Freezing a Custom Component
When a custom component is inactive, it can be frozen so that its state variable does not respond to updates. That is, the @Watch decorated method is not called, and the node associated with the state variable is not re-rendered. You can use the freezeWhenInactive attribute to specify whether to freeze a custom component. If no parameter is passed in, the feature is disabled. This feature works in following scenarios: page routing, <TabContent>, and LazyforEach.
NOTE
Custom component freezing is supported since API version 11.
Use Scenarios
Page Routing
-
When page A calls the router.pushUrl API to jump to page B, page A is hidden and invisible. In this case, if the state variable on page A is updated, page A is not re-rendered.
-
The freezing feature does not work when the application is running in the background.
Page A:
import router from '@ohos.router';
@Entry
@Component({ freezeWhenInactive: true })
struct FirstTest {
@StorageLink('PropA') @Watch("first") storageLink: number = 47;
first() {
console.info("first page " + `${this.storageLink}`)
}
build() {
Column() {
Text(`From fist Page ${this.storageLink}`).fontSize(50)
Button('first page storageLink + 1').fontSize(30)
.onClick(() => {
this.storageLink += 1
})
Button('go to next page').fontSize(30)
.onClick(() => {
router.pushUrl({ url: 'pages/second' })
})
}
}
}
Page B:
import router from '@ohos.router';
@Entry
@Component({ freezeWhenInactive: true })
struct SecondTest {
@StorageLink('PropA') @Watch("second") storageLink2: number = 1;
second() {
console.info("second page: " + `${this.storageLink2}`)
}
build() {
Column() {
Text(`second Page ${this.storageLink2}`).fontSize(50)
Button('Change Divider.strokeWidth')
.onClick(() => {
router.back()
})
Button('second page storageLink2 + 2').fontSize(30)
.onClick(() => {
this.storageLink2 += 2
})
}
}
}
In the preceding example:
-
When the button first page storLink + 1 on page A is clicked, the storLink state variable is updated, and the @Watch decorated first method is called.
-
Through router.pushUrl({url:'pages/second'}), page B is displayed, and page A is hidden with its state changing from active to inactive.
-
