Camera
Overview
Function
The OpenHarmony camera driver model provides the camera hardware device interface (HDI) and the camera pipeline model to manage camera devices. The camera driver model is divided into three layers:
- HDI implementation layer: implements standard ohos (OpenHarmony operating system) APIs for cameras.
- Framework layer: interacts with the HDI implementation layer to set up data channels and operate camera devices.
- Device adaptation layer: supports different platforms by shielding the differences in underlying chips and operating systems.
Working Principles
The camera module is used to initialize services and devices, set up data channels, and configure, create, deliver, and capture streams. The following figure shows the camera driver model.
Figure 1 HDF-based camera driver model
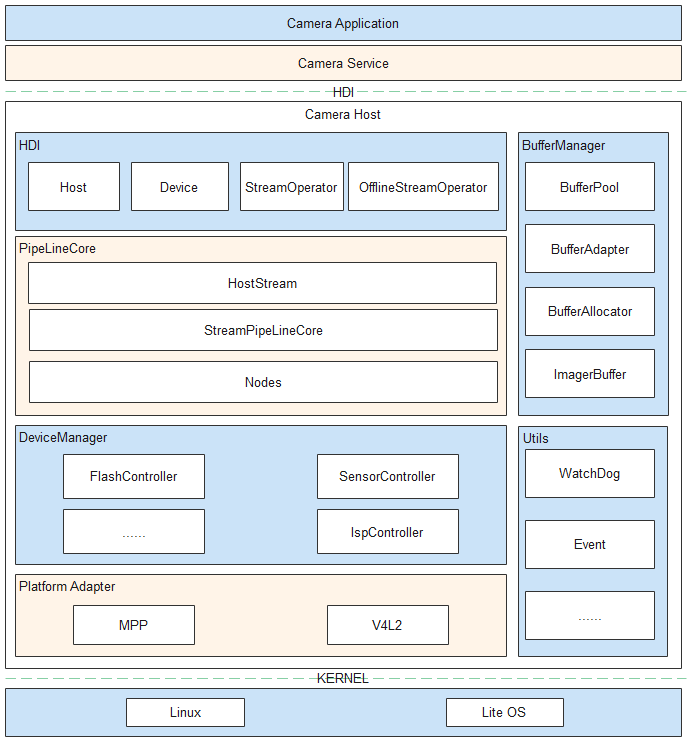
-
When the system starts, the camera_host process is created. The process enumerates underlying devices, creates a DeviceManager instance (to manage the device tree), an object for each underlying device, and a CameraHost instance, and registers the CameraHost instance with the user-mode HDF (UHDF) service. Through the UHDF service, the camera service can obtain the underlying CameraDeviceHost services to operate the hardware devices. The DeviceManager instance can also be created by using the configuration table.
-
The Camera Service obtains the CameraHost instance through the CameraDeviceHost service.
The CameraHost instance can be used to obtain the underlying camera capabilities, turn on the flashlight, call Open() to start a camera and set up a connection with the camera, create a DeviceManager instance (to power on the hardware modules), and create a CameraDevice instance (to provide the device control interface for the upper layer).
When the CameraDevice instance is created, the PipelineCore modules will be instantiated. The StreamPipelineCore module creates pipelines, and the MetaQueueManager module reports metadata.
-
The Camera Service configures stream and creates a Stream class through the CameraDevice module. The StreamPipelineStrategy module creates the node connection mode of the corresponding stream by using the mode issued by the upper layer and querying the configuration table. The StreamPipelineBuilder module creates a node and returns the pipeline to the StreamPipelineDispatcher module through the connection. The StreamPipelineDispatcher module dispatches pipelines.
-
The Camera Service controls the stream operations through the Stream instance.
AttachBufferQueue() delivers the buffer queue requested from the display module to the bottom layer. The CameraDeviceDriverModel manages the buffer. After Capture() is called to deliver commands, the bottom layer transfers the buffer to the upper layer. The Image Signal Processor (ISP) node obtains a specified number of buffers from the buffer queue and delivers the buffers to the bottom-layer ISP hardware. After filling the buffers, the ISP hardware transfers the buffers to the CameraDeviceDriverModel. The CameraDeviceDriverModel fills the created pipeline with the received buffers by using a loop thread. Each node processes the pipeline data and transfers the data to the upper layer in a callback. At the same time, the buffers are freed to the buffer queue for reuse.
-
The Camera Service delivers the photographing command through Capture(). ChangeToOfflineStream() is used to query the position of the photographing buffer. If the ISP hardware has output an image and sent the image data to the IPP node, the common photographing stream can be converted into an offline stream. Otherwise, the close process is executed. ChangeToOfflineStream() passes StreamInfo to enable the offline stream to obtain the stream information of the common stream, determines the node connection mode of the offline stream based on the configuration table, and creates the node connection for the offline stream (if the node connection has been created, the node required by the non-offline stream will be closed by CloseCamera.) When the buffer is transferred from the pipeline to the upper layer, the pipeline resources are released.
-
The Camera Service sends the CaptureSetting parameter to the CameraDeviceDriverModel through UpdateSettings() of the CameraDevice instance. The CameraDeviceDriverModel forwards the parameter to each node through the StreamPipelineDispatcher module. The CaptureSetting parameter carried in StartStreamingCapture() and Capture() is forwarded to the node to which the stream belongs through the StreamPipelineDispatcher module.
