NNRt接入适配指导
概述
功能简介
NNRt(Neural Network Runtime,神经网络运行时)是面向AI领域的跨芯片推理计算运行时,作为中间桥梁连通上层AI推理框架和底层加速芯片,实现AI模型的跨芯片推理计算。
NNRt开放了设备接口,芯片厂商通过设备接口将专有加速芯片接入NNRt,从而实现与OpenHarmony社区生态的对接。以下内容将介绍芯片如何接入NNRt。
基本概念
在开发前,开发者需要先了解以下概念,以便更好地理解全文内容:
- HDI(Hardware Device Interface):OpenHarmony硬件设备接口,定义系统中跨进程通信的接口,实现服务间的跨进程通信。
- IDL(Interface Description Language):接口描述语言,是HDI接口的语言格式。
约束与限制
- 系统版本:OpenHarmony主干版本。
- 开发环境:Ubuntu 18.04及以上。
- 接入设备:具备AI计算能力的芯片。
运作机制
NNRt通过HDI接口实现与设备芯片的对接,由HDI接口实现跨进程通信。
图1 NNRt架构图
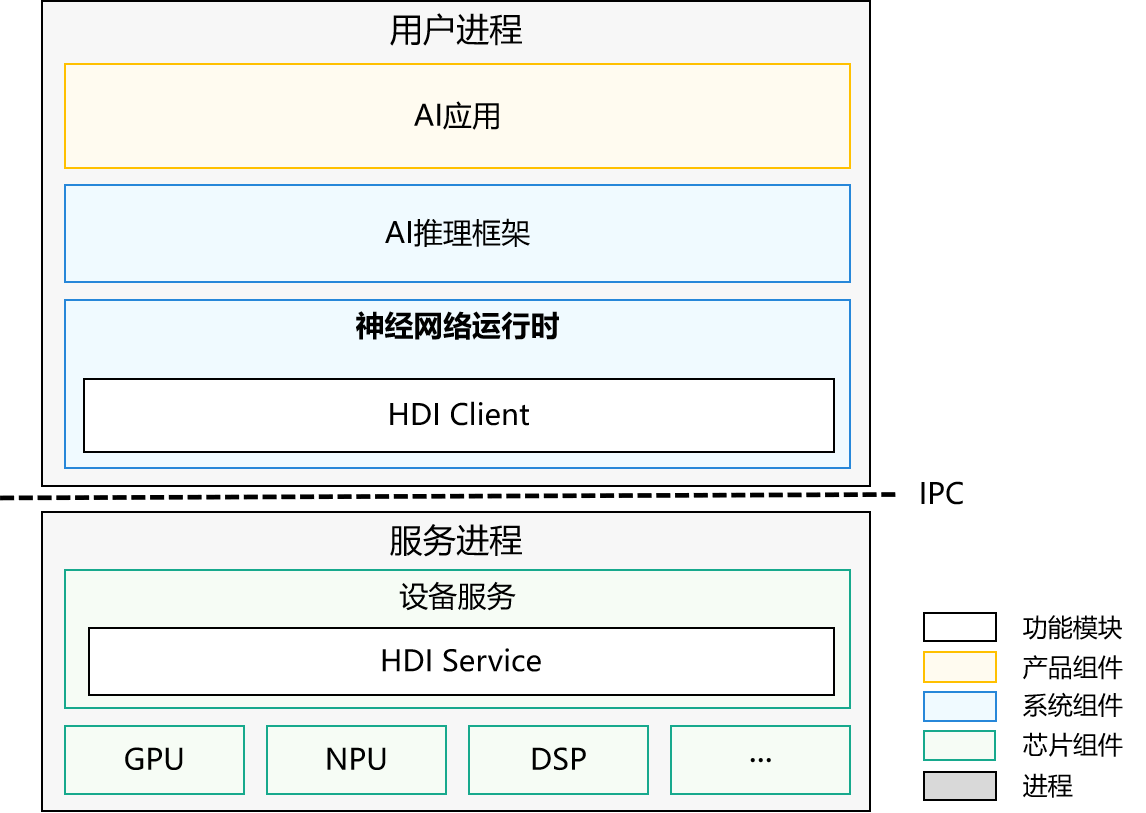
整个架构主要分为三层,AI应用在应用层,AI推理框架和NNRt在系统层,设备服务在芯片层。AI应用如果要使用AI专用加速芯片进行模型推理,需要经过AI推理框架和NNRt才能调用到底层AI专用加速芯片,NNRt就是负责适配底层各种AI专用加速芯片的中间层。NNRt开放了标准统一的HDI设备接口,众多AI专用加速芯片都可以通过HDI接口接入OpenHarmony。此外NNRt也开放了标准统一的接口对接上层各种AI推理框架。
程序运行时,AI应用、AI推理框架、NNRt都运行在用户进程中,底层AI芯片设备服务运行在HDI服务进程中。NNRt根据HDI接口实现了HDI Client,服务端也需要根据HDI接口实现HDI Service,两者通过OpenHarmony标准的HDF子系统实现跨进程通信。
开发指导
场景介绍
当需要将一款AI加速芯片接入NNRt的时候,可以参考下文。下文以RK3568芯片为例,展示RK3568 CPU如何通过NNRt的V2.0版本HDI接口接入NNRt,并完成AI模型推理。V1.0版本HDI接口接入NNRt的流程与此类似。
依赖说明:该教程展示的RK3568 CPU接入NNRt并没有真正实现CPU的驱动,而是借用了MindSpore Lite的runtime和CPU算子,因此会依赖MindSpore Lite的动态库以及头文件。实际开发时并不需要依赖MindSpore Lite的任何库或者头文件。
开发流程
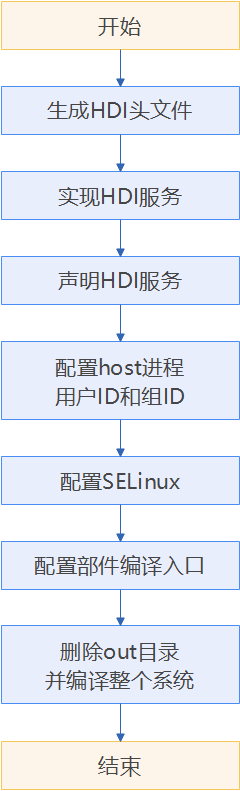
AI专用加速芯片接入NNRt的整体流程如下:
图2 AI专用加速芯片接入NNRt流程
开发步骤
AI芯片设备HDI服务开发者具体可通过以下步骤实现AI专用加速芯片对接NNRt:
生成HDI头文件
开源社区下载OpenHarmony的代码,编译drivers_interface部件,生成HDI接口的头文件。
-
下载源码。
-
进入OpenHarmony源码根目录,编译NNRt的IDL接口文件(以RK3568产品为例):
./build.sh --product-name rk3568 –ccache --build-target drivers_interface_nnrt编译完成后,会在
out/rk3568/gen/drivers/interface/nnrt/v2_0目录下生成C++类型的HDI头文件。若需要生成C类型的头文件,请在编译之前使用如下命令对drivers/interface/nnrt/v2_0/BUILD.gn文件中的language配置项进行设置。language = "c"生成头文件目录如下所示:
out/rk3568/gen/drivers/interface/nnrt └── v2_0 ├── drivers_interface_nnrt__libnnrt_proxy_2.0_external_deps_temp.json ├── drivers_interface_nnrt__libnnrt_stub_2.0_external_deps_temp.json ├── innrt_device.h # 设备接口头文件 ├── iprepared_model.h # 编译AI模型对象头文件 ├── libnnrt_proxy_2.0__notice.d ├── libnnrt_stub_2.0__notice.d ├── model_types.cpp # AI模型结构定义实现文件 ├── model_types.h # AI模型结构定义头文件 ├── nnrt_device_driver.cpp # 设备驱动实现参考样例 ├── nnrt_device_proxy.cpp ├── nnrt_device_proxy.h ├── nnrt_device_service.cpp # 设备服务端实现参考样例 ├── nnrt_device_service.h # 设备服务端头文件 ├── nnrt_device_stub.cpp ├── nnrt_device_stub.h ├── nnrt_types.cpp # 数据类型定义实现文件 ├── nnrt_types.h # 数据类型定义头文件 ├── node_attr_types.cpp # AI模型算子属性定义实现文件 ├── node_attr_types.h # AI模型算子属性定义 ├── prepared_model_proxy.cpp ├── prepared_model_proxy.h ├── prepared_model_service.cpp # 编译AI模型对象服务端实现参考样例 ├── prepared_model_service.h # 编译AI模型对象服务端头文件 ├── prepared_model_stub.cpp └── prepared_model_stub.h
