Web Development
How do HTML5 pages interact with ArkTS? (API version 10)
Problem
Currently, javaScriptProxy supports only synchronous invoking. This means that no execution results can be obtained for asynchronous invoking.
Solution
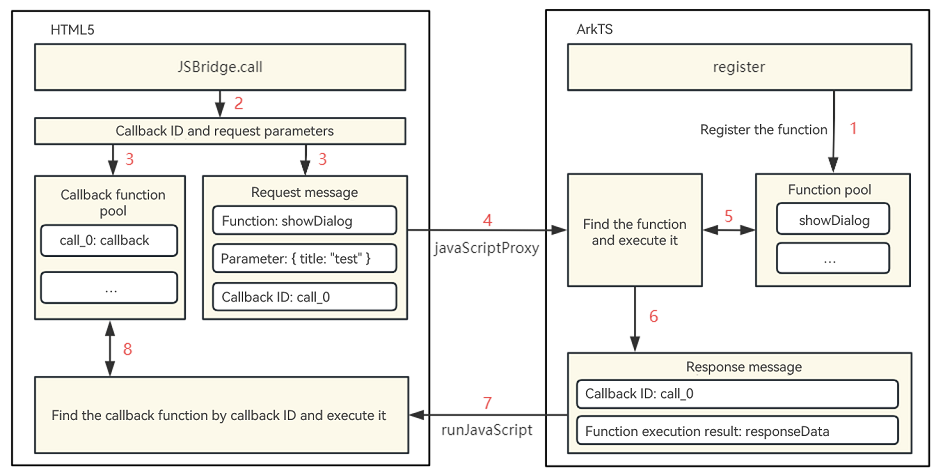
Encapsulate javaScriptProxy and runJavaScript to implement the JSBridge communication scheme. This method is applicable to the scenario where HTML5 calls native functions. Use the <Web> component javaScriptProxy to inject the native API to the window object of HTML5 pages, use the runJavaScript API to execute the JS script on HTML5 pages, and obtain the script execution result from the callback. The following figure shows the invoking process.
-
Use the javaScriptProxy attribute of the <Web> component to register the JSBridgeHandle object with the HTML5 window as the native channel for HTML5 to call. When the HTML5 page starts to be loaded, the initJSBridge() method is called in the onPageBegin callback to initialize the JSBridge.
// javaScriptProxy object public get javaScriptProxy() { return { object: { call: this.call }, name: "JSBridgeHandle", methodList: ['call'], controller: this.controller, } }// Use the <Web> component to load the HTML5 page. @Component struct JsProxy { private controller: WebviewController = new WebView.WebviewController() private jsBridge: JSBridge = new JSBridge(this.controller) build() { Column(){ Web({ src: $rawfile('index.html'), controller: this.controller }) .javaScriptProxy(this.jsBridge.javaScriptProxy) .onPageBegin(() => { this.jsBridge.initJSBridge() }) } } } -
In the initJSBridge method, use webviewControll.runJavaScript() to inject the JSBridge initialization script into the HTML5 page for execution. When HTML5 is called, the window.callID is generated to identify the callback function, and then the callID and request parameters are transferred to the native side using JSBridgeHandle.call. Use JSBridgeCallback to receive the execution result from the native side, find the callback based on the ID and execute it, and then release the memory.
// bridgeKey and bridgeMethod dynamically generate the entry for invoking on the HTML5 side. bridgeKey: string = 'JSBridge' bridgeMethod: string = 'call' // Inject the initialization script to the HTML5 side. public initJSBridge() { try { this.controller.runJavaScript(` // Receive the result from the native side and execute callback. function JSBridgeCallback(id, params){ window.JSBridgeMap[id](params) }; // Declare the invoking entry. window.${this.bridgeKey} = { ${this.bridgeMethod}(method, params, callback){ window.JSBridgeMap[id] = callback || (() => {}); JSBridgeHandle.call(method, JSON.stringify(paramsObj)); }, }`) } } -
JSBridgeHandle.call() is the unified entry for HTML5 to call native APIs. In this method, find the matching API to call based on the name of the method called by HTML5. After the call is complete, use the this.callback() method to return the result to HTML5. In the callback, use webviewControll.runJavaScript() to call JSBridgeCallback of HTML5 to return the callID and result.
// The call method calls the native method and receives the result. private call = (fun, params) => { try { const paramsObj = JSON.parse(params) const events = this.exposeManage.methodMap.get(fun) const results = [] events.forEach(callFun => { results.push(callFun(paramsObj.data)) }) Promise.all(results.filter(i => !!i)).then(res => { this.callback(paramsObj.callID, res.length > 1 ? res : res[0]) }) } } // Use runJavaScript to call JSBridgeCallback to execute the callback. private callback(id, data) { this.controller.runJavaScript(`__JSBridgeCallback__("${id}", ${JSON.stringify(data)})`); }
How does the return result of onUrlLoadIntercept affect onInterceptRequest in the <Web> component? (API version 9)
Solution
The operation that follows onUrlLoadIntercept is subject to its return result.
-
If true is returned, the URL request is intercepted.
-
If false is returned , the onInterceptRequest callback is performed.
Reference
What should I do if the onKeyEvent event of the <Web> component is not triggered as expected? (API version 9)
Problem
The onKeyEvent event is set for the <Web> component to listen for keyboard events. However, it is not triggered when a key is pressed or lifted.