-
The Camera Service uses EnableResult() and DisableResult() to control the reporting of underlying metadata. If the underlying metadata needs to be reported, the pipeline creates a buffer queue in the CameraDeviceDriverModel to collect and transfer metadata, queries the configuration table based on the StreamPipelineStrategy module, and creates and connects to the specified node through the StreamPipelineBuilder module. The MetaQueueManager module delivers the buffer to the bottom layer, and the bottom-layer node fills in data. The MetaQueueManager module then invokes the upper-layer callback to transfer the data to the upper layer.
-
The Camera Service calls Close() of the CameraDevice class, and the CameraDevice instance calls the corresponding DeviceManager module to power off each hardware. If an offline stream exists in the subpipeline of the IPP node, the offline stream must be reserved until the execution is complete.
-
To implement dynamic frame control, a CollectBuffer thread is started in the StreamOperator. The CollectBuffer thread obtains a buffer from the buffer queue of each stream. If the frame rate of a stream needs to be controlled (1/n of the sensor output frame rate), the CollectBuffer thread can control the buffer packaging of each frame as required, and determine whether to collect the buffer of the stream. For example, if the output frame rate of the sensor is 120 fps and the preview stream frame rate is 30 fps, the CollectBuffer thread collects the buffer of the preview stream every 4 fps.
Development Guidelines
When to Use
The camera module encapsulates camera operations in camera preview, photographing, and video streams to implement camera hardware operations and improve development efficiency.
Available APIs
The following table describes the C++ APIs generated from the Interface Definition Language (IDL). For details about the interface declaration, see the IDL files in https://gitee.com/openharmony/drivers_interface/tree/master/camera/v1_1/.
The parameters passed in the HDI cannot exceed the capability range obtained by GetCameraAbility. Even if the parameters beyond the capability range can be passed in APIs such as UpdateSettings, CommitStreams, and Capture with no error returned, unexpected behavior may be caused.
- icamera_device.h
| API | Description |
|---|---|
| int32_t GetStreamOperator_V1_1(const sptr<OHOS::HDI::Camera::V1_0::IStreamOperatorCallback>& callbackObj,sptr<OHOS::HDI::Camera::V1_1::IStreamOperator>& streamOperator) | Obtains the stream controller. |
- icamera_host.h
| API | Description |
|---|---|
| int32_t OpenCamera_V1_1(const std::string& cameraId, const sptr<OHOS::HDI::Camera::V1_0::ICameraDeviceCallback>& callbackObj, sptr<OHOS::HDI::Camera::V1_1::ICameraDevice>& device) | Opens a camera. |
| int32_t PreLaunch(const PrelaunchConfig& config) | Pre-starts the camera. |
- istream_operator.h
| API | Description |
|---|---|
| int32_t IsStreamsSupported_V1_1(OperationMode mode, const std::vector<uint8_t>& modeSetting, const std::vector<StreamInfo_V1_1>& infos, StreamSupportType& type) |
Checks whether a stream can be added. |
| int32_t CreateStreams_V1_1(const std::vector<StreamInfo_V1_1>& streamInfos) | Creates streams. |
How to Develop
The camera driver development procedure is as follows:
-
Register a CameraHost instance.
Define the HdfDriverEntry structure to define the method for initializing CameraHost. For details about the code, see drivers/peripheral/camera/interfaces/hdi_ipc/camera_host_driver.cpp.
struct HdfDriverEntry g_cameraHostDriverEntry = { .moduleVersion = 1, .moduleName = "camera_service", .Bind = HdfCameraHostDriverBind, .Init = HdfCameraHostDriverInit, .Release = HdfCameraHostDriverRelease, }; HDF_INIT(g_cameraHostDriverEntry); // Register the HdfDriverEntry structure with the HDF. -
Initialize the CameraHost service.
The HdfCameraHostDriverBind() method defined in the HdfDriverEntry structure registers CameraServiceDispatch() and CameraHostStubInstance(). CameraServiceDispatch() is used to remotely call the CameraHost methods, such as OpenCamera() and SetFlashlight(). CameraHostStubInstance() is called during the system startup to initialize the camera.
static int HdfCameraHostDriverBind(struct HdfDeviceObject *deviceObject) { HDF_LOGI("HdfCameraHostDriverBind enter"); auto *hdfCameraHostHost = new (std::nothrow) HdfCameraHostHost; if (hdfCameraHostHost == nullptr) { HDF_LOGE("%{public}s: failed to create HdfCameraHostHost object", __func__); return HDF_FAILURE; } hdfCameraHostHost->ioService.Dispatch = CameraHostDriverDispatch; // Provide a method to remotely call a CameraHost method. hdfCameraHostHost->ioService.Open = NULL; hdfCameraHostHost->ioService.Release = NULL; auto serviceImpl = ICameraHost::Get(true); if (serviceImpl == nullptr) { HDF_LOGE("%{public}s: failed to get of implement service", __func__); delete hdfCameraHostHost; return HDF_FAILURE; } hdfCameraHostHost->stub = OHOS::HDI::ObjectCollector::GetInstance().GetOrNewObject(serviceImpl, ICameraHost::GetDescriptor()); // Initialize the camera. if (hdfCameraHostHost->stub == nullptr) { HDF_LOGE("%{public}s: failed to get stub object", __func__); delete hdfCameraHostHost; return HDF_FAILURE; } deviceObject->service = &hdfCameraHostHost->ioService; return HDF_SUCCESS; }The following functions are the implementation of the methods of the CameraHost:
int32_t CameraHostStub::CameraHostServiceStubOnRemoteRequest(int cmdId, MessageParcel &data, MessageParcel &reply, MessageOption &option) { switch(cmdId) { case CMD_CAMERA_HOST_SET_CALLBACK: { return CameraHostStubSetCallback(data, reply, option); } case CMD_CAMERA_HOST_GET_CAMERAID: { return CameraHostStubGetCameraIds(data, reply, option); } case CMD_CAMERA_HOST_GET_CAMERA_ABILITY: { return CameraHostStubGetCameraAbility(data, reply, option); } case CMD_CAMERA_HOST_OPEN_CAMERA: { return CameraHostStubOpenCamera(data, reply, option); } case CMD_CAMERA_HOST_SET_FLASH_LIGHT: { return CameraHostStubSetFlashlight(data, reply, option); } default: { HDF_LOGE("%s: not support cmd %d", __func__, cmdId); return HDF_ERR_INVALID_PARAM; } } return HDF_SUCCESS; }CameraHostStubInstance() finally calls CameraHostImpl::Init() to obtain the physical camera and initialize the DeviceManager and PipelineCore modules.
