Silent Access via the DatamgrService
When to Use
In a typical cross-application data access scenario, the data provider may be started multiple times.
To minimize the startup times of the data provider and speed up data access, OpenHarmony provides the silent access feature, which allows access to the database without starting the data provider.
In silent access, the DatamgrService accesses and modifies data without starting the data provider.
The DatamgrService supports basic database access and data hosting only. If service processing is required, the service processing logic must be encapsulated into APIs for the data consumer to call.
If the service is too complex, use DataShareExtensionAbility to start the data provider.
Working Principles
The DatamgrService can serve as a proxy to access the following data:
-
Persistent data: data in the database of the data provider. It is stored in the sandbox directory of the data provider and can be shared in declaration mode by the data provider. Persistent data is configured as data tables for access.
-
Process data: process data, in the JSON or byte format, managed by the DatamgrService. It is stored in the DatamgrService sandbox directory, and is automatically deleted 10 days after no subscription.
-
Dynamic data: data stored in the memory of a device. It is automatically deleted after the device is restarted. Currently, the dynamic data refers to only the data set by enableSilentProxy and disableSilentProxy.
| Data Type | Location | Data Format | Validity Period | Usage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Persistent data | Sandbox directory of the data provider | Database tables | Permanent | RDB data used for schedules and meetings. |
| Process data | DatamgrService sandbox directory | JSON or byte | Automatically deleted 10 days after no subscription | Time-sensitive data in simple format used for step count, weather, and heart rate monitoring. |
| Dynamic data | DatamgrService memory | KV pair | Automatically deleted after the device is restarted | Data generated when silent access is dynamically disabled or enabled. For example, to ensure data accuracy, silent access needs to be disabled in upgrade and enabled after the upgrade by using APIs. The "enabled" or "disabled" status generated by using the API is cleared after the device is restarted. The dynamic data refers to only the data set by enableSilentProxy and disableSilentProxy. |
Figure 1 Silent access
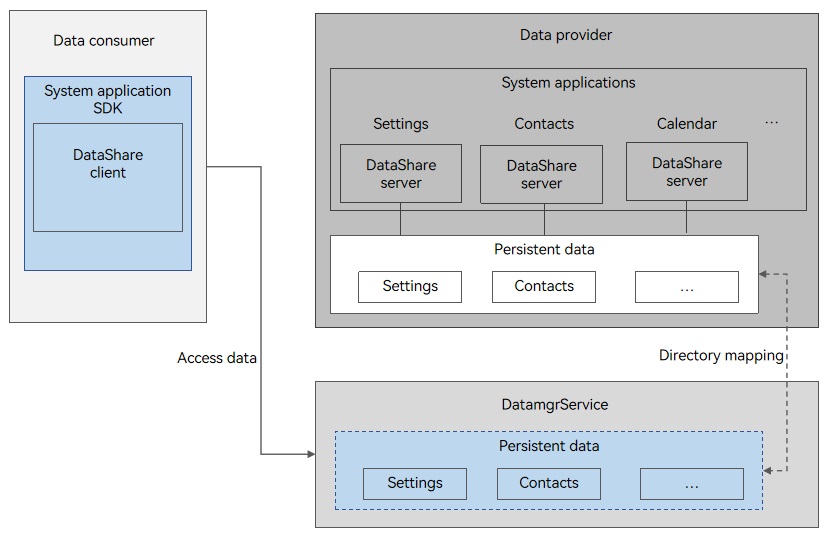
-
In silent access, DatamgrService obtains the access rules configured by the data provider through directory mapping, performs preprocessing based on rules, and accesses the database.
-
To use silent access, the URIs must be in the following format: datashareproxy://{bundleName}/{dataPath}
The DatamgrService obtains the data provider application based on bundleName, reads the configuration, verifies the permission, and accesses data.
dataPath identifies the data. It can be customized and must be unique in the same data provider application.
Constraints
- Currently, only the RDB stores support silent access.
- The system supports a maximum of 16 concurrent query operations. Excess query requests need to be queued for processing.
- The proxy is not allowed to create a database for persistent data. To create a database, you must start the data provider.
- If the data provider is an application with a normal signature, the data read/write permission must be system_basic or higher.