Solution
Currently, the <Web> component does not support the onKeyEvent event. To listen for keyboard events for the <Web> component, you can use the onInterceptKeyEvent callback function.
Reference
What should I do if page loading fails when onInterceptRequest is called? (API version 9)
Problem
The onInterceptRequest API intercepts URLs specified by src and returns the custom HTML file. However, the content in the script tag in the HTML file is not loaded.
Solution
If only setResponseData is set for the interceptor, the kernel cannot identify the HTML file. You must also set parameters such as setResponseEncoding, setResponseMimeType, and setResponseHeader for the kernel to identify the HTML file.
Example
Web({ src: 'www.example.com', controller: this.controller })
.onInterceptRequest((event) => {
console.log('url:' + event.request.getRequestUrl())
this.responseweb = new WebResourceResponse();
var head1:Header = {
headerKey:"Connection",
headerValue:"keep-alive"
}
var length = this.heads.push(head1)
this.responseweb.setResponseHeader(this.heads)
this.responseweb.setResponseData(this.webdata)
this.responseweb.setResponseEncoding('utf-8')
this.responseweb.setResponseMimeType('text/html')
this.responseweb.setResponseCode(200)
this.responseweb.setReasonMessage('OK')
return this.responseweb
})
Reference
How do I execute JS functions in HTML in ArkTS code? (API version 9)
Solution
Use the runJavaScript API in WebviewController to asynchronously execute JavaScript scripts and obtain the execution result in a callback.
NOTE runJavaScript can be invoked only after loadUrl is executed. For example, it can be invoked in onPageEnd.
Reference
How do I invoke an ArkTS method on a local web page? (API version 9)
Solution
-
Prepare an HTML file. Below is the sample code:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <title>Document</title> </head> <body> <h1>Title</h1> <h5 id="h5"></h5> <h5 id = "h6"></h5> <button onclick="handleFromH5">Invoke ArkTS method </button> <script type="text/javascript"> function handleFromH5(){ let result = window.objName.test(); document.getElementById('h6').innerHTML = result; } </script> </body> </html> -
Use the JavaScriptProxy API in ArkTs to register the object in ArkTS with the window object of HTML5, and then use the window object to call the method in HTML5. In the following example, the testObj object in ArkTS is registered with the HTML5 window object under the alias objName. In HTML5, window.objName can then be used to access the object.
// xxx.ets import web_webview from '@ohos.web.webview' @Entry @Component struct Index { @State message: string = 'Hello World' controller: web_webview.WebviewController = new web_webview.WebviewController() testObj = { test: (data1, data2, data3) => { console.log("data1:" + data1); console.log("data2:" + data2); console.log("data3:" + data3); return "AceString"; }, toString: () => { console.log('toString' + "interface instead."); } } build() { Row() { Column() { Web({ src:$rawfile('index.html'), controller:this.controller }) .javaScriptAccess(true) .javaScriptProxy({ object: this.testObj, name: "objName", methodList: ["test", "toString"], controller: this.controller, }) } .width('100%') } .height('100%') } }
Reference
How do I set the domStorageAccess attribute of the <Web> component? (API version 9)
Solution
The domStorageAccess attribute sets whether to enable the DOM Storage API. By default, this feature is disabled.
Reference
What should I do if the network status fails to be detected on the loaded HTML page? (API version 9)
Problem
When window.navigator.onLine is used on the HTML page to obtain the network status, the value is false no matter the network connection is set up or not.
Solution
Configure the permission for the application to obtain network information: ohos.permission.GET_NETWORK_INFO
Reference
How do I set the UserAgent parameter through string concatenation? (API version 9)
Solution
By default, the value of UserAgent needs to be obtained through the WebviewController. Specifically, it is obtained by calling the getUserAgent API in a WebviewController object after it is bound to the <Web> component. Therefore, to set UserAgent through string concatenation before page loading:
-
Use @State to define the initial UserAgent and bind it to the <Web> component.
-
In the onUrlLoadIntercept callback of the <Web> component, use WebviewController.getUserAgent() to obtain the default UserAgent and update the bound UserAgent.
Example
import web_webview from '@ohos.web.webview'
@Entry
@Component
struct Index {
private controller: web_webview.WebviewController = new web_webview.WebviewController()
@State userAgentPa: string = ''
build() {
Row() {
Column() {
Web({ src: 'http://www.example.com', controller: this.controller }) // Replace the URL with the actual URL.
.width('100%')
.userAgent(this.userAgentPa)
.onUrlLoadIntercept((event) => {
let userAgent = this.controller.getUserAgent();
this.userAgentPa = userAgent + ' 111111111'
return false;
})
}
.width('100%')
}
.height('100%')
}
}
Reference
How do I enable the <Web> component to return to the previous web page following a swipe gesture? (API version 9)
Solution
Override the onBackPress API to define the return logic and use WebviewController to determine whether to return to the previous web page.
Example
import web_webview from '@ohos.web.webview';
@Entry
@Component
struct Index {
controller: web_webview.WebviewController = new web_webview.WebviewController();
build() {
Column() {
Web({ src: 'http://www.example.com', controller: this.controller })// Replace the URL with the actual URL.
}
}
onBackPress() {
// Check whether a specific number of steps forward or backward can be performed on the current page. A positive number indicates forward, and a negative number indicates backward.
if (this.controller.accessStep(-1)) {
this.controller.backward(); // Return to the previous web page.
// Execute the custom return logic.
return true
} else {
// Execute the default return logic to return to the previous page.
return false
}
}
}
Reference