-
Obtain the CameraHost service.
Use Get() to obtain the CameraHost from the CameraService. The Get() method is as follows:
sptr<ICameraHost> ICameraHost::Get(const char *serviceName) { do { using namespace OHOS::HDI::ServiceManager::V1_0; auto servMgr = IServiceManager::Get(); if (servMgr == nullptr) { HDF_LOGE("%s: IServiceManager failed!", __func__); break; } auto remote = servMgr->GetService(serviceName); // Obtain the CameraHost based on serviceName. if (remote != nullptr) { sptr<CameraHostProxy> hostSptr = iface_cast<CameraHostProxy>(remote); // Return the CameraHostProxy object that contains interfaces such as OpenCamera() to the caller. return hostSptr; } HDF_LOGE("%s: GetService failed! serviceName = %s", __func__, serviceName); } while(false); HDF_LOGE("%s: get %s failed!", __func__, serviceName); return nullptr; } -
Open a camera device.
The CameraHostProxy class provides SetCallback(), GetCameraIds(), GetCameraAbility(), OpenCamera(), and SetFlashlight(). The following describes OpenCamera(). Use OpenCamera() to call the remote CameraHostStubOpenCamera() through the CMD_CAMERA_HOST_OPEN_CAMERA to obtain an ICameraDevice object.
int32_t CameraHostProxy::OpenCamera(const std::string& cameraId, const sptr<ICameraDeviceCallback>& callbackObj, sptr<ICameraDevice>& device) { MessageParcel cameraHostData; MessageParcel cameraHostReply; MessageOption cameraHostOption(MessageOption::TF_SYNC); if (!cameraHostData.WriteInterfaceToken(ICameraHost::GetDescriptor())) { HDF_LOGE("%{public}s: failed to write interface descriptor!", __func__); return HDF_ERR_INVALID_PARAM; } if (!cameraHostData.WriteCString(cameraId.c_str())) { HDF_LOGE("%{public}s: write cameraId failed!", __func__); return HDF_ERR_INVALID_PARAM; } if (!cameraHostData.WriteRemoteObject(OHOS::HDI::ObjectCollector::GetInstance().GetOrNewObject(callbackObj, ICameraDeviceCallback::GetDescriptor()))) { HDF_LOGE("%{public}s: write callbackObj failed!", __func__); return HDF_ERR_INVALID_PARAM; } int32_t cameraHostRet = Remote()->SendRequest(CMD_CAMERA_HOST_OPEN_CAMERA, cameraHostData, cameraHostReply, cameraHostOption); if (cameraHostRet != HDF_SUCCESS) { HDF_LOGE("%{public}s failed, error code is %{public}d", __func__, cameraHostRet); return cameraHostRet; } device = hdi_facecast<ICameraDevice>(cameraHostReply.ReadRemoteObject()); return cameraHostRet; }Remote()->SendRequest calls CameraHostServiceStubOnRemoteRequest(), locates CameraHostStubOpenCamera() based on cmdId, and finally calls CameraHostImpl::OpenCamera() to obtain a CameraDevice and power on the camera hardware.
int32_t CameraHostImpl::OpenCamera(const std::string& cameraId, const sptr<ICameraDeviceCallback>& callbackObj, sptr<ICameraDevice>& device) { CAMERA_LOGD("OpenCamera entry"); DFX_LOCAL_HITRACE_BEGIN; if (CameraIdInvalid(cameraId) != RC_OK || callbackObj == nullptr) { CAMERA_LOGW("open camera id is empty or callback is null."); return INVALID_ARGUMENT; } auto itr = cameraDeviceMap_.find(cameraId); if (itr == cameraDeviceMap_.end()) { CAMERA_LOGE("camera device not found."); return INSUFFICIENT_RESOURCES; } CAMERA_LOGD("OpenCamera cameraId find success."); std::shared_ptr<CameraDeviceImpl> cameraDevice = itr->second; if (cameraDevice == nullptr) { CAMERA_LOGE("camera device is null."); return INSUFFICIENT_RESOURCES; } CamRetCode ret = cameraDevice->SetCallback(callbackObj); CHECK_IF_NOT_EQUAL_RETURN_VALUE(ret, HDI::Camera::V1_0::NO_ERROR, ret); CameraHostConfig *config = CameraHostConfig::GetInstance(); CHECK_IF_PTR_NULL_RETURN_VALUE(config, INVALID_ARGUMENT); std::vector<std::string> phyCameraIds; RetCode rc = config->GetPhysicCameraIds(cameraId, phyCameraIds); if (rc != RC_OK) { CAMERA_LOGE("get physic cameraId failed."); return DEVICE_ERROR; } if (CameraPowerUp(cameraId, phyCameraIds) != RC_OK) { // Power on the camera hardware. CAMERA_LOGE("camera powerup failed."); CameraPowerDown(phyCameraIds); return DEVICE_ERROR; } auto sptrDevice = deviceBackup_.find(cameraId); if (sptrDevice == deviceBackup_.end()) { #ifdef CAMERA_BUILT_ON_OHOS_LITE deviceBackup_[cameraId] = cameraDevice; #else deviceBackup_[cameraId] = cameraDevice.get(); #endif } device = deviceBackup_[cameraId]; cameraDevice->SetStatus(true); CAMERA_LOGD("open camera success."); DFX_LOCAL_HITRACE_END; return HDI::Camera::V1_0::NO_ERROR; } -
Obtain streams.