When the button this.storLink2 += 2 on page B is clicked, only the @Watch decorated second method of page B is called, because page A has been frozen when inactive.
-
When the back button is clicked, page B is destroyed, and page A changes from inactive to active. At this time, if the state variable of page A is updated, the @Watch decorated first method of page A is called again.
<TabContent>
-
You can freeze invisible <TabContent> components in the <Tabs> container so that they do not trigger UI re-rendering.
-
During initial rendering, only the <TabContent> component that is being displayed is created. All <TabContent> components are created only after all of them have been switched to.
@Entry
@Component
struct TabContentTest {
@State @Watch("onMessageUpdated") message: number = 0;
onMessageUpdated() {
console.info(`TabContent message callback func ${this.message}`)
}
build() {
Row() {
Column() {
Button('change message').onClick(() => {
this.message++
})
Tabs() {
TabContent() {
FreezeChild({ message: this.message })
}
TabContent() {
FreezeChild({ message: this.message })
}
}
}
.width('100%')
}
.height('100%')
}
}
@Component({ freezeWhenInactive: true })
struct FreezeChild {
@Link @Watch("onMessageUpdated") message: number
private index: number = 0
onMessageUpdated() {
console.info(`FreezeChild message callback func ${this.message}, index: ${this.index}`)
}
build() {
Text("message" + `${this.message}, index: ${this.index}`)
.fontSize(50)
.fontWeight(FontWeight.Bold)
}
}
In the preceding example:
-
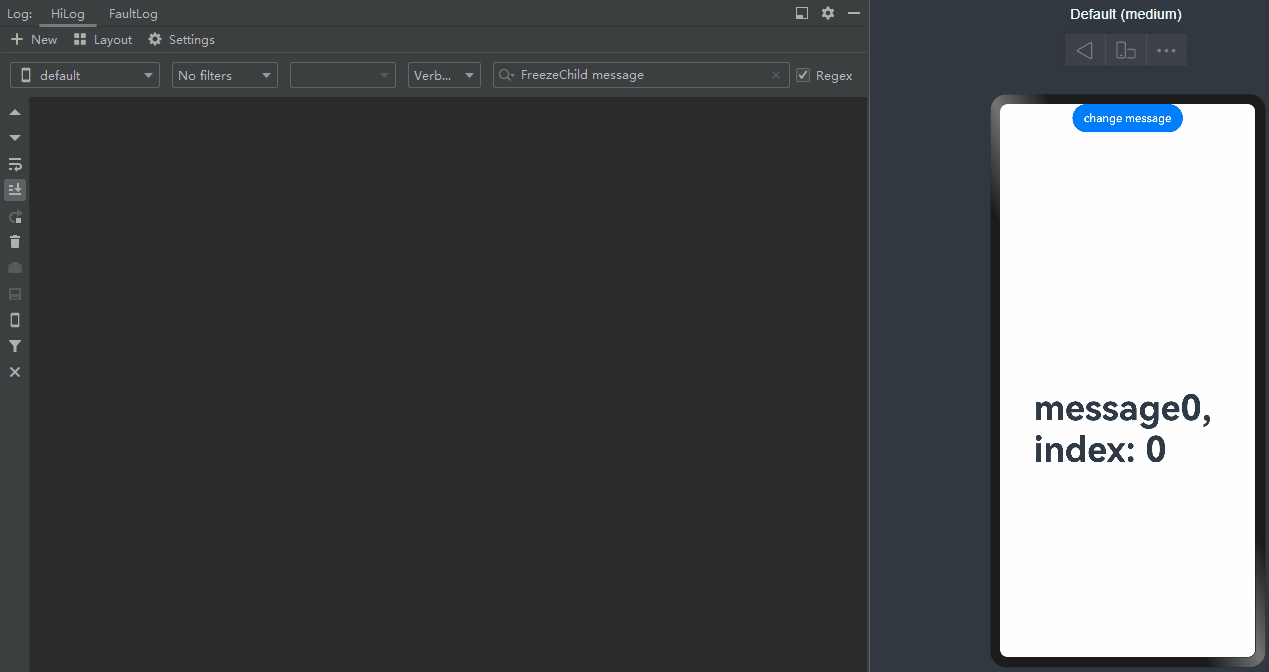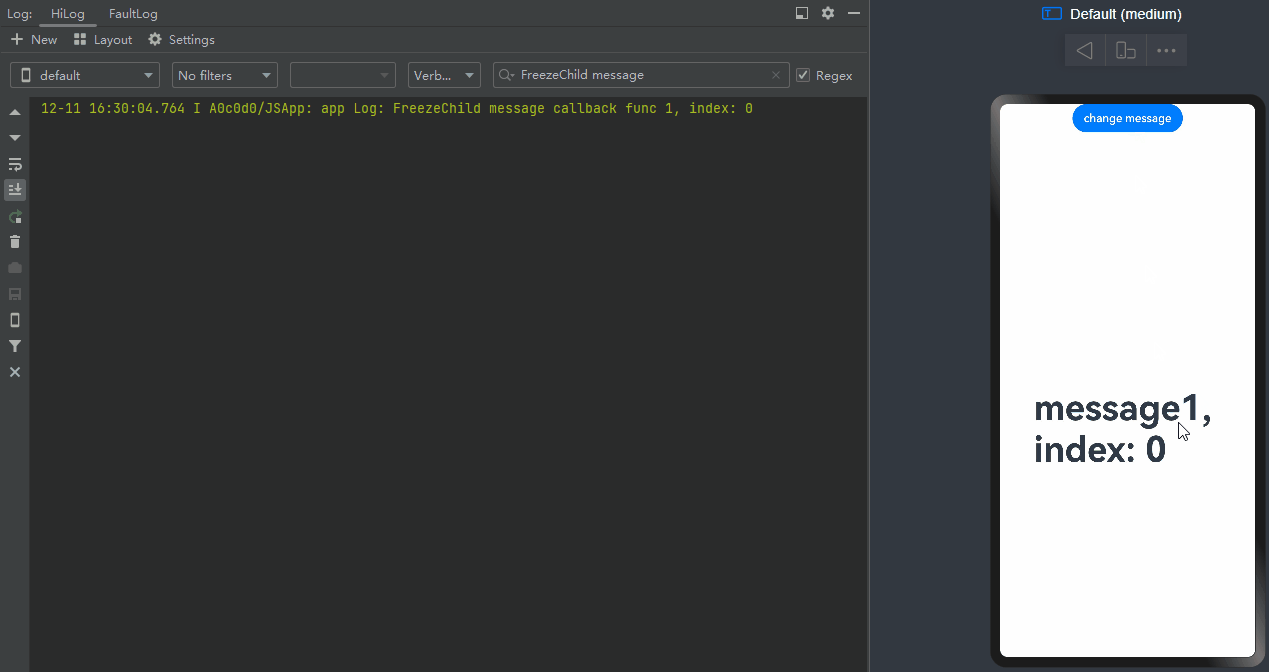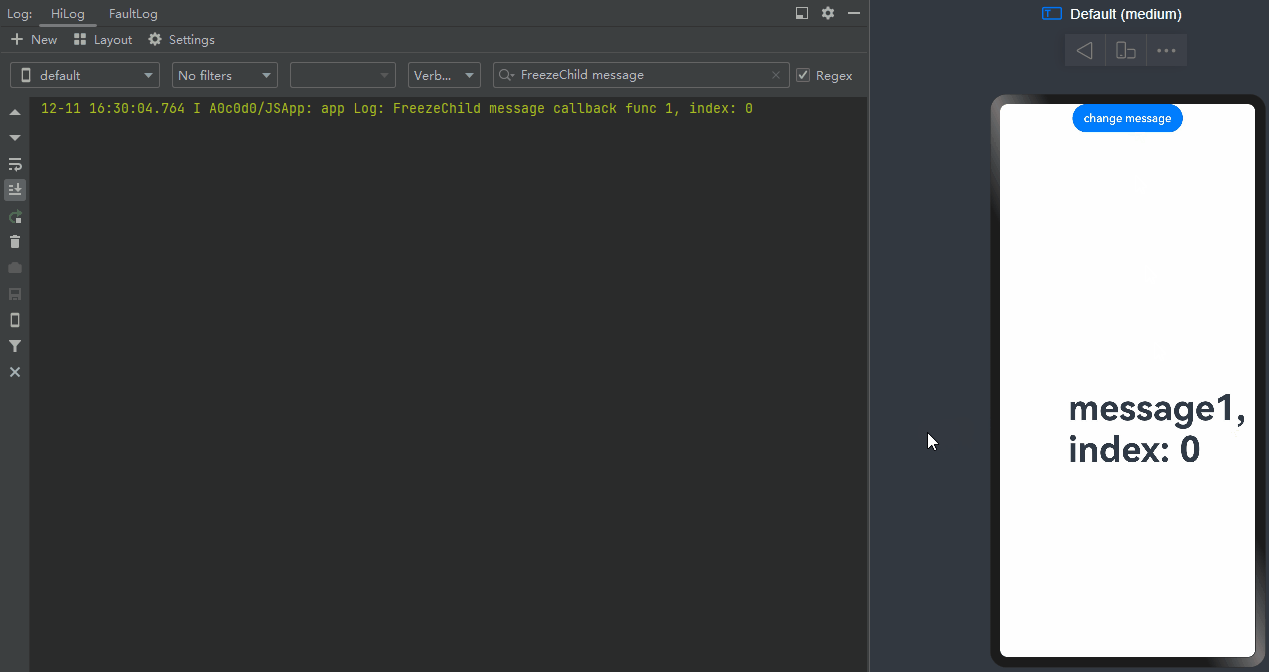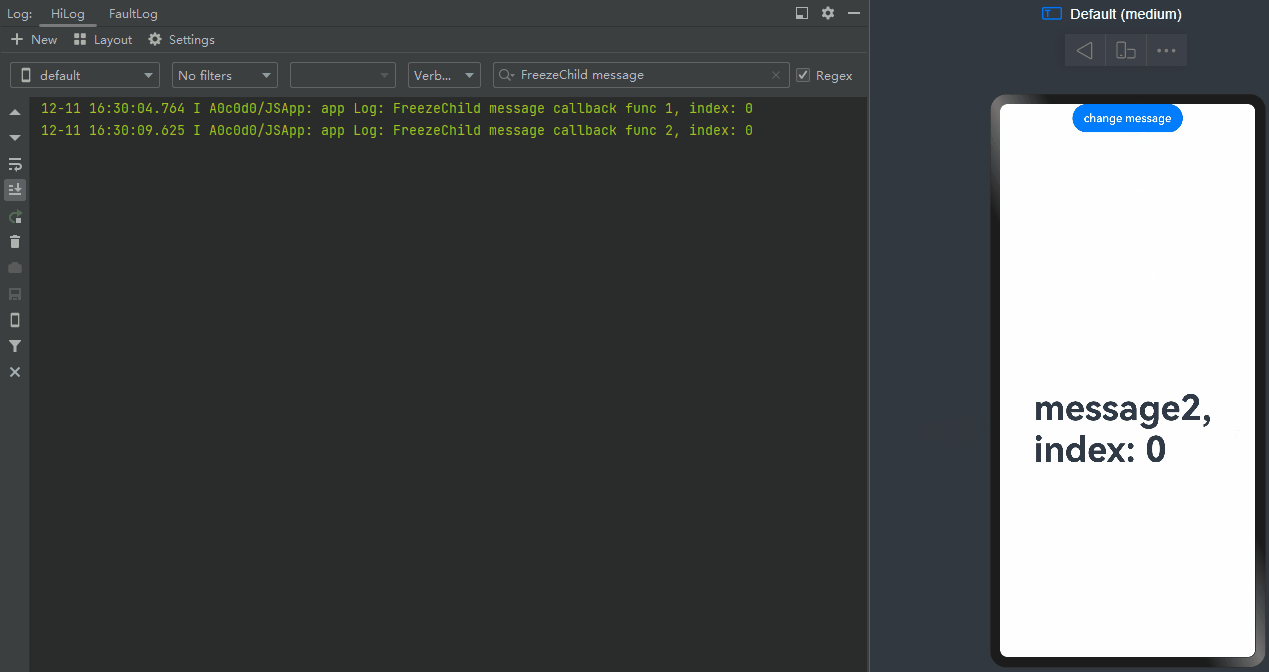
When change message is clicked, the value of message changes, and the @Watch decorated onMessageUpdated method of the <TabContent> component being displayed is called.
-
When you switch to another <TabContent> component, it switches from inactive to active, and the corresponding @Watch decorated onMessageUpdated method is called.
-
When change message is clicked again, the value of message changes, and only the @Watch decorated onMessageUpdated method of the <TabContent> component being displayed is called.
