Setting Up the Development Environment
In embedded development, Windows-based tools, such as Visual Studio Code, are widely used in code editing. Yet, because the source code of most development boards, such as Hi3861 and Hi3516, cannot be built in Windows, these development boards require the Ubuntu build environment. Therefore, for these development boards, you need Ubuntu to build source code and Windows to burn images.
Set up the Windows and Ubuntu development environments that meet the Windows Requirements and Ubuntu Requirements, respectively. Then enable Windows to remotely access Ubuntu. No specific requirements are placed on the development devices.
NOTE
OpenHarmony also provides the Docker environment, which can significantly simplify the environment configuration before compilation. You can build your source code in the Docker environment if you are more accustomed to using the command line.
Windows Requirements
64-bit Windows 10
Ubuntu Requirements
-
OS: Ubuntu 18.04 or later, X86_64 architecture, and 16 GB or more of RAM (recommended)
-
User name: cannot contain Chinese characters
Preparing for Remote Access
When burning images in Windows, you need to remotely access the source code and image files in Ubuntu. To achieve this, use a file transfer or sharing tool.
In this example the Samba server is used.
Configuring the Samba Server
Perform the following operations in Ubuntu:
-
Install the Samba software package.
sudo apt-get install samba samba-common -
Configure the sharing information in the Samba configuration file.
Open the smb.conf file.
sudo gedit /etc/samba/smb.confAppend the following information to the configuration file:
[Share] # Name of the root folder mapped in Windows (Share is used as an example) comment = Shared Folder # Information about the sharing path = /home/share # Shared directory valid users = username # User who can access the shared directory (user name in Ubuntu) directory mask = 0775 # Default directory permissions create mask = 0775 # Default file permissions public = yes # Whether to enable public access writable = yes # Whether to enable write access available = yes # Whether the directory is available browseable = yes # Whether the directory is browseable -
Add the user name and password for accessing the Samba server.
sudo smbpasswd -a username # Enter the Ubuntu user name. Then set the password as prompted. -
Run the following command to restart the Samba service:
sudo service smbd restart
Mapping a Network Drive in Windows
Perform the following operations in Windows:
-
Right-click This PC and choose Map network drive from the shortcut menu. In the Drive list, select a drive letter. In the Folder field, enter the path in the format of \Ubuntu device IP address\Ubuntu shared folder.
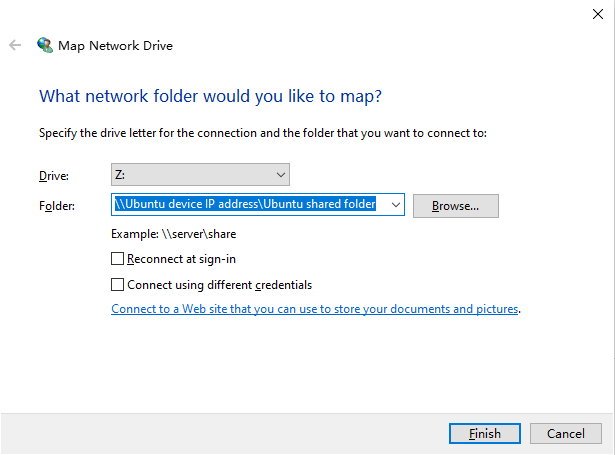
-
Enter the user name and password for accessing the Samba server, which has been set up in Configuring the Samba Server.
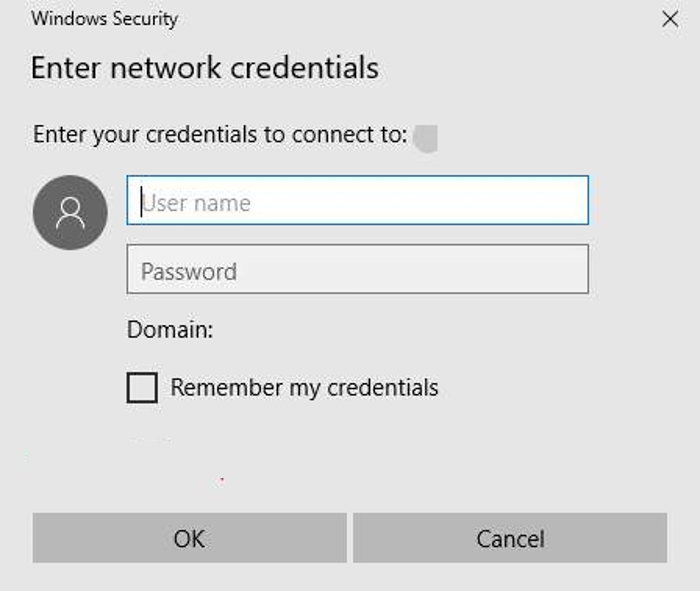
-
The shared directory is displayed in Windows and available for access.