CameraDeviceImpl defines GetStreamOperator(), UpdateSettings(), SetResultMode(), and GetEnabledResult(). Use GetStreamOperator() to obtain steams.
int32_t CameraDeviceImpl::GetStreamOperator(const sptr<IStreamOperatorCallback>& callbackObj, sptr<IStreamOperator>& streamOperator) { HDI_DEVICE_PLACE_A_WATCHDOG; DFX_LOCAL_HITRACE_BEGIN; if (callbackObj == nullptr) { CAMERA_LOGW("input callback is null."); return INVALID_ARGUMENT; } spCameraDeciceCallback_ = callbackObj; if (spStreamOperator_ == nullptr) { #ifdef CAMERA_BUILT_ON_OHOS_LITE // Create a spStreamOperator_ object and pass it to the caller for subsequent stream operations. spStreamOperator_ = std::make_shared<StreamOperator>(spCameraDeciceCallback_, shared_from_this()); #else spStreamOperator_ = new(std::nothrow) StreamOperator(spCameraDeciceCallback_, shared_from_this()); #endif if (spStreamOperator_ == nullptr) { CAMERA_LOGW("create stream operator failed."); return DEVICE_ERROR; } spStreamOperator_->Init(); ismOperator_ = spStreamOperator_; } streamOperator = ismOperator_; #ifndef CAMERA_BUILT_ON_OHOS_LITE CAMERA_LOGI("CameraDeviceImpl %{public}s: line: %{public}d", __FUNCTION__, __LINE__); pipelineCore_->GetStreamPipelineCore()->SetCallback( [this](const std::shared_ptr<CameraMetadata> &metadata) { OnMetadataChanged(metadata); }); #endif DFX_LOCAL_HITRACE_END; return HDI::Camera::V1_0::NO_ERROR; } -
Create streams.
Fill in the StreamInfo structure before creating streams by calling CreateStreams().
using StreamInfo = struct _StreamInfo { int streamId_; int width_; // Stream width int height_; // Stream height int format_; // Stream format, for example, PIXEL_FMT_YCRCB_420_SP int dataSpace_; StreamIntent intent_; // StreamIntent, for example, PREVIEW bool tunneledMode_; ufferProducerSequenceable bufferQueue_; // Use streamCustomer->CreateProducer() to create a buffer queue for streams. int minFrameDuration_; EncodeType encodeType_; };CreateStreams() is a method in the StreamOperator class (StreamOperatorImpl is the base class of StreamOperator). Use CreateStreams() to create a StreamBase object, which initializes operations such as CreateBufferPool through its Init() method.
int32_t StreamOperator::CreateStreams(const std::vector<StreamInfo>& streamInfos) { PLACE_A_NOKILL_WATCHDOG(requestTimeoutCB_); DFX_LOCAL_HITRACE_BEGIN; for (const auto& it : streamInfos) { CHECK_IF_NOT_EQUAL_RETURN_VALUE(CheckStreamInfo(it), true, INVALID_ARGUMENT); CAMERA_LOGI("streamId:%{public}d and format:%{public}d and width:%{public}d and height:%{public}d", it.streamId_, it.format_, it.width_, it.height_); if (streamMap_.count(it.streamId_) > 0) { CAMERA_LOGE("stream [id = %{public}d] has already been created.", it.streamId_); return INVALID_ARGUMENT; } std::shared_ptr<IStream> stream = StreamFactory::Instance().CreateShared( // Create a stream instance. IStream::g_availableStreamType[it.intent_], it.streamId_, it.intent_, pipelineCore_, messenger_); if (stream == nullptr) { CAMERA_LOGE("create stream [id = %{public}d] failed.", it.streamId_); return INSUFFICIENT_RESOURCES; } StreamConfiguration scg; StreamInfoToStreamConfiguration(scg, it); RetCode rc = stream->ConfigStream(scg); if (rc != RC_OK) { CAMERA_LOGE("configure stream %{public}d failed", it.streamId_); return INVALID_ARGUMENT; } if (!scg.tunnelMode && (it.bufferQueue_)->producer_ != nullptr) { CAMERA_LOGE("stream [id:%{public}d] is not tunnel mode, can't bind a buffer producer", it.streamId_); return INVALID_ARGUMENT; } if ((it.bufferQueue_)->producer_ != nullptr) { auto tunnel = std::make_shared<StreamTunnel>(); CHECK_IF_PTR_NULL_RETURN_VALUE(tunnel, INSUFFICIENT_RESOURCES); rc = tunnel->AttachBufferQueue((it.bufferQueue_)->producer_); CHECK_IF_NOT_EQUAL_RETURN_VALUE(rc, RC_OK, INVALID_ARGUMENT); if (stream->AttachStreamTunnel(tunnel) != RC_OK) { CAMERA_LOGE("attach buffer queue to stream [id = %{public}d] failed", it.streamId_); return INVALID_ARGUMENT; } } { std::lock_guard<std::mutex> l(streamLock_); streamMap_[stream->GetStreamId()] = stream; } CAMERA_LOGI("create stream success [id:%{public}d] [type:%{public}s]", stream->GetStreamId(), IStream::g_availableStreamType[it.intent_].c_str()); } DFX_LOCAL_HITRACE_END; return HDI::Camera::V1_0::NO_ERROR; } -
Configure streams.