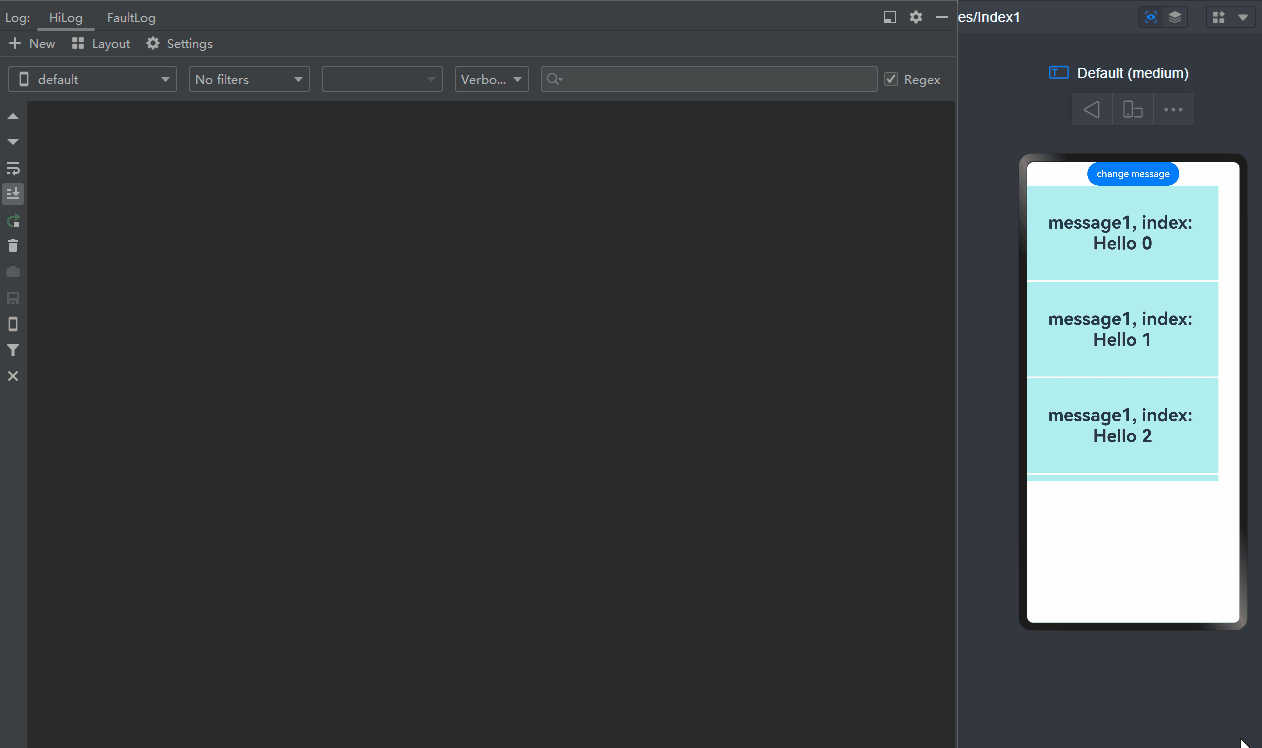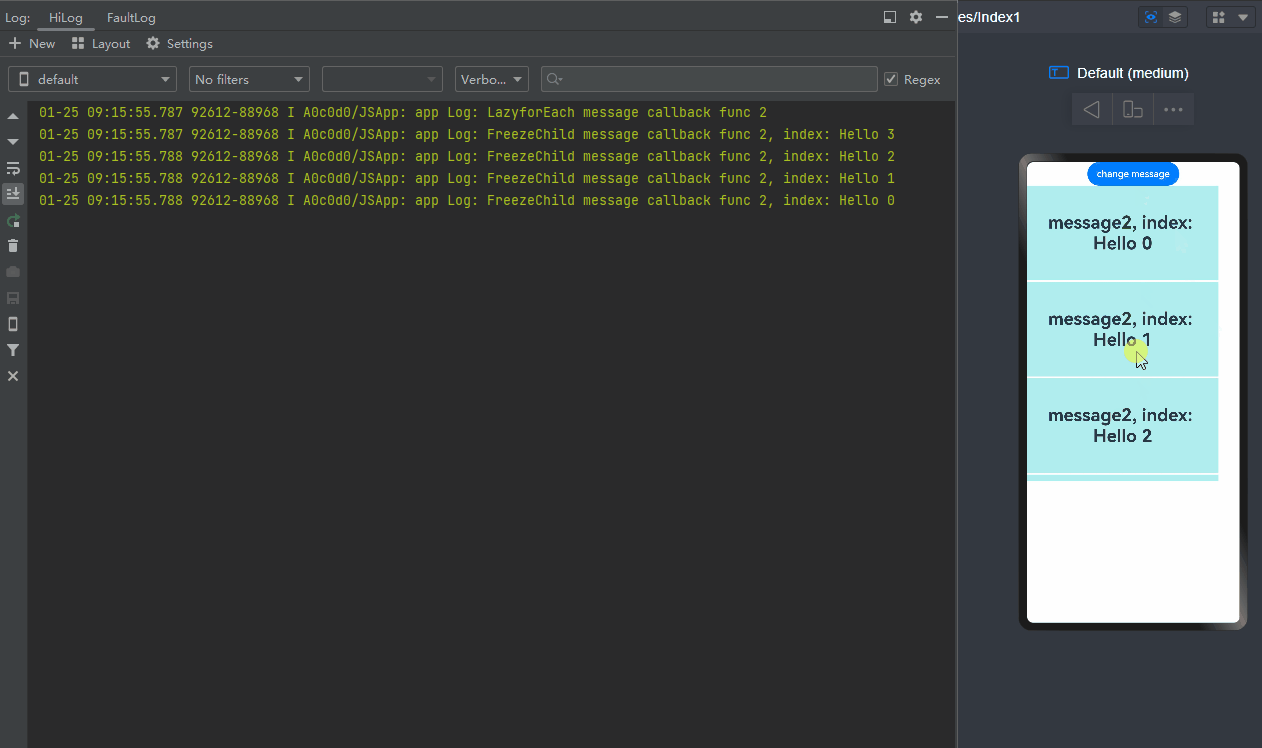