Available APIs
Most of the APIs for silent access are executed asynchronously in callback or promise mode. In the following table, callback-based APIs are used as an example. For more information about the APIs, see Data Sharing.
Universal APIs
| API | Description |
|---|---|
| createDataShareHelper(context: Context, uri: string, options: DataShareHelperOptions, callback: AsyncCallback<DataShareHelper>): void | Creates a DataShareHelper instance. |
APIs for Accessing Persistent Data
| API | Description |
|---|---|
| insert(uri: string, value: ValuesBucket, callback: AsyncCallback<number>): void | Inserts a row of data into a table. |
| delete(uri: string, predicates: dataSharePredicates.DataSharePredicates, callback: AsyncCallback<number>): void | Deletes one or more data records from the database. |
| query(uri: string, predicates: dataSharePredicates.DataSharePredicates, columns: Array<string>, callback: AsyncCallback<DataShareResultSet>): void | Queries data in the database. |
| update(uri: string, predicates: dataSharePredicates.DataSharePredicates, value: ValuesBucket, callback: AsyncCallback<number>): void | Updates data in the database. |
| addTemplate(uri: string, subscriberId: string, template: Template): void | Adds a data template with the specified subscriber. |
| on(type: 'rdbDataChange', uris: Array<string>, templateId: TemplateId, callback: AsyncCallback<RdbDataChangeNode>): Array<OperationResult | Subscribes to the changes of the data corresponding to the specified URI and template. |
APIs for Accessing Process Data
| API | Description |
|---|---|
| publish(data: Array<PublishedItem>, bundleName: string, version: number, callback: AsyncCallback<Array<OperationResult>>): void | Publish data to the DatamgrService. |
| on(type: 'publishedDataChange', uris: Array<string>, subscriberId: string, callback: AsyncCallback<PublishedDataChangeNode>): Array<OperationResult> | Subscribes to changes of the published data. |
APIs for Accessing Dynamic Data
| API | Description |
|---|---|
| enableSilentProxy(context: Context, uri?: string): Promise<void> | Enables silent access by the data provider dynamically. When the data consumer calls the DataShare API through silent access, the system verifies the silent access status. If silent access is enabled, the DataShare API will be executed. |
| disableSilentProxy(context: Context, uri?: string): Promise<void> | Disables silent access by the data provider dynamically. When the data consumer calls the DataShare API through silent access, the system verifies the silent access status. If silent access is disabled, the DataShare API will be denied. |
Accessing Persistent Data
The following walks you through on how to share an RDB store.
Data Provider Application
-
In the module.json5 file, set the data to be shared in proxyData. For details about the configuration, see module.json5 Configuration File.
Table 1 proxyData in module.json5
| Name | Description | Mandatory |
|---|---|---|
| uri | URI of the data proxy, which is the unique identifier for cross-application data access. | Yes |
| requiredReadPermission | Permission required for reading data from the data proxy. If this parameter is not set, other applications are not allowed to access data. For details about the permissions, see Permissions for All Applications. | No |
| requiredWritePermission | Permission required for writing data to the data proxy. If this parameter is not set, other applications are not allowed to write data to the data proxy. For details about the permissions, see Permissions for All Applications. | No |
| metadata | Metadata of the data source, including the name and resource fields. The name field identifies the configuration, which has a fixed value of dataProperties. The value of resource is $profile:{fileName}, indicating that the name of the configuration file is {fileName}.json. |
Yes |
module.json5 example
"proxyData":[
{
"uri": "datashareproxy://com.acts.ohos.data.datasharetest/test",
"requiredReadPermission": "ohos.permission.GET_BUNDLE_INFO",
"requiredWritePermission": "ohos.permission.KEEP_BACKGROUND_RUNNING",
"metadata": {
"name": "dataProperties",
"resource": "$profile:my_config"
}
}
]
Table 2 Fields in my_config.json
| Name | Description | Mandatory |
|---|---|---|
| path | Data source path, in the Database_name/Table_name format. Currently, only RDB stores are supported. | Yes |
| type | Database type. Currently, only rdb is supported. | Yes |
| scope | Scope of the database. - module indicates that the database is located in this module. - application indicates that the database is located in this application. |
No |
my_config.json example
{
"path": "DB00/TBL00",
"type": "rdb",
"scope": "application"
}
Data Consumer Application
-
Import dependencies.