Use CommitStreams() to configure streams, including initializing and creating PipelineCore. CommitStreams() must be called after the streams are created.
int32_t StreamOperator::CommitStreams(OperationMode mode, const std::vector<uint8_t>& modeSetting) { CAMERA_LOGV("enter"); CHECK_IF_PTR_NULL_RETURN_VALUE(streamPipeline_, DEVICE_ERROR); PLACE_A_NOKILL_WATCHDOG(requestTimeoutCB_); if (modeSetting.empty()) { CAMERA_LOGE("input vector is empty"); return INVALID_ARGUMENT; } DFX_LOCAL_HITRACE_BEGIN; std::vector<StreamConfiguration> configs = {}; { std::lock_guard<std::mutex> l(streamLock_); std::transform(streamMap_.begin(), streamMap_.end(), std::back_inserter(configs), [](auto &iter) { return iter.second->GetStreamAttribute(); }); } std::shared_ptr<CameraMetadata> setting; MetadataUtils::ConvertVecToMetadata(modeSetting, setting); DynamicStreamSwitchMode method = streamPipeline_->CheckStreamsSupported(mode, setting, configs); if (method == DYNAMIC_STREAM_SWITCH_NOT_SUPPORT) { return INVALID_ARGUMENT; } if (method == DYNAMIC_STREAM_SWITCH_NEED_INNER_RESTART) { std::lock_guard<std::mutex> l(streamLock_); for (auto it : streamMap_) { it.second->StopStream(); } } { std::lock_guard<std::mutex> l(streamLock_); for (auto it : streamMap_) { if (it.second->CommitStream() != RC_OK) { CAMERA_LOGE("commit stream [id = %{public}d] failed.", it.first); return DEVICE_ERROR; } } } RetCode rc = streamPipeline_->PreConfig(setting); // Configure the device stream. if (rc != RC_OK) { CAMERA_LOGE("prepare mode settings failed"); return DEVICE_ERROR; } rc = streamPipeline_->CreatePipeline(mode); // Create a pipeline. if (rc != RC_OK) { CAMERA_LOGE("create pipeline failed."); return INVALID_ARGUMENT; } DFX_LOCAL_HITRACE_END; return HDI::Camera::V1_0::NO_ERROR; } -
Capture images.
Fill in the CaptureInfo structure before calling Capture().
using CaptureInfo = struct _CaptureInfo { int[] streamIds_; // IDs of the streams to capture. unsigned char[] captureSetting_; // Use the camera ability obtained by GetCameraAbility() of CameraHost to fill in the settings. bool enableShutterCallback_; };Use the Capture() method in StreamOperator to capture data streams.
int32_t StreamOperator::Capture(int32_t captureId, const CaptureInfo& info, bool isStreaming) { CHECK_IF_EQUAL_RETURN_VALUE(captureId < 0, true, INVALID_ARGUMENT); PLACE_A_NOKILL_WATCHDOG(requestTimeoutCB_); DFX_LOCAL_HITRACE_BEGIN; for (auto id : info.streamIds_) { std::lock_guard<std::mutex> l(streamLock_); auto it = streamMap_.find(id); if (it == streamMap_.end()) { return INVALID_ARGUMENT; } } { std::lock_guard<std::mutex> l(requestLock_); auto itr = requestMap_.find(captureId); if (itr != requestMap_.end()) { return INVALID_ARGUMENT; } } std::shared_ptr<CameraMetadata> captureSetting; MetadataUtils::ConvertVecToMetadata(info.captureSetting_, captureSetting); CaptureSetting setting = captureSetting; auto request = std::make_shared<CaptureRequest>(captureId, info.streamIds_.size(), setting, info.enableShutterCallback_, isStreaming); for (auto id : info.streamIds_) { RetCode rc = streamMap_[id]->AddRequest(request); if (rc != RC_OK) { return DEVICE_ERROR; } } { std::lock_guard<std::mutex> l(requestLock_); requestMap_[captureId] = request; } return HDI::Camera::V1_0::NO_ERROR; } -
Cancel the capture and release the offline stream.
Use CancelCapture() in the StreamOperatorImpl class to cancel the stream capture based on captureId.
int32_t StreamOperator::CancelCapture(int32_t captureId) { CHECK_IF_EQUAL_RETURN_VALUE(captureId < 0, true, INVALID_ARGUMENT); PLACE_A_NOKILL_WATCHDOG(requestTimeoutCB_); DFX_LOCAL_HITRACE_BEGIN; std::lock_guard<std::mutex> l(requestLock_); auto itr = requestMap_.find(captureId); // Search for the CameraCapture object in the Map based on the captureId. if (itr == requestMap_.end()) { CAMERA_LOGE("can't cancel capture [id = %{public}d], this capture doesn't exist", captureId); return INVALID_ARGUMENT; } RetCode rc = itr->second->Cancel(); // Call Cancel() in CameraCapture to cancel the stream capture. if (rc != RC_OK) { return DEVICE_ERROR; } requestMap_.erase(itr); // Erase the CameraCapture object. DFX_LOCAL_HITRACE_END; return HDI::Camera::V1_0::NO_ERROR; }Use ReleaseStreams() in the StreamOperatorImpl class to release the streams created by using CreateStream() and CommitStreams() and destroy the pipeline.
