init Module FAQs
FAQs Related to Service Processes
System Service Process Does Not Automatically Restart After Exit
Check whether once is set to 1 in the .cfg file of the service process. If once is set to 1, the process is a one-time process and will not be started by the init process after exit.
How to Disable System Service Processes by Default
The disable option in the .cfg file of the service is not enabled. You can configure the start-mode option to control the startup mode.
How to Close the System Service Process Sandbox
Configure sandbox in the .cfg file of the service. The value 0 indicates that the service is not moved to the sandbox, and the value 1 indicates the opposite. The default value is 0.
Service Does Not Exist
Symptom
"Failed get servName" is recorded in the kernel log.
Cause Analysis
After a code review on the init process, it is found that the service does not exist.
Solution
-
Check whether the service is correctly configured in the .cfg file.
-
Check whether the .cfg file of the service is loaded normally.
-
Check whether the format of the .cfg file is correct.
FAQs Related to init Process Startup
System Stuck at the Startup Logo Screen
-
Cause analysis: The level-2 startup of the init process is not complete.
Solution:
Run the begetctl setloglevel 0 command, restart the device, and view the kernel log through the serial port. Check whether the level-2 startup of the init process is complete. The key log information is as follows:
[32.173144][pid=1] [Init] [INFO] [init.c:206]Start init second stage. [33.173144][pid=1] [Init] [DEBUG] [init.c:206]Parse init configs from /etc/init.cfg.
If the hdcd service is not started or the partition is not properly mounted, the begetctl command cannot be executed. You need to modify the init process code to set the log level. Ensure that the debug log of the init process can be properly generated.
-
Cause analysis: The init.cfg file fails to be parsed.
-
Incorrect format of the .cfg file
-
No permission or restricted permission
Solution:
-
Check the format of the .cfg file. Make sure that the file complies with the JSON format.
-
The log contains permission denied, and the init process reports a permission error. Check whether the fault is caused by SELinux. Disable SELinux, and perform the verification again. If the verification is successful, no permission error is reported. If the fault persists, the fault is probably caused by incorrect SELinux policy configuration. Configure the SELinux policy correctly. For details, see the readme in the base/security/selinux_adapter repository.
-
-
Cause analysis: The required partition is not properly mounted.
-
The required partition is not configured in cmdline or the format is incorrect.
-
The fstag.required file does not exist in the ramdisk.
Solution:
-
View the log to check whether the required partition is configured in the kernel cmdline. If yes, check whether the command format is correct and make modifications as needed.
[0.000000] Kernel command line: currentslot=0 bootslots=0 rw rootwait earlycon=uart8250,mmio32,0xfe660000 console=ttyFIQ0 ohos.boot.eng_mode=on root=PARTUUID=614e0000-0000 hardware=rk3568 default_boot_device=fe310000.sdhci ohos.required_mount.system=/dev/block/platform/fe310000.sdhci/by-name/system@/usr@ext4@ro,barrier=1@wait,required ohos.required_mount.vendor=/dev/block/platform/fe310000.sdhci/by-name/vendor@/vendor@ext4@ro,barrier=1@wait,required ohos.required_mount.misc=/dev/block/platform/fe310000.sdhci/by-name/misc@none@none@none@wait,required ohos.required_mount.bootctrl=/dev/block/platform/fe310000.sdhci/by-name/bootctrl@none@none@none@wait,requiredYou can also run the cat /proc/cmdline command on the device to view the information.
-
Check whether the fstab.required file exists in ramdisk.img.
-
-
Cause analysis: com.ohos.launcher is not started. As a result, no startup animation is displayed.
Solution: Run the ps -ef command to check whether com.ohos.launcher is available. Analyze the fault cause based on the log.
-
Cause analysis: The bootanimation service fails to start.
Solution:
-
Check whether the bootanimation service is started.
-
Check whether the bootanimation is repeatedly started.
The following log information indicates that the bootanimation service is started.
[10.175192] [pid=1] [Init] [INFO] [init_service_manager.c:1088]Start service bootanimation
-
-
Cause analysis: The data partition is not properly mounted.
-
The userdata partition is not configured in the device partition table.
-
The fstab file of the device does not have the mounting configuration of the data partition.
