动画衔接
UI界面除了运行动画之外,还承载着与用户进行实时交互的功能。当用户行为根据意图变化发生改变时,UI界面应做到即时响应。例如用户在应用启动过程中,上滑退出,那么启动动画应该立即过渡到退出动画,而不应该等启动动画完成后再退出,从而减少用户等待时间。对于桌面翻页类从跟手到离手触发动画的场景,离手后动画的初始速度应承继手势速度,避免由于速度不接续导致停顿感的产生。针对以上场景,动画与动画、手势与动画之间的衔接能力,保证各类场景下动画平稳光滑地过渡的同时,尽可能降低开发难度。
假设对于某一可动画属性,存在正在运行的动画。当UI侧行为改变该属性终点值时,开发者仅需在animateTo动画闭包中改变属性值或者改变animation接口作用的属性值,即可产生动画。系统会自动衔接之前的动画和当前的动画,开发者仅需要关注当前单次动画的实现。
import curves from '@ohos.curves'
class SetSlt{
scaleToggle:boolean = true
set():void{
this.scaleToggle = !this.scaleToggle;
}
}
let CurAn:Record<string,curves> = {'curve':curves.springMotion()}
// 第一步:声明相关状态变量
@state scaleToggle: boolean = true;
...
Column() {
Button()
// 第二步:将状态变量设置到相关可动画属性接口
.scale(this.scaleToggle ? 1 : 0.5)
// 第三步:通过点击事件改变状态变量值,影响可动画属性值
.onclick(() => {
let sets = new SetSlt()
sets.set()
})
// 第四步:通过隐式动画接口开启隐式动画,动画终点值改变时,系统自动添加衔接动画
.animation(CurAn)
}
...
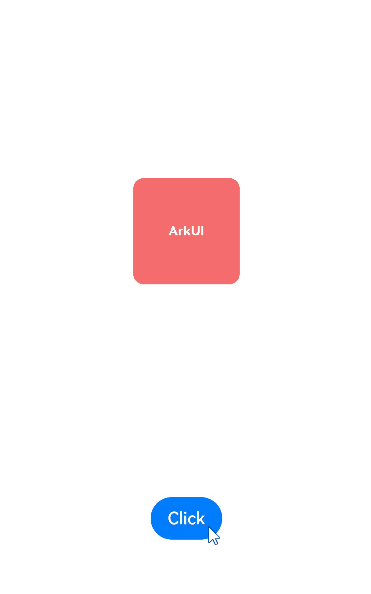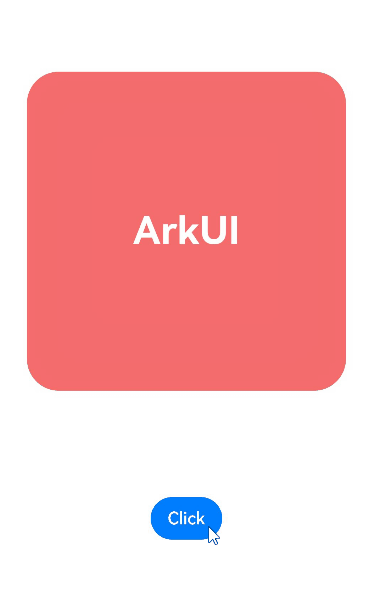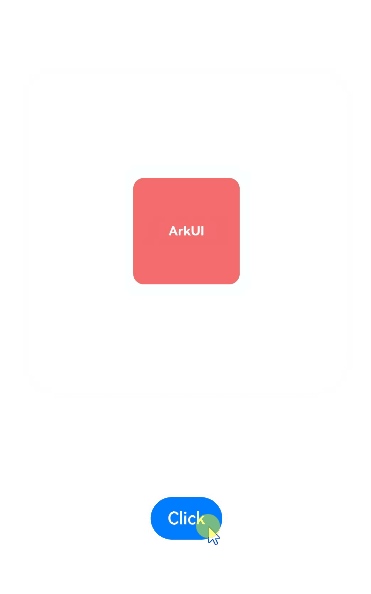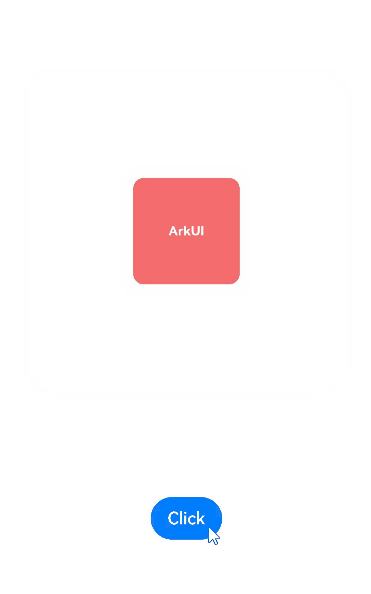
完整示例如下。通过点击click,红色方块的缩放属性会发生变化。当连续快速点击click时,缩放属性的终点值连续发生变化,当前动画也会平滑过渡到朝着新的缩放属性终点值运动。
import curves from '@ohos.curves';
class SetSlt{
isAnimation:boolean = true
set():void{
this.isAnimation = !this.isAnimation;
}
}
@Entry
@Component
struct AnimationToAnimationDemo {
@State SetAnimation: SetSlt = new SetSlt();
build() {
Column() {
Text('ArkUI')
.fontWeight(FontWeight.Bold)
.fontSize(12)
.fontColor(Color.White)
.textAlign(TextAlign.Center)
.borderRadius(10)
.backgroundColor(0xf56c6c)
.width(100)
.height(100)
.scale({ x: this.SetAnimation.isAnimation ? 2 : 1, y: this.SetAnimation.isAnimation ? 2 : 1 })
.animation({ curve: curves.springMotion(0.4, 0.8) })
Button('Click')
.margin({ top: 200 })
.onClick(() => {
this.SetAnimation.set()
})
}
.width('100%')
.height('100%')
.justifyContent(FlexAlign.Center)
}
}
手势与动画的衔接
使用滑动、捏合、旋转等手势的场景中,跟手过程中一般会触发属性的改变。离手后,这部分属性往往会继续发生变化,直到到达属性终点值。
离手阶段的属性变化初始速度应与离手前一刻的属性改变速度保持一致。如果离手后属性变化速度从0开始,就好像正在运行的汽车紧急刹车,造成观感上的骤变是用户和开发者都不希望看到的。
针对在手势和动画之间进行衔接的场景(如列表滑动),可以在跟手阶段每一次更改组件属性时,都做成使用跟手弹簧曲线的属性动画。离手时再用离手弹簧曲线产生离手阶段的属性动画。对于采用springMotion曲线的动画,离手阶段动画将自动继承跟手阶段动画的速度,并以跟手动画当前位置为起点,运动到指定的属性终点。
import curves from '@ohos.curves'
class SetOffset{