int32_t StreamOperator::ReleaseStreams(const std::vector<int32_t>& streamIds) { PLACE_A_NOKILL_WATCHDOG(requestTimeoutCB_); DFX_LOCAL_HITRACE_BEGIN; for (auto id : streamIds) { std::lock_guard<std::mutex> l(streamLock_); auto it = streamMap_.find(id); if (it == streamMap_.end()) { continue; } if (it->second->IsRunning()) { it->second->StopStream(); } it->second->DumpStatsInfo(); streamMap_.erase(it); } for (auto id : streamIds) { CHECK_IF_EQUAL_RETURN_VALUE(id < 0, true, INVALID_ARGUMENT); } DFX_LOCAL_HITRACE_END; return HDI::Camera::V1_0::NO_ERROR; } -
Close the camera device.
Use Close() in the CameraDeviceImpl class to close the camera device. The PowerDown() in DeviceManager is called to power off the device.
Development Example
There is a ohos_camera_demo in the /drivers/peripheral/camera/hal/test/demo directory. After the system is started, the executable file ohos_camera_demo is generated in the /vendor/bin directory. This demo implements basic camera capabilities such as preview and photographing. The following uses the demo to describe how to use the HDI to implement PreviewOn() and CaptureON().
-
Construct a CameraDemo object in the main function. This object contains methods for initializing the camera and starting, stopping, and releasing streams. The mainDemo->InitSensors() function is used to initialize the CameraHost, and the mainDemo->InitCameraDevice() function is used to initialize the CameraDevice.
int main(int argc, char** argv) { RetCode rc = RC_OK; auto mainDemo = std::make_shared<CameraDemo>(); rc = mainDemo->InitSensors(); // Initialize the CameraHost. if (rc == RC_ERROR) { CAMERA_LOGE("main test: mainDemo->InitSensors() error\n"); return -1; } rc = mainDemo->InitCameraDevice(); // Initialize the CameraDevice. if (rc == RC_ERROR) { CAMERA_LOGE("main test: mainDemo->InitCameraDevice() error\n"); return -1; } rc = PreviewOn(0, mainDemo); // Configure and enable streams. if (rc != RC_OK) { CAMERA_LOGE("main test: PreviewOn() error demo exit"); return -1; } ManuList(mainDemo, argc, argv); // Print the menu to the console. return RC_OK; }The function used to initialize the CameraHost is implemented as follows, where the HDI ICameraHost::Get() is called to obtain the demoCameraHost and set the callback:
RetCode OhosCameraDemo::InitSensors() { int rc = 0; CAMERA_LOGD("demo test: InitSensors enter"); if (demoCameraHost_ != nullptr) { return RC_OK; } #ifdef CAMERA_BUILT_ON_OHOS_LITE demoCameraHost_ = OHOS::Camera::CameraHost::CreateCameraHost(); #else constexpr const char *DEMO_SERVICE_NAME = "camera_service"; demoCameraHost_ = ICameraHost::Get(DEMO_SERVICE_NAME, false); #endif if (demoCameraHost_ == nullptr) { CAMERA_LOGE("demo test: ICameraHost::Get error"); return RC_ERROR; } #ifdef CAMERA_BUILT_ON_OHOS_LITE hostCallback_ = std::make_shared<DemoCameraHostCallback>(); #else hostCallback_ = new DemoCameraHostCallback(); #endif rc = demoCameraHost_->SetCallback(hostCallback_); if (rc != HDI::Camera::V1_0::NO_ERROR) { CAMERA_LOGE("demo test: demoCameraHost_->SetCallback(hostCallback_) error"); return RC_ERROR; } CAMERA_LOGD("demo test: InitSensors exit"); return RC_OK; }The function for initializing the CameraDevice is implemented as follows. The GetCameraIds(cameraIds_), GetCameraAbility(cameraId, ability_), and OpenCamera(cameraIds_.front(), callback, demoCameraDevice_) methods are used to obtain the demoCameraHost.
RetCode OhosCameraDemo::InitCameraDevice() { int rc = 0; CAMERA_LOGD("demo test: InitCameraDevice enter"); if (demoCameraHost_ == nullptr) { CAMERA_LOGE("demo test: InitCameraDevice demoCameraHost_ == nullptr"); return RC_ERROR; } (void)demoCameraHost_->GetCameraIds(cameraIds_); if (cameraIds_.empty()) { return RC_ERROR; } const std::string cameraId = cameraIds_.front(); demoCameraHost_->GetCameraAbility(cameraId, cameraAbility_); MetadataUtils::ConvertVecToMetadata(cameraAbility_, ability_); GetFaceDetectMode(ability_); GetFocalLength(ability_); GetAvailableFocusModes(ability_); GetAvailableExposureModes(ability_); GetExposureCompensationRange(ability_); GetExposureCompensationSteps(ability_); GetAvailableMeterModes(ability_); GetAvailableFlashModes(ability_); GetMirrorSupported(ability_); GetStreamBasicConfigurations(ability_); GetFpsRange(ability_); GetCameraPosition(ability_); GetCameraType(ability_); GetCameraConnectionType(ability_); GetFaceDetectMaxNum(ability_); #ifdef CAMERA_BUILT_ON_OHOS_LITE std::shared_ptr<CameraDeviceCallback> callback = std::make_shared<CameraDeviceCallback>(); #else sptr<DemoCameraDeviceCallback> callback = new DemoCameraDeviceCallback(); #endif rc = demoCameraHost_->OpenCamera(cameraIds_.front(), callback, demoCameraDevice_); if (rc != HDI::Camera::V1_0::NO_ERROR || demoCameraDevice_ == nullptr) { CAMERA_LOGE("demo test: InitCameraDevice OpenCamera failed"); return RC_ERROR; } CAMERA_LOGD("demo test: InitCameraDevice exit"); return RC_OK; } -
Implement PreviewOn() to configure streams, enable preview streams, and start stream capture. After PreviewOn() is called, the camera preview channel starts running. Two streams are enabled: preview stream and capture or video stream. Only the preview stream will be captured.