实现HDI服务
-
进入OpenHarmony源码根目录,在
drivers/peripheral目录下新建开发目录nnrt,用于HDI服务开发。开发目录结构如下所示:drivers/peripheral/nnrt ├── bundle.json ├── v2_0 ├── BUILD.gn # 代码编译脚本文件 └── hdi_cpu_service # 自定义目录 ├── BUILD.gn # 代码编译脚本文件 ├── include │ ├── nnrt_device_service.h # 设备服务端头文件 │ ├── node_functions.h # 非必须,由具体实现决定 │ ├── node_registry.h # 非必须,由具体实现决定 │ └── prepared_model_service.h # 编译AI模型对象服务端头文件 └── src ├── nnrt_device_driver.cpp # 设备驱动实现文件 ├── nnrt_device_service.cpp # 设备服务端实现文件 ├── nnrt_device_stub.cpp # 非必须,由具体实现决定 ├── node_attr_types.cpp # 非必须,由具体实现决定 ├── node_functions.cpp # 非必须,由具体实现决定 ├── node_registry.cpp # 非必须,由具体实现决定 └── prepared_model_service.cpp # 编译AI模型对象服务端实现文件 -
实现设备驱动,无特殊需求可直接使用IDL文件编译生成的
nnrt_device_driver.cpp文件,否则根据具体驱动开发。 -
实现服务接口,可参考
nnrt_device_service.cpp和prepared_model_service.cpp实现文件,接口定义可以参考NNRt的HDI接口定义。 -
编译驱动和服务的实现文件为共享库。
在
drivers/peripheral/nnrt/v2_0/hdi_cpu_service/下新建BUILD.gn文件,文件内容如下所示,相关参数配置内容可参考Build教程。import("//build/ohos.gni") import("//drivers/hdf_core/adapter/uhdf2/uhdf.gni") ohos_shared_library("libnnrt_service_2.0") { include_dirs = [] sources = [ "src/nnrt_device_service.cpp", "src/node_functions.cpp", "src/node_registry.cpp", "src/prepared_model_service.cpp", "src/shared_buffer_parser.cpp", "src/validation.cpp", ] external_deps = [ "c_utils:utils", "drivers_interface_nnrt:libnnrt_stub_2.0", "hdf_core:libhdf_utils", "hilog_native:libhilog", "ipc:ipc_core", ] install_images = [ chipset_base_dir ] subsystem_name = "hdf" part_name = "drivers_peripheral_nnrt" } ohos_shared_library("libnnrt_driver") { include_dirs = [] sources = [ "src/nnr_device_driver.cpp" ] deps = [ ":libnnrt_service_2.0" ] external_deps = [ "c_utils:utils", "drivers_interface_nnrt:libnnrt_stub_2.0", "hdf_core:libhdf_host", "hdf_core:libhdf_ipc_adapter", "hdf_core:libhdf_utils", "hdf_core:libhdi", "hilog_native:libhilog", "ipc:ipc_core", ] install_images = [ chipset_base_dir ] subsystem_name = "hdf" part_name = "drivers_peripheral_nnrt" } group("hdf_nnrt_service") { deps = [ ":libnnrt_driver", ":libnnrt_service_2.0", ] }将
group("hdf_nnrt_service")添加到drivers/peripheral/nnrt/v2_0/BUILD.gn文件中,以便在更上目录层级就能引用。if (defined(ohos_lite)) { group("nnrt_entry") { deps = [] } } else { group("nnrt_entry") { deps = [ "./hdi_cpu_service:hdf_nnrt_service" ] } }新建