-
The file system configured in the fstab file of the device does not match the actual file system of the userdata image. For example, ext4 is configured in the fstab file, but the actual file system of the userdata image is f2fs.
Solution:
Check the kernel log and rectify the fault based on the log information.
-
"wait for file:/dev/block/platform/soc/10100000.himci.eMMC/by-name/userdata failed after"
-
No mounting information of the userdata partition in the log
-
"Mount /dev/block/platform/soc/10100000.himci.eMMC/by-name/userdata to /data failed"
If nofail is configured in the fstab file, "Mount no fail device /dev/block/platform/soc/10100000.himci.eMMC/by-name/userdata to /data failed" is recorded in the log. nofail indicates that a device mounting failure is not allowed.
-
System Stuck at the Startup Animation Screen
Cause Analysis
-
The startup animation does not exit properly.
-
System application spawning fails.
-
The reported boot events are incomplete. Not all services that have registered bootevent reported a boot event.
Solution
-
Check whether any service is repeatedly restarted and whether critical is configured for the service.
-
Run the ps -ef | grep ohos command to check whether the system application exists. If the log contains permission denied, the init process has reported a permission error. Apply for the required system application permission, disable SELinux, and perform verification again. If the verification is successful, the problem is caused by incorrect SELinux policy configuration. Modify or add the corresponding SELinux permission. For details about SELinux policy configuration, see the readme in the base/security/selinux_adapter repository.
-
Identify the services that do not report a boot event. If a certain service, for example, systemUI, does not report a boot event, the startup animation may be suspended.
Automatic Service Restart
Cause Analysis
-
The importance attribute is defined in the init service.
-
If the critical attribute is configured for a service, key processes that meet specified conditions will restart.
-
A panic occurs because the init process is suspended.
Solution
-
For a small system, set the importance attribute to 0. The value 0 indicates that the service is restarted, and the value 1 indicates the opposite.
-
Determine whether to configure the critical attribute for a service.
-
Execute execv ("/bin/sh", NULL) before CloseStdio();.
Failed to Restart the System Using the reboot Command
Cause Analysis
-
Unsuccessful reboot plug-in installation
-
Incorrect reboot command
-
Invalid parameter setting of ohos.startup.powerctrl reboot
-
Restricted permission of reboot selinux
Solution
-
Check whether /system/lib/init/reboot/librebootmodule.z.so is successfully installed on the board.
-
Run the begetctl setloglevel 0 command to set the log level. The log information is as follows:
08-10 18:48:07.653 1421 1421 D C02c0b/BEGET: [init_reboot_innerkits.c:51]Reboot cmd rebootCheck the number of reboot commands and make sure that it does not exceed 96.
-
Run the param set ohos.startup.powerctrl reboot command in hdc shell to check whether the system is restarted. If the system is restarted, the system parameters are set successfully.
-
Check whether the log contains permission denied. If yes, the init process has reported a permission error. Disable SELinux, and perform verification again. If the verification is successful, the problem is caused by incorrect SELinux policy configuration. Modify or add the corresponding SELinux permission. For details about SELinux policy configuration, see the readme in the base/security/selinux_adapter repository.
System Startup Interrupted Due to "parse failed!" Error
Symptom
During system startup, the error message "[Init] InitReadCfg, parse failed! please check file /etc/init.cfg format." is printed, and the startup is interrupted, as shown in the following figure.
Figure 1 Error information
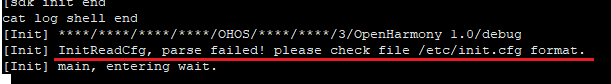
Possible Causes
During modification of the init.cfg file, required commas (,) or parentheses are missing or unnecessary ones are added. As a result, the file's JSON format becomes invalid.
Solution
Check the init.cfg file and ensure that its format meets the JSON specifications.
Requesting FD Proxy for Other Services Failed
Symptom
"Service' xxx '(pid = xxx) is not valid or request with unexpected process(pid = xxx)" is recorded in the kernel log.
Cause Analysis
The kernel log is printed by the init process. After a code review on the init process, it is found that FD proxy is requested for other services.
Solution
Request FD proxy for the current service, but not other services.