static RetCode PreviewOn(int mode, const std::shared_ptr<OhosCameraDemo>& mainDemo) { RetCode rc = RC_OK; CAMERA_LOGD("main test: PreviewOn enter"); rc = mainDemo->StartPreviewStream(); // Configure the preview stream. if (rc != RC_OK) { CAMERA_LOGE("main test: PreviewOn StartPreviewStream error"); return RC_ERROR; } if (mode == 0) { rc = mainDemo->StartCaptureStream(); // Configure the capture stream. if (rc != RC_OK) { CAMERA_LOGE("main test: PreviewOn StartCaptureStream error"); return RC_ERROR; } } else { rc = mainDemo->StartVideoStream(); // Configure the video stream. if (rc != RC_OK) { CAMERA_LOGE("main test: PreviewOn StartVideoStream error"); return RC_ERROR; } } rc = mainDemo->CaptureON(STREAM_ID_PREVIEW, CAPTURE_ID_PREVIEW, CAPTURE_PREVIEW); if (rc != RC_OK) { CAMERA_LOGE("main test: PreviewOn mainDemo->CaptureON() preview error"); return RC_ERROR; } CAMERA_LOGD("main test: PreviewOn exit"); return RC_OK; }The StartCaptureStream(), StartVideoStream(), and StartPreviewStream() methods call CreateStream() with different input parameters.
Use CreateStream() to call an HDI API to configure and create streams. Specifically, CreateStream() calls the HDI to obtain a StreamOperation object and then creates a StreamInfo object. Call CreateStreams() and CommitStreams() to create and configure streams.
RetCode OhosCameraDemo::CreateStream(const int streamId, std::shared_ptr<StreamCustomer> &streamCustomer, StreamIntent intent) { int rc = 0; CAMERA_LOGD("demo test: CreateStream enter"); GetStreamOpt(); // Obtain a StreamOperator object. if (streamOperator_ == nullptr) { CAMERA_LOGE("demo test: CreateStream GetStreamOpt() is nullptr\n"); return RC_ERROR; } StreamInfo streamInfo = {0}; SetStreamInfo(streamInfo, streamCustomer, streamId, intent); // Fills in the StreamInfo stream. if (streamInfo.bufferQueue_->producer_ == nullptr) { CAMERA_LOGE("demo test: CreateStream CreateProducer(); is nullptr\n"); return RC_ERROR; } std::vector<StreamInfo> streamInfos; streamInfos.push_back(streamInfo); rc = streamOperator_->CreateStreams(streamInfos); // Create a stream. if (rc != HDI::Camera::V1_0::NO_ERROR) { CAMERA_LOGE("demo test: CreateStream CreateStreams error\n"); return RC_ERROR; } rc = streamOperator_->CommitStreams(NORMAL, cameraAbility_); if (rc != HDI::Camera::V1_0::NO_ERROR) { CAMERA_LOGE("demo test: CreateStream CommitStreams error\n"); std::vector<int> streamIds; streamIds.push_back(streamId); streamOperator_->ReleaseStreams(streamIds); return RC_ERROR; } CAMERA_LOGD("demo test: CreateStream exit"); return RC_OK; }Use CaptureON() to call the Capture() method of StreamOperator to obtain camera data, flip the buffer, and start a thread to receive data of the corresponding type.