drivers/peripheral/nnrt/bundle.json用于定义新增的drivers_peripheral_nnrt部件。{ "name": "drivers_peripheral_nnrt", "description": "Neural network runtime device driver", "version": "4.0", "license": "Apache License 2.0", "component": { "name": "drivers_peripheral_nnrt", "subsystem": "hdf", "syscap": [""], "adapter_system_type": ["standard"], "rom": "1024KB", "ram": "2048KB", "deps": { "components": [ "c_utils", "hdf_core", "hilog_native", "ipc" ], "third_part": [ "bounds_checking_function" ] }, "build": { "sub_component": [ "//drivers/peripheral/nnrt/v2_0:nnrt_entry" ], "test": [ ], "inner_kits": [ ] } } }
声明HDI服务
在对应产品的uhdf hcs配置文件中声明NNRt的用户态驱动与服务。例如针对RK3568,服务需要在vendor/hihope/rk3568/hdf_config/uhdf/device_info.hcs文件中新增如下配置:
nnrt :: host {
hostName = "nnrt_host";
priority = 50;
uid = "";
gid = "";
caps = ["DAC_OVERRIDE", "DAC_READ_SEARCH"];
nnrt_device :: device {
device0 :: deviceNode {
policy = 2;
priority = 100;
moduleName = "libnnrt_driver.z.so";
serviceName = "nnrt_device_service";
}
}
}
注意:修改hcs文件需要删除out目录重新编译,才能生效。
配置host进程用户ID和组ID
对于新增的nnrt_host进程的场景,需要配置对应进程的用户ID和组ID。 进程的用户ID在文件base/startup/init/services/etc/passwd中配置,进程的组ID在文件base/startup/init/services/etc/group中配置。
# 在base/startup/init/services/etc/passwd新增
nnrt_host:x:3311:3311:::/bin/false
# 在base/startup/init/services/etc/group新增
nnrt_host:x:3311:
配置SELinux
OpenHarmony已经开启SELinux特性,需要对新增的进程和服务配置相应的SELinux规则,用于运行host进程访问某些资源、发布HDI服务等。
-
在
base/security/selinux/sepolicy/ohos_policy/drivers/adapter/public/hdf_service_contexts文件中新增配置:# 新增配置 nnrt_device_service u:object_r:hdf_nnrt_device_service:s0nnrt_host为声明HDI服务步骤中配置的进程名称,下同。 -
在
base/security/selinux/sepolicy/ohos_policy/drivers/adapter/public/hdf_service.te文件中新增配置:# 新增配置 type hdf_nnrt_device_service, hdf_service_attr; -
在
base/security/selinux/sepolicy/ohos_policy/drivers/adapter/public/hdfdomain.te文件中新增配置:# 新增配置 neverallow { domain -hdfdomain -sadomain } { hdfdomain -nnrt_host -allocator_host -hdf_public_domain }:binder call; -
在
base/security/selinux/sepolicy/ohos_policy/drivers/adapter/public/type.te文件中新增配置:# 新增配置 type nnrt_host, hdfdomain, domain; -
在
base/security/selinux/sepolicy/ohos_policy/drivers/adapter/vendor/hdf_devmgr.te文件中新增配置:# 新增配置 allow hdf_devmgr nnrt_host:binder { call transfer }; allow hdf_devmgr nnrt_host:dir { search }; allow hdf_devmgr nnrt_host:file { open read write }; allow hdf_devmgr nnrt_host:process { getattr }; -
