UI Development (ArkTS-based Declarative Development Paradigm) Overview
Powered by the ArkTS-based declarative development paradigm, ArkUI is a simplified, high-performance UI development framework for cross-device applications. It provides the capabilities required for building the application UI, including:
-
ArkTS
ArkTS is the preferred programming language for application development in OpenHarmony. As a superset of TypeScript (TS for short), it contains all TS features and added features – declarative UI description, custom components, dynamic extension of UI elements, state management, and rendering control. State management provides clear page re-render processes and pipes through decorators with different functions. State management covers UI component states and application states, with which you are able to build an application-wide data update and UI rendering process. To learn more about ArkTS, see Getting Started with ArkTS.
-
Layout
The layout defines how components are laid out in the UI. ArkUI offers a diverse array of layouts. Besides the basic layouts – linear, stack, flex, relative, and grid, you also have access to the advanced list, grid, and swiper layouts.
-
Component
Components are essential elements of the UI, working together to shape the UI. They can be classified as built-in components – those directly provided by the ArkUI framework, and custom components – those defined by developers. The built-in components include buttons, radio buttons, progress indicators, and text. You can set the rendering effect of these components in method chaining mode. You can combine built-in components to form custom components. In this way, page components are divided into independent UI units to implement independent creation, development, and reuse of different units on pages, making pages more engineering-oriented.
-
Page routing and component navigation
An application may contain a good many pages, and each page may come with multiple components. You can implement page routing to navigate users between pages and use navigation component to navigate them between components.
-
Graphics
ArkUI offers diversified graphics capabilities, including capabilities to display images in various formats and custom drawing capabilities. By leveraging these capabilities, you can easily bring your custom drawing ideas into reality.
-
Animation
Apart from animations embedded in components, ArkUI offers additional animation features: attribute animation, explicit animation, transition animation, and animation APIs. You can customize animation tracks by calling the provided animation APIs in addition to using the encapsulated physical models.
-
Interaction event
Interaction events are important for interactions between the UI and users. ArkUI allows users to interact with your application UI, with support for various universal events and gesture events. Universal events include touch events, mouse events, key events, and focus events. Gesture events accept single gestures (tap, long press, pan, pinch, rotation, and swipe), and a combination of gestures.
Highlights
-
Simplified and efficient development
- Simple code: You can describe the UI in pseudo-natural language, without caring about how the framework implements UI drawing and rendering.
- Data-driven UI change: This allows you to better focus on your service logic processing. When the UI changes, you do not need to write code for switching between different UIs. Instead, you only need to write the data that causes the UI change and let the framework take over the rest.
- Improved development experience: Just code to get the UI developed.
-
High performance
- Declarative UI frontend and backend layering: The UI backend, constructed using the C++ programming language, provides basic components, layout, animations, interaction events, component state management, and rendering pipelines for the frontend.
- Language compiler and runtime optimization: The productivity punch includes unified bytecode, efficient Foreign Function Interface (FFI), ahead-of-time (AOT), engine minimization, and type optimization.
-
Promising ecosystem ArkUI can gain traction with its relatively neutral and friendly programming language. It can tap on the ecosystems of mainstream languages ecosystem and pushed toward a steady revolutionary path with standards organizations.
Architecture
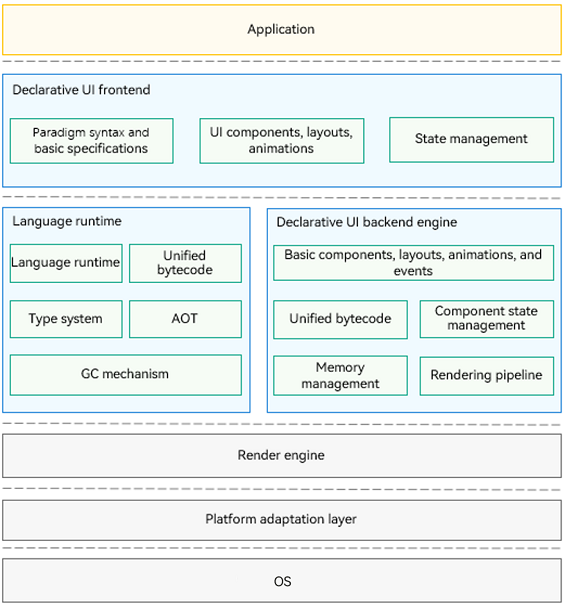
Figure 1 Overall architecture
-
Declarative UI frontend Provides basic language specifications of the UI development paradigm, built-in UI components, layouts, and animations, and multiple state management mechanisms, with a wide array of APIs for you to call as required.
-
Language runtime Provides the parsing capability for the UI paradigm syntax and allows for cross-language API calls for a high-performance operating environment of the TS language.
-
Declarative UI backend engine Provides UI rendering pipelines that are compatible with different development paradigms, multiple basic components, layout calculation, dynamic effects, and interaction events, with state management and drawing capabilities.
-
Render engine Provides efficient drawing capabilities, which enable rendering instructions collected by the rendering pipeline to be drawn to the screen.
-
Platform adaptation layer Provides abstract APIs to connect to different systems, such as system rendering pipelines and lifecycle scheduling.
Development Process
The table below lists the main tasks involved in UI development with ArkUI. You can familiarize yourself with the UI development process by getting started with a simple project.
| Task | Description | Guide |
|---|---|---|
| Get started with ArkTS | Learn the basic syntax, state management, and rendering control scenarios of ArkTS. | - Basic Syntax Overview - State Management - Rendering Control |
| Develop the layout | Understand the common layouts. | - Layout Overview |
| Add components | Learn the usage of common built-in components, custom components, and GUI elements supported by APIs. | - Common Components - Custom Components - Popup and Menu |
| Set page routing and component navigation | Learn how to set page routes and navigation between components. | - Page Routing - Navigation |
| Use graphics | Understand how to display images, draw custom geometry, and make custom graphics on the canvas. | - Displaying Images - Drawing Geometric Shapes - Drawing Custom Graphics Using the Canvas |
| Apply animations | Learn the typical scenarios of applying animations on components and pages. | - Property Animation - Transition Animation - Component Animation - Animated Curve - Animation Smoothing - Animation Effects |
| Bind events | Learn the basic concepts of events and how to use common events and gesture events. | - Universal Events - Gesture Events |