Developing Animations
Animations are classified into Static Animation and Continuous Animation.
Static Animation
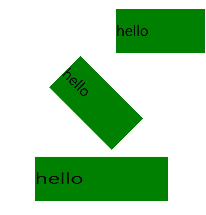
The transform attributes are the core of the static animation. A static animation can transform in the following three ways and only once in each way at a time:
-
translate: moves a specified component horizontally or vertically.
-
scale: scales a specified component horizontally or vertically to the required scale.
-
rotate: rotates a specified component by a specified angle along the horizontal axis, vertical axis, or center point.
For more information, see Component Methods. The following is an example:
<!-- xxx.hml -->
<div class="container">
<text class="translate">hello</text>
<text class="rotate">hello</text>
<text class="scale">hello</text>
</div>
/* xxx.css */
.container {
width: 100%;
flex-direction: column;
align-items: center;
}
.translate {
height: 150px;
width: 300px;
margin: 50px;
font-size: 50px;
background-color: #008000;
transform: translate(200px);
}
.rotate {
height: 150px;
width: 300px;
margin: 50px;
font-size: 50px;
background-color: #008000;
transform-origin: 200px 100px;
transform: rotate(45deg);
}
.scale {
height: 150px;
width: 300px;
margin: 50px;
font-size: 50px;
background-color: #008000;
transform: scaleX(1.5);
}
Figure 1 Static animation
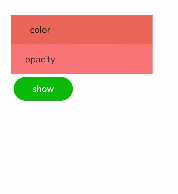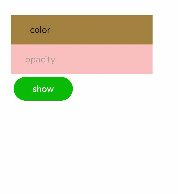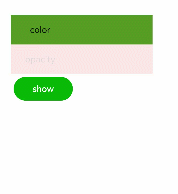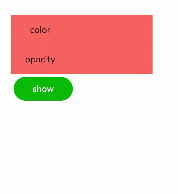
Continuous Animation
The static animation has only the start and end states. To set the transition state and conversion effect, use continuous animations.
The core of a continuous animation is animation attributes, which define the start and end states of the animation and the curve of time and speed. Animation attributes can implement the following effects:
-
animation-name: background color, opacity, width, height, and transformation type applied to the element after the animation is executed
-
animation-delay and animation-duration: element delay and duration after the animation is executed
-
animation-timing-function: speed curve of an animation, which makes the animation more fluent
-
animation-iteration-count: number of animation playback times
-
animation-fill-mode: whether to restore the initial state after the animation is executed
To use the animation attributes, you need to define a @keyframes rule in the .css file, set the animation transition effect in @keyframes, and invoke the effect through a style class in the .hml file. The following is an example for animation-name:
<!-- xxx.hml -->
<div class="item-container">
<div class="item {{colorParam}}">
<text class="txt">color</text>
</div>
<div class="item {{opacityParam}}">
<text class="txt">opacity</text>
</div>
<input class="button" type="button" name="" value="show" onclick="showAnimation"/>
</div>
/* xxx.css */
.item-container {
margin: 60px;
flex-direction: column;
}
.item {
width: 80%;
background-color: #f76160;
}
.txt {
text-align: center;
width: 200px;
height: 100px;
}
.button {
width: 200px;
margin: 10px;
font-size: 30px;
background-color: #09ba07;
}
.color {
animation-name: Color;
animation-duration: 8000ms;
}
.opacity {
animation-name: Opacity;
animation-duration: 8000ms;
}
@keyframes Color {
from {
background-color: #f76160;
}
to {
background-color: #09ba07;
}
}
@keyframes Opacity {
from {
opacity: 0.9;
}
to {
opacity: 0.1;
}
}
// xxx.js
export default {
data: {
colorParam: '',
opacityParam: '',
},
showAnimation: function () {
this.colorParam = '';
this.opacityParam = '';
this.colorParam = 'color';
this.opacityParam = 'opacity';
}
}
Figure 2 Continuous animation effect