE(g_vibratorInfo, nullptr);
printf("intensity = %d, intensityMaxValue = %d, intensityMinValue = %d\n\t",
g_vibratorInfo->isSupportIntensity, g_vibratorInfo->intensityMaxValue, g_vibratorInfo->intensityMinValue);
printf("frequency = %d, frequencyMaxValue = %d, frequencyMinValue = %d\n\t",
g_vibratorInfo->isSupportFrequency, g_vibratorInfo->frequencyMaxValue, g_vibratorInfo->frequencyMinValue);
}
/* Trigger vibration with the given duration, frequency, and intensity. */
HWTEST_F(HdfVibratorTest, EnableVibratorModulation_001, TestSize.Level1)
{
int32_t startRet;
ASSERT_NE(nullptr, g_vibratorDev);
EXPECT_GT(g_duration, 0);
if ((g_vibratorInfo->isSupportIntensity == 1) || (g_vibratorInfo->isSupportFrequency == 1)) {
EXPECT_GE(g_intensity1, g_vibratorInfo->intensityMinValue);
EXPECT_LE(g_intensity1, g_vibratorInfo->intensityMaxValue);
EXPECT_GE(g_frequency1, g_vibratorInfo->frequencyMinValue);
EXPECT_LE(g_frequency1, g_vibratorInfo->frequencyMaxValue);
startRet = g_vibratorDev->EnableVibratorModulation(g_duration, g_intensity1, g_frequency1);
EXPECT_EQ(startRet, HDF_SUCCESS);
OsalMSleep(g_sleepTime1);
startRet = g_vibratorDev->Stop(VIBRATOR_MODE_ONCE);
EXPECT_EQ(startRet, HDF_SUCCESS);
}
}