在
base/security/selinux/sepolicy/ohos_policy/drivers/adapter/vendor/init.te文件中新增配置:# 新增配置 allow init nnrt_host:process { rlimitinh siginh transition }; -
在
base/security/selinux/sepolicy/ohos_policy/startup/init/public/chipset_init.te文件中作如下修改:找到chipset_init这一行:
allow chipset_init { light_host input_user_host wifi_host camera_host power_host audio_host }:process { rlimitinh siginh transition };在host列表中增加nnrt_host:
allow chipset_init { light_host input_user_host wifi_host camera_host power_host audio_host nnrt_host }:process { rlimitinh siginh transition }; -
新建
nnrt_host.te配置文件:# 创建nnrt文件夹 mkdir base/security/selinux/sepolicy/ohos_policy/drivers/peripheral/nnrt # 创建vendor文件夹 mkdir base/security/selinux/sepolicy/ohos_policy/drivers/peripheral/nnrt/vendor # 创建nnrt_host.te文件 touch base/security/selinux/sepolicy/ohos_policy/drivers/peripheral/nnrt/vendor/nnrt_host.te -
将所需的权限写入
nnrt_host.te文件中:allow nnrt_host dev_hdf_kevent:chr_file { ioctl }; allow nnrt_host hilog_param:file { read open map }; allow nnrt_host sh:binder { transfer }; allow nnrt_host samgr:binder { call }; allow nnrt_host dev_ashmem_file:chr_file { open }; allow nnrt_host dev_unix_socket:dir { search }; allow nnrt_host hdf_device_manager:hdf_devmgr_class { get }; allow nnrt_host hdf_nnrt_device_service:hdf_devmgr_class { add get }; allow nnrt_host dev_console_file:chr_file { read write }; allow nnrt_host debug_param:file { read open map }; allow nnrt_host sa_device_service_manager:samgr_class { get }; allow nnrt_host hdf_devmgr:binder { call transfer }; allow nnrt_host hdf_nnrt_device_service:binder { call }; allow nnrt_host sysfs_devices_system_cpu:file { read open getattr }; allow sh hdf_nnrt_device_service:hdf_devmgr_class { add get }; allow sh hdf_hci_interface_service:hdf_devmgr_class { get }; allow sh nnrt_host:dir { getattr search }; allow sh nnrt_host:file { open read }; allow sh nnrt_host:process { getattr }; allow sh nnrt_host:binder { call }; allow sh nnrt_host:fd { use }; -
由于SELinux是白名单访问的权限机制,需要根据实际权限需求配置。将服务启动之后,可通过以下dmesg命令查看avc告警, avc告警会给出缺少的权限。SELinux的配置也可以参考OpenHarmony SELinux子系统的说明。
hdc_std shell dmesg | grep nnrt
配置部件编译入口
以RK3568产品为例:
vim //productdefine/common/inherit/chipset_common.json
在"subsystems", "subsystem":"hdf", "components"中添加:
{
"component": "drivers_peripheral_nnrt",
"features": []
}
删除out目录并编译整个系统
# 删除out目录
rm -rf ./out