import dataShare from '@ohos.data.dataShare'; import dataSharePredicates from '@ohos.data.dataSharePredicates'; import UIAbility from '@ohos.app.ability.UIAbility'; import { ValuesBucket } from '@ohos.data.ValuesBucket'; import window from '@ohos.window'; import { BusinessError } from '@ohos.base'; -
Define the URI string for communicating with the data provider.
let dseUri = ('datashareproxy://com.acts.ohos.data.datasharetest/test'); -
Create a DataShareHelper instance.
let dsHelper: dataShare.DataShareHelper | undefined = undefined; let abilityContext: Context; export default class EntryAbility extends UIAbility { onWindowStageCreate(windowStage: window.WindowStage) { abilityContext = this.context; dataShare.createDataShareHelper(abilityContext, dseUri, { isProxy: true }, (err, data) => { dsHelper = data; }); } } -
Use DataShareHelper APIs to access the services provided by the provider, for example, adding, deleting, modifying, and querying data.
// Construct a piece of data. let key1 = 'name'; let key2 = 'age'; let key3 = 'isStudent'; let key4 = 'Binary'; let valueName1 = 'ZhangSan'; let valueName2 = 'LiSi'; let valueAge1 = 21; let valueAge2 = 18; let valueIsStudent1 = false; let valueIsStudent2 = true; let valueBinary = new Uint8Array([1, 2, 3]); let valuesBucket: ValuesBucket = { key1: valueName1, key2: valueAge1, key3: valueIsStudent1, key4: valueBinary }; let updateBucket: ValuesBucket = { key1: valueName2, key2: valueAge2, key3: valueIsStudent2, key4: valueBinary }; let predicates = new dataSharePredicates.DataSharePredicates(); let valArray = ['*']; if (dsHelper != undefined) { // Insert a piece of data. (dsHelper as dataShare.DataShareHelper).insert(dseUri, valuesBucket, (err, data) => { console.info(`dsHelper insert result:${data}`); }); // Update data. (dsHelper as dataShare.DataShareHelper).update(dseUri, predicates, updateBucket, (err, data) => { console.info(`dsHelper update result:${data}`); }); // Query data. (dsHelper as dataShare.DataShareHelper).query(dseUri, predicates, valArray, (err, data) => { console.info(`dsHelper query result:${data}`); }); // Delete data. (dsHelper as dataShare.DataShareHelper).delete(dseUri, predicates, (err, data) => { console.info(`dsHelper delete result:${data}`); }); } -
Subscribe to data.
function onCallback(err: BusinessError, node: dataShare.RdbDataChangeNode) { console.info("uri " + JSON.stringify(node.uri)); console.info("templateId " + JSON.stringify(node.templateId)); console.info("data length " + node.data.length); for (let i = 0; i < node.data.length; i++) { console.info("data " + node.data[i]); } } let key21: string = "p1"; let value21: string = "select * from TBL00"; let key22: string = "p2"; let value22: string = "select name from TBL00"; let template: dataShare.Template = { predicates: { key21: value21, key22: value22, }, scheduler: "" } if(dsHelper != undefined) { (dsHelper as dataShare.DataShareHelper).addTemplate(dseUri, "111", template); } let templateId: dataShare.TemplateId = { subscriberId: "111", bundleNameOfOwner: "com.acts.ohos.data.datasharetestclient" } if(dsHelper != undefined) { // When the DatamgrService modifies data, onCallback is invoked to return the data queried based on the rules in the template. let result: Array<dataShare.OperationResult> = (dsHelper as dataShare.DataShareHelper).on("rdbDataChange", [dseUri], templateId, onCallback); }
Accessing Process Data
The following walks you through on how to host process data.
(Optional) Data Provider Application
In the module.json5 file, set the data to be hosted in proxyData. For details about the configuration, see module.json5 Configuration File.
NOTE
- The configuration of proxyData is optional.
- If proxyData is not configured, the hosted data cannot be accessed by other applications.
- If proxyData is not configured, you do not need to use the full data path. For example, you can use weather instead of datashareproxy://com.acts.ohos.data.datasharetest/weather when publishing, subscribing to, and querying data.