offsetX:number = 0;
offsetY:number = 0;
set(x:number,y:number):void{
this.offsetX = x;
this.offsetY = y;
}
}
// 第一步:声明相关状态变量
@state offsetX: number = 0;
@State offsetY: number = 0;
targetOffsetX: number = 100;
targetOffsetY: number = 100;
...
Column()
// 第二步:将状态变量设置到相关可动画属性接口
.translate({ x: this.offsetX, y: this.offsetY})
.gesture(
PanGesture({})
.onActionUpdate((event?: GestureEvent) => {
// 第三步:在跟手过程改变状态变量值,并且采用reponsiveSpringMotion动画运动到新的值
animateTo({
curve: curves.responsiveSpringMotion()
}, () => {
if(event){
let setxy = new SetOffset();
setxy.set(event.offsetX,event.offsetY)
}
})
})
.onActionEnd(() => {
// 第四步:在离手过程设定状态变量终点值,并且用springMotion动画运动到新的值,springMotion动画将继承跟手阶段的动画速度
animateTo({
curve: curves.SpringMotion()
}, () => {
let setxy = new SetOffset();
setxy.set(targetOffsetX,targetOffsetY)
})
})
)
...
完整的示例和效果如下。
import curves from '@ohos.curves';
@Entry
@Component
struct SpringMotionDemo {
@State positionX: number = 100;
@State positionY: number = 100;
diameter: number = 50;
build() {
Column() {
Row() {
Circle({ width: this.diameter, height: this.diameter })
.fill(Color.Blue)
.position({ x: this.positionX, y: this.positionY })
.onTouch((event?: TouchEvent) => {
if(event){
if (event.type === TouchType.Move) {
// 跟手过程,使用responsiveSpringMotion曲线
animateTo({ curve: curves.responsiveSpringMotion() }, () => {
// 减去半径,以使球的中心运动到手指位置
this.positionX = event.touches[0].windowX - this.diameter / 2;
this.positionY = event.touches[0].windowY - this.diameter / 2;
console.info(`move, animateTo x:${this.positionX}, y:${this.positionY}`);
})
} else if (event.type === TouchType.Up) {
// 离手时,使用springMotion曲线
animateTo({ curve: curves.springMotion() }, () => {
this.positionX = 100;
this.positionY = 100;
console.info(`touchUp, animateTo x:100, y:100`);
})
}
}
})
}
.width("100%").height("80%")
.clip(true) // 如果球超出父组件范围,使球不可见
.backgroundColor(Color.Orange)
Flex({ direction: FlexDirection.Row, alignItems: ItemAlign.Start, justifyContent: FlexAlign.Center }) {
Text("拖动小球").fontSize(16)
}
.width("100%")
Row() {
Text('点击位置: [x: ' + Math.round(this.positionX) + ', y:' + Math.round(this.positionY) + ']').fontSize(16)
}
.padding(10)
.width("100%")
}.height('100%').width('100%')
}
}