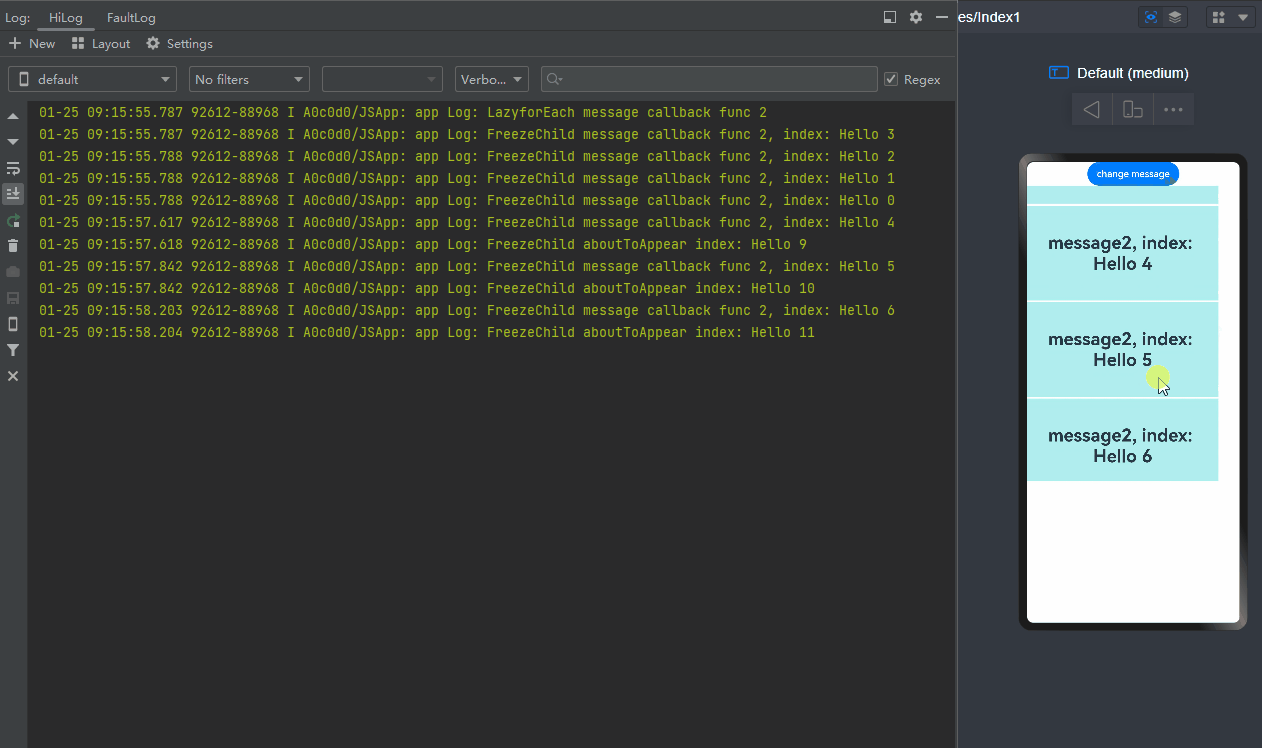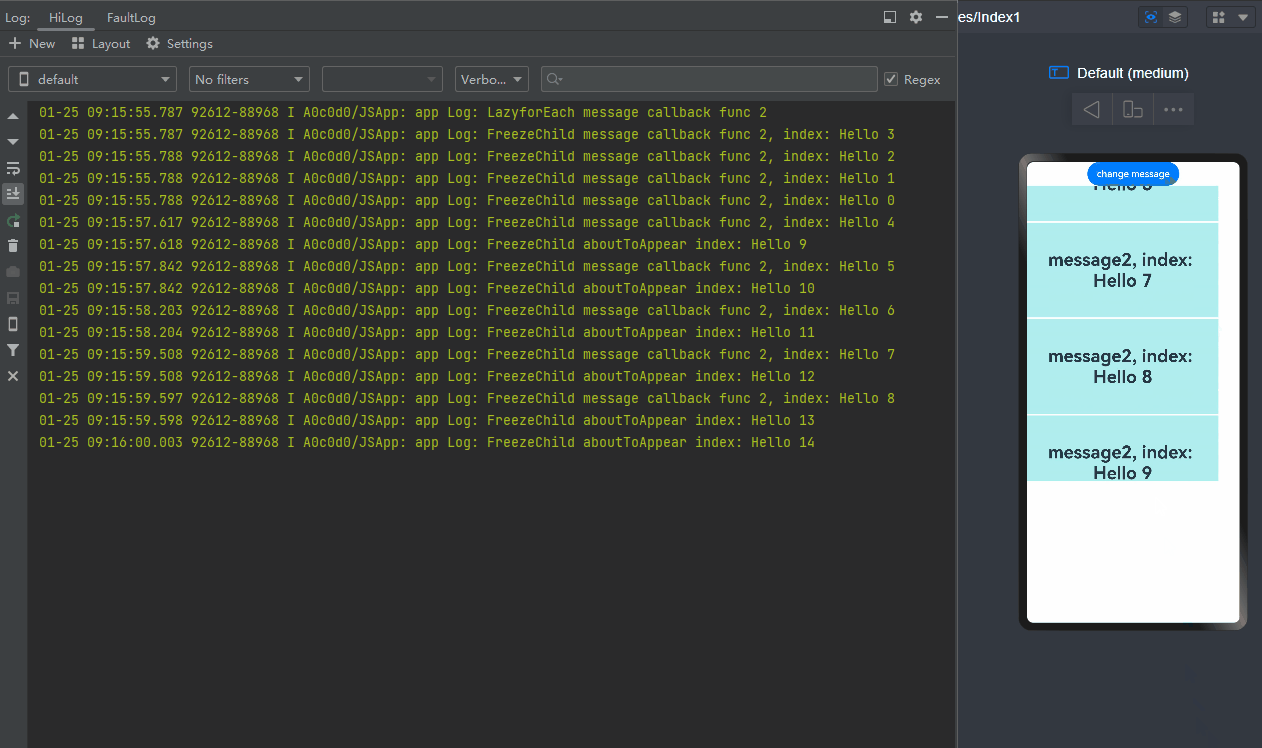
LazyforEach
- You can freeze custom components cached in LazyforEach so that they do not trigger UI re-rendering.
