Introduction to ArkData
Function
ArkData provides data storage, management, and sync capabilities. For example, you can store the Contacts application data in database for secure management and shared access, and synchronize the contacts information with a smart watch.
-
Unified data definition: OpenHarmony provides unified data definitions, including the data types and structs, for different applications and devices.
-
Data storage: provides capabilities for persisting user preference data, key-value (KV) store data, and relational database (RDB) store data.
-
Data management: provides efficient data management capabilities, including permission management, data backup and restore, and dataShare framework.
-
Data sync: provides data sync across devices. For example, distributed data objects support sharing of memory objects across devices, and distributed databases support database access across devices.
The database stores created by an application are saved to the application sandbox directory. When the application is uninstalled, the database stores are automatically deleted.
Working Principles
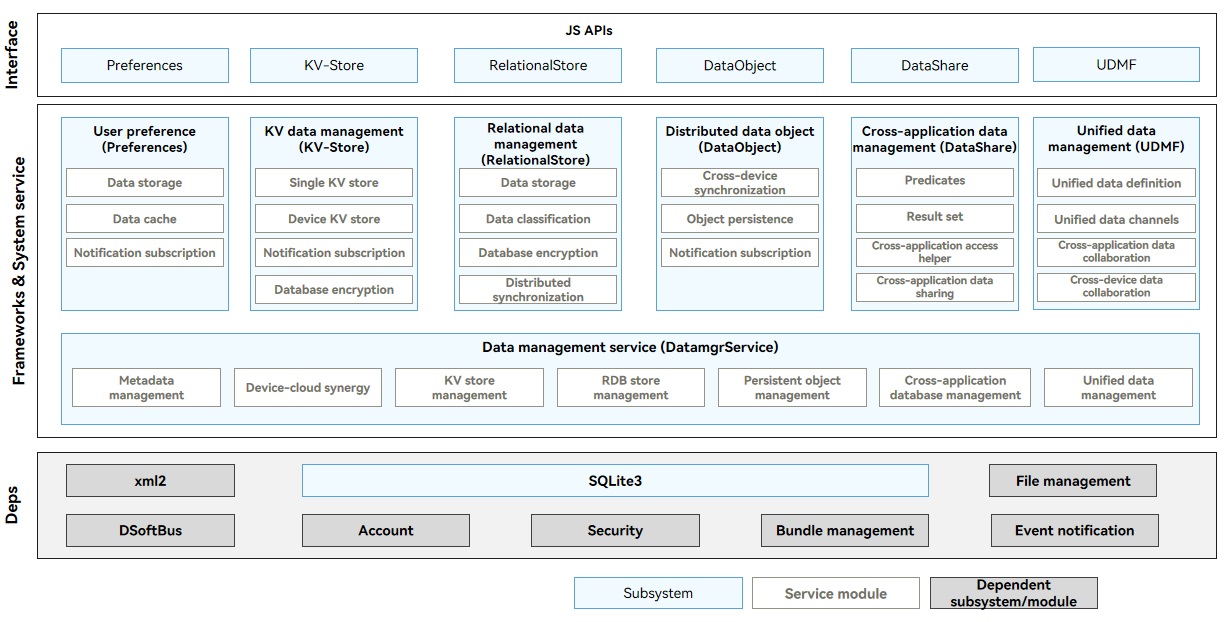
The data management module includes preferences, KV data management (KV-Store), relational data management (RelatoinalStore), distributed data object (DataObject), cross-application data management (DataShare), and unified data management framework (UDMF). The interface layer provides standard JavaScript APIs for application development. The Frameworks & System service layer implements storage and sync of component data, and provides dependencies for SQLite and other subsystems.
Figure 1 Data management architecture
-
Preferences: implements persistence of lightweight configuration data and supports subscription of data change notifications. Preferences are used to store application configuration information and user preference settings and do not support distributed sync.
-
KV-Store: implements read, write, encryption, and manual backup of data in KV stores and notification subscription. When an application needs to use the distributed capabilities of a KV store, KV-Store sends a sync request to DatamgrService, which implements data sync across devices.
-
RelationalStore: implements addition, deletion, modification, query, encryption, manually backup of data in RDB stores, and notification subscription. When an application needs to use the distributed capabilities of an RDB store, RelationalStore sends a sync request to DatamgrService, which implements data sync across devices.
-
DataObject: independently provides distributed capabilities for data objects. DatamgrService implements temporary storage of the object data, which is still required after the application (either the application of your device or cross-device application) is restarted.
-
DataShare: provides the data provider-consumer mode to implement addition, deletion, modification, and query of cross-application data on a device, and notification subscription. DataShare is not bound to any database and can interact with RDB and KV stores. You can also encapsulate your own databases for C/C++ applications.
In addition to the provider-consumer mode, DataShare provides silent access, which allows direct access to the provider's data via the DatamgrService proxy instead of starting the provider. Currently, only the RDB stores support silent access. -
UDMF: defines the language and data standards for cross-application and cross-device data interaction, improving data interaction efficiency. The UDMF provides secure and standard data transmission channels and supports different levels of data access permissions and lifecycle management policies. It helps implement efficient data sharing across applications and devices.
-
DatamgrService: implements sync and cross-application sharing for other components, including cross-device sync of RelationalStore and KV-Store, silent access to provider data of DataShare, and temporary storage of DataObject data.