# 编译
./build.sh --product-name rk3568 –ccache --jobs=4
调测验证
服务开发完成后,可以使用XTS用例验证基本功能和兼容性。开发者可通过以下步骤进行验证:
-
编译NNRt的hats用例,用例在
test/xts/hats/ai/nnrt/hdi目录下。# 进入hats目录 cd test/xts/hats # 编译hats测试用例 ./build.sh suite=hats system_size=standard product_name=rk3568 # 回到代码根目录 cd -编译好的测试用例可执行文件
HatsHdfNnrtFunctionTest会输出到out/rk3568/suites/hats/testcases/下。 -
将测试用例push到RK3568设备的
/data/local/tmp/目录下。# 将测试用例可执行文件推送到设备上,HatsHdfNnrtFunctionTest是测试用例可执行文件。 hdc_std file send out/rk3568/suites/hats/testcases/HartsHdfNnrtFunctionTest /data/local/tmp/ # 给测试用例可执行文件加上权限。 hdc_std shell "chmod +x /data/local/tmp/HatsHdfNnrtFunctionTest" -
执行用例并查看结果。
# 执行测试用例 hdc_std shell "/data/local/tmp/HatsHdfNnrtFunctionTest"测试报告显示已通过47个用例,说明所有hats用例已执行成功,服务已通过兼容性测试。
... [----------] Global test environment tear-down Gtest xml output finished [==========] 47 tests from 3 test suites ran. (515 ms total) [ PASSED ] 47 tests.
开发实例
完整Demo代码可以参考社区实现。
-
进入OpenHarmony源码根目录,在
drivers/peripheral路径下创建nnrt目录,拷贝NNRt源码路径foundation/ai/neural_network_runtime下的example/driver/nnrt/v2_0目录到drivers/peripheral/nnrt路径下。cp -r example/drivers/nnrt/v2_0 drivers/peripheral/nnrt -
在
drivers/peripheral/nnrt下补充bundle.json文件,bundle.json的写法参考本教程上面开发步骤中的实现HDI服务章节。 -
由于Demo依赖MindSpore Lite CPU算子,因此需要添加MindSpore Lite依赖文件:
- 下载MindSpore Lite的头文件,MindSpore Lite 1.8.1。
- 在
drivers/peripheral/nnrt/v2_0下创建mindspore目录,用于存放mindspore动态库和头文件。mkdir drivers/peripheral/nnrt/v2_0/mindspore - 解压
mindspore-lite-1.8.1-android-aarch64.tar.gz文件,将runtime/include目录拷贝到drivers/peripheral/nnrt/v2_0/mindspore目录下。cp mindspore-lite-1.8.1-android-aarch64/runtime/include drivers/peripheral/nnrt/v2_0/mindspore - Demo还依赖mindspore的
schema文件:# 创建mindspore_schema目录 mkdir drivers/peripheral/nnrt/v2_0/hdi_cpu_service/include/mindspore_schema # 从third_party目录拷贝mindspore schema文件 cp third_party/mindspore/mindspore/lite/schema/* drivers/peripheral/nnrt/v2_0/hdi_cpu_service/include/mindspore_schema/ - 编译OpenHarmony的MindSpore Lite动态库,并将动态库拷贝到
mindspore目录下。# 编译mindspore动态库 ./build.sh --product-name rk3568 -ccaache --jobs 4 --build-target mindspore_lib # 在drivers/peripheral/nnrt/v2_0/mindspore下创建mindspore目录 mkdir drivers/peripheral/nnrt/v2_0/mindspore/mindspore # 从out目录将mindspore动态库拷贝到drivers/peripheral/nnrt/v2_0/mindspore/mindspore下 cp out/rk3568/package/phone/system/lib/libmindspore-lite.huawei.so drivers/peripheral/nnrt/v2_0/mindspore/mindspore/
-
其他配置请参考本教程上面的开发步骤章节。