Sharing an Application File
An application can share a file with another application based on the file descriptor (FD) or uniform resource identifier (URI) of the file.
-
URI-based file sharing: You can use wantConstant.Flags to specify the read or read/write permission on the file for the target application (application with which the file is shared). The target application can call fs.open to open the file based on the URI and perform read and write operations. Currently, only temporary authorization is supported. The permission on the shared file is revoked once the target application exits.
-
FD-based sharing: You can use open() of the ohos.file.fs module to specify the read or read/write permission on the file for the target application. After parsing the FD in Want, the target application can read or write the file by using read() or write() API of ohos.file.fs based on the permission granted.
After the FD of a shared file is closed, the target application can no longer open the shared file. Therefore, FD-based file sharing is not recommended. This topic describes how to share an application file and use a shared file based on the file URI.
Shareable Application Directories
| Application Sandbox Path | Physical Path | Description |
|---|---|---|
| /data/storage/el1/base | /data/app/el1/<currentUserId>/base/<PackageName> | Encrypted database directory under /el1. |
| /data/storage/el2/base | /data/app/el2/<currentUserId>/base/<PackageName> | Encrypted database directory under /el2. |
| /data/storage/el2/distributedfiles | /mnt/hmdfs/<currentUserId>/account/device_view/<networkId>/data/<PackageName> | Distributed data directory under el2/. |
File URI Specifications
The file URIs are in the following format:
file://<bundleName>/<path>
-
file: indicates a file URI.
-
bundleName: specifies the owner of the file, that is, the application that shares the file.
-
path: specifies the application sandbox path of the file.
Sharing an Application File
Before sharing an application file, you need to obtain the application file path.
-
Obtain the application sandbox path of the file and convert it into the file URI.
import UIAbility from '@ohos.app.ability.UIAbility'; import fileUri from '@ohos.file.fileuri'; import window from '@ohos.window'; export default class EntryAbility extends UIAbility { onWindowStageCreate(windowStage: window.WindowStage) { // Obtain the application sandbox path of the file. let pathInSandbox = this.context.filesDir + "/test.txt"; // Convert the application sandbox path into a URI. let uri = fileUri.getUriFromPath(pathInSandbox); // The obtained URI is file://com.example.demo/data/storage/el2/base/files/test.txt. } } -
Set the target application and grant permissions on the file.
Use startAbility to start the target application. You need to pass in the obtained URI in uri of the want parameter, set the type of the file to share, set action to ohos.want.action.sendData, and set the granted permission on the file in flags. For details, see Want.NOTE
The write permission granted includes the read permission.
import fileUri from '@ohos.file.fileuri'; import window from '@ohos.window'; import wantConstant from '@ohos.app.ability.wantConstant'; import UIAbility from '@ohos.app.ability.UIAbility'; import Want from '@ohos.app.ability.Want'; import { BusinessError } from '@ohos.base'; export default class EntryAbility extends UIAbility { onWindowStageCreate(windowStage: window.WindowStage) { // Obtain the application sandbox path of the file. let filePath = this.context.filesDir + '/test.txt'; // Convert the application sandbox path into a URI. let uri = fileUri.getUriFromPath(filePath); let want: Want = { // Grant the read and write permissions on the shared file to the target application. flags: wantConstant.Flags.FLAG_AUTH_WRITE_URI_PERMISSION | wantConstant.Flags.FLAG_AUTH_READ_URI_PERMISSION, // Set the implicit startup rule for the target application. action: 'ohos.want.action.sendData', uri: uri, type: 'text/plain' } this.context.startAbility(want) .then(() => { console.info('Invoke getCurrentBundleStats succeeded.'); }) .catch((err: BusinessError) => { console.error(`Invoke startAbility failed, code is ${err.code}, message is ${err.message}`); }); } // ... }
Figure 1 Example
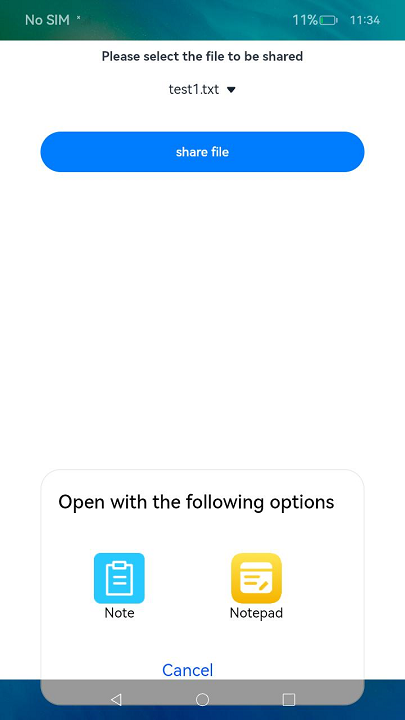
Using a Shared File
In the module.json5 file of the target application, set actions to ohos.want.action.sendData to allow the application to receive files shared by others and set uris to the type of the URI to receive. In the following example, the target application receives only .txt files with scheme of file.
{
"module": {
...
"abilities": [
{
...
"skills": [
{
...
"actions": [
"ohos.want.action.sendData"
],
"uris": [
{
"scheme": "file",
"type": "text/plain"
}
]
}
]
}
]
}
}
After the UIAbility starts, the target application obtains want information via onCreate() or onNewWant.
After obtaining the URI of the shared file from want, the target application can call fs.open to open the file and then read or write the file.
// xxx.ets
import fs from '@ohos.file.fs';
import Want from '@ohos.app.ability.Want';
import { BusinessError } from '@ohos.base';
function getShareFile() {
try {
let want: Want = {}; // The value should be the want information passed by the application that shares the file.
// Obtain the uri field from the want information.
let uri = want.uri;
if (uri == null || uri == undefined) {
console.info('uri is invalid');
return;
}
try {
// Perform operations on the URI of the shared file as required. For example, open the URI to obtain the file object in read/write mode.
let file = fs.openSync(uri, fs.OpenMode.READ_WRITE);
console.info('open file successfully!');
} catch (err) {
let error: BusinessError = err as BusinessError;
console.error(`Invoke openSync failed, code is ${error.code}, message is ${error.message}`);
}
} catch (error) {
let err: BusinessError = error as BusinessError;
console.error(`Invoke openSync failed, code is ${err.code}, message is ${err.message}`);
}
}