// Basic implementation of IDataSource to handle data listener
class BasicDataSource implements IDataSource {
private listeners: DataChangeListener[] = [];
private originDataArray: string[] = [];
public totalCount(): number {
return 0;
}
public getData(index: number): string {
return this.originDataArray[index];
}
// This method is called by the framework to add a listener to the LazyForEach data source.
registerDataChangeListener(listener: DataChangeListener): void {
if (this.listeners.indexOf(listener) < 0) {
console.info('add listener');
this.listeners.push(listener);
}
}
// This method is called by the framework to remove the listener from the LazyForEach data source.
unregisterDataChangeListener(listener: DataChangeListener): void {
const pos = this.listeners.indexOf(listener);
if (pos >= 0) {
console.info('remove listener');
this.listeners.splice(pos, 1);
}
}
// Notify LazyForEach that all child components need to be reloaded.
notifyDataReload(): void {
this.listeners.forEach(listener => {
listener.onDataReloaded();
})
}
// Notify LazyForEach that a child component needs to be added for the data item with the specified index.
notifyDataAdd(index: number): void {
this.listeners.forEach(listener => {
listener.onDataAdd(index);
})
}
// Notify LazyForEach that the data item with the specified index has changed and the child component needs to be rebuilt.
notifyDataChange(index: number): void {
this.listeners.forEach(listener => {
listener.onDataChange(index);
})
}
// Notify LazyForEach that the child component that matches the specified index needs to be deleted.
notifyDataDelete(index: number): void {
this.listeners.forEach(listener => {
listener.onDataDelete(index);
})
}
}
class MyDataSource extends BasicDataSource {
private dataArray: string[] = [];
public totalCount(): number {
return this.dataArray.length;
}
public getData(index: number): string {
return this.dataArray[index];
}
public addData(index: number, data: string): void {
this.dataArray.splice(index, 0, data);
this.notifyDataAdd(index);
}
public pushData(data: string): void {
this.dataArray.push(data);
this.notifyDataAdd(this.dataArray.length - 1);
}
}
@Entry
@Component
struct LforEachTest {
private data: MyDataSource = new MyDataSource();
@State @Watch("onMessageUpdated") message: number = 0;
onMessageUpdated() {
console.info(`LazyforEach message callback func ${this.message}`)
}
aboutToAppear() {
for (let i = 0; i <= 20; i++) {
this.data.pushData(`Hello ${i}`)
}
}
build() {
Column() {
Button('change message').onClick(() => {
this.message++
})
List({ space: 3 }) {
LazyForEach(this.data, (item: string) => {
ListItem() {
FreezeChild({ message: this.message,
index: item })
}
}, (item: string) => item)
}.cachedCount(5).height(500)
}
}
}
@Component({ freezeWhenInactive: true })
struct FreezeChild {
@Link @Watch("onMessageUpdated") message: number;
private index: string = "";
aboutToAppear() {
console.info(`FreezeChild aboutToAppear index: ${this.index}`)
}
onMessageUpdated() {
console.info(`FreezeChild message callback func ${this.message}, index: ${this.index}`)
}
build() {
Text("message" + `${this.message}, index: ${this.index}`)
.width('90%')
.height(160)
.backgroundColor(0xAFEEEE)
.textAlign(TextAlign.Center)
.fontSize(30)
.fontWeight(FontWeight.Bold)
}
}
In the preceding example:
-
When change message is clicked, the value of message changes, the @Watch decorated onMessageUpdated method of the list items being displayed is called, and that of the cached list items is not called. (If the component is not frozen, the @Watch decorated onMessageUpdated method of both list items that are being displayed and cached list items is called.)
-
When a list item moves from outside the list content area into the list content area, it switches from inactive to active, and the corresponding @Watch decorated onMessageUpdated method is called.
-
When change message is clicked again, the value of message changes, and only the @Watch decorated onMessageUpdated method of the list items being displayed is called.