Table 3 proxyData in module.json5
| Name | Description | Mandatory |
|---|---|---|
| uri | URI of the data proxy, which is the unique identifier for cross-application data access. | Yes |
| requiredReadPermission | Permission required for reading data from the data proxy. If this parameter is not set, other applications are not allowed to access data. For details about the permissions, see Permissions for All Applications. | No |
| requiredWritePermission | Permission required for writing data to the data proxy. If this parameter is not set, other applications are not allowed to write data to the dta proxy. For details about the permissions, see Permissions for All Applications. | No |
module.json5 example
"proxyData": [
{
"uri": "datashareproxy://com.acts.ohos.data.datasharetest/weather",
"requiredReadPermission": "ohos.permission.GET_BUNDLE_INFO",
"requiredWritePermission": "ohos.permission.KEEP_BACKGROUND_RUNNING"
}
]
Data Consumer Application
-
Import dependencies.
import dataShare from '@ohos.data.dataShare'; import UIAbility from '@ohos.app.ability.UIAbility'; import window from '@ohos.window'; import { BusinessError } from '@ohos.base'; -
Define the URI string for communicating with the data provider.
let dseUri = ('datashareproxy://com.acts.ohos.data.datasharetest/weather'); -
Create a DataShareHelper instance.
let dsHelper: dataShare.DataShareHelper | undefined = undefined; let abilityContext: Context; export default class EntryAbility extends UIAbility { onWindowStageCreate(windowStage: window.WindowStage) { abilityContext = this.context; dataShare.createDataShareHelper(abilityContext, dseUri, {isProxy : true}, (err, data) => { dsHelper = data; }); } } -
Use the DataShareHelper APIs to access the services provided by the provider, for example, adding, deleting, modifying, and querying data.
// Construct two pieces of data. The first data is not configured with proxyDatas and cannot be accessed by other applications. let data : Array<dataShare.PublishedItem> = [ {key:"city", subscriberId:"11", data:"xian"}, {key:"datashareproxy://com.acts.ohos.data.datasharetest/weather", subscriberId:"11", data:JSON.stringify("Qing")}]; // Publish data. if (dsHelper != undefined) { let result: Array<dataShare.OperationResult> = await (dsHelper as dataShare.DataShareHelper).publish(data, "com.acts.ohos.data.datasharetestclient"); } -
Subscribe to data.
function onPublishCallback(err: BusinessError, node:dataShare.PublishedDataChangeNode) { console.info("onPublishCallback"); } let uris:Array<string> = ["city", "datashareproxy://com.acts.ohos.data.datasharetest/weather"]; if (dsHelper != undefined) { let result: Array<dataShare.OperationResult> = (dsHelper as dataShare.DataShareHelper).on("publishedDataChange", uris, "11", onPublishCallback); }
Accessing Dynamic Data
Only the data provider is involved. The following walks you through on how to dynamically enable silent access.
Data Provider Application
The data provider calls the enableSilentProxy API to dynamically enable silent access. This API must be used with the isSilentProxyEnable field in the data_share_config.json file. For details, see data_share_config.json configuration.
NOTE
- In the data_share_config.json file, the default value of isSilentProxyEnable is true, which means silent access is enabled.
- To verify whether silent access is enabled, the system first checks the silent access status set by the enableSilentProxy or disableSilentProxy API called, and then checks the value of isSilentProxyEnable in the data_share_config.json file.
- If enableSilentProxy or disableSilentProxy has not been called, the value of isSilentProxyEnable in the data_share_config.json file is preferentially checked.
- Silent access is enabled by default if enableSilentProxy or disableSilentProxy has not been called and isSilentProxyEnable in the data_share_config.json file is not configured.
-
Import dependencies.
import dataShare from '@ohos.data.dataShare'; import UIAbility from '@ohos.app.ability.UIAbility'; import window from '@ohos.window'; -
Define the URI string for communicating with the data provider.
let dseUri = ('datashare:///com.acts.datasharetest/entry/DB00/TBL00'); -
Create a DataShareHelper instance.
let abilityContext: Context; export default class EntryAbility extends UIAbility { onWindowStageCreate(windowStage: window.WindowStage) { abilityContext = this.context; dataShare.enableSilentProxy(abilityContext, dseUri); } }