RetCode OhosCameraDemo::CaptureON(const int streamId, const int captureId, CaptureMode mode) { CAMERA_LOGI("demo test: CaptureON enter streamId == %{public}d and captureId == %{public}d and mode == %{public}d", streamId, captureId, mode); std::lock_guard<std::mutex> l(metaDatalock_); if (mode == CAPTURE_SNAPSHOT) { constexpr double latitude = 27.987500; // dummy data: Qomolangma latitde constexpr double longitude = 86.927500; // dummy data: Qomolangma longituude constexpr double altitude = 8848.86; // dummy data: Qomolangma altitude constexpr size_t entryCapacity = 100; constexpr size_t dataCapacity = 2000; captureSetting_ = std::make_shared<CameraSetting>(entryCapacity, dataCapacity); captureQuality_ = OHOS_CAMERA_JPEG_LEVEL_HIGH; captureOrientation_ = OHOS_CAMERA_JPEG_ROTATION_270; mirrorSwitch_ = OHOS_CAMERA_MIRROR_ON; gps_.push_back(latitude); gps_.push_back(longitude); gps_.push_back(altitude); captureSetting_->addEntry(OHOS_JPEG_QUALITY, static_cast<void*>(&captureQuality_), sizeof(captureQuality_)); captureSetting_->addEntry(OHOS_JPEG_ORIENTATION, static_cast<void*>(&captureOrientation_), sizeof(captureOrientation_)); captureSetting_->addEntry(OHOS_CONTROL_CAPTURE_MIRROR, static_cast<void*>(&mirrorSwitch_), sizeof(mirrorSwitch_)); captureSetting_->addEntry(OHOS_JPEG_GPS_COORDINATES, gps_.data(), gps_.size()); } std::vector<uint8_t> setting; MetadataUtils::ConvertMetadataToVec(captureSetting_, setting); captureInfo_.streamIds_ = {streamId}; if (mode == CAPTURE_SNAPSHOT) { captureInfo_.captureSetting_ = setting; } else { captureInfo_.captureSetting_ = cameraAbility_; } captureInfo_.enableShutterCallback_ = false; int rc = streamOperator_->Capture(captureId, captureInfo_, true); // The capture starts, and buffer starts to flip. if (rc != HDI::Camera::V1_0::NO_ERROR) { CAMERA_LOGE("demo test: CaptureStart Capture error\n"); streamOperator_->ReleaseStreams(captureInfo_.streamIds_); return RC_ERROR; } if (mode == CAPTURE_PREVIEW) { streamCustomerPreview_->ReceiveFrameOn(nullptr); // Create a preview thread to receive the passed buffer. } else if (mode == CAPTURE_SNAPSHOT) { streamCustomerCapture_->ReceiveFrameOn([this](void* addr, const uint32_t size) { // Create a capture thread to receive the passed buffer through the StoreImage callback. StoreImage(addr, size); }); } else if (mode == CAPTURE_VIDEO) { OpenVideoFile(); streamCustomerVideo_->ReceiveFrameOn([this](void* addr, const uint32_t size) { // Create a video thread to receive the passed buffer through the StoreImage callback. StoreVideo(addr, size); }); } CAMERA_LOGD("demo test: CaptureON exit"); return RC_OK; } -
Implement ManuList() to obtain characters from the console through fgets(). Different characters correspond to different capabilities provided by the demo, and the functionality menu is printed.
static void ManuList(const std::shared_ptr<OhosCameraDemo>& mainDemo, const int argc, char** argv) { int idx, c; bool isAwb = true; const char *shortOptions = "h:cwvaeqof:"; c = getopt_long(argc, argv, shortOptions, LONG_OPTIONS, &idx); while (1) { switch (c) { case 'h': c = PutMenuAndGetChr(); // Print the menu. break; case 'f': FlashLightTest(mainDemo); // Verify the flashlight capability. c = PutMenuAndGetChr(); break; case 'o': OfflineTest(mainDemo); // Verify the offline capability. c = PutMenuAndGetChr(); break; case 'c': CaptureTest(mainDemo); // Verify the capture capability. c = PutMenuAndGetChr(); break; case 'w': // Verify the AWB capability. if (isAwb) { mainDemo->SetAwbMode(OHOS_CAMERA_AWB_MODE_INCANDESCENT); } else { mainDemo->SetAwbMode(OHOS_CAMERA_AWB_MODE_OFF); } isAwb = !isAwb; c = PutMenuAndGetChr(); break; case 'a': // Verify the AE capability. mainDemo->SetAeExpo(); c = PutMenuAndGetChr(); break; case'e': // Verify the metadata operations. mainDemo->SetMetadata(); c = PutMenuAndGetChr(); break; case'v': // Verify the video function. VideoTest(mainDemo); c = PutMenuAndGetChr(); break; case 'q': // Exit the demo. PreviewOff(mainDemo); mainDemo->QuitDemo(); return; default: CAMERA_LOGE("main test: command error please retry input command"); c = PutMenuAndGetChr(); break; } } }Use PutMenuAndGetChr() to print the menu of the demo and call fgets() to wait for commands from the console.
static int PutMenuAndGetChr(void) { constexpr uint32_t inputCount = 50; int c = 0; char strs[inputCount]; Usage(stdout); CAMERA_LOGD("pls input command(input -q exit this app)\n"); fgets(strs, inputCount, stdin); for (int i = 0; i < inputCount; i++) { if (strs[i] != '-') { c = strs[i]; break; } } return c; }The console outputs the menu details as follows:
"Options:\n" "-h | --help Print this message\n" "-o | --offline stream offline test\n" "-c | --capture capture one picture\n" "-w | --set WB Set white balance Cloudy\n" "-v | --video capture Video of 10s\n" "-a | --Set AE Set Auto exposure\n" "-e | --Set Metadeta Set Metadata\n" "-f | --Set Flashlight Set flashlight ON 5s OFF\n" "-q | --quit stop preview and quit this app\n"); -
Compile and build the ohos_camera_demo.
Add init:ohos_camera_demo to deps in the drivers/peripheral/camera/BUILD.gn file. The sample code is as follows:deps = [ "vdi_base/common/buffer_manager:camera_buffer_manager", "vdi_base/common/device_manager:camera_device_manager", "vdi_base/common/hdi_impl:camera_host_service_1.0", "vdi_base/common/pipeline_core:camera_pipeline_core", "vdi_base/common/utils:camera_utils", "test/common:ohos_camera_demo", ]The following uses RK3568 development board as an example.
- Run the ./build.sh --product-name rk3568 --ccache command to generate the executable binary file ohos_camera_demo in out/rk3568/packages/phone/vendor/bin/.
- Import the executable file ohos_camera_demo to the development board, modify the permission, and run the file.
Reference
HCS Configuration
The system provides default HCS configuration for the camera module. You can modify the HCS files as required. The HCS files of the camera module are located in /vendor/hihope/rk3568/hdf_config/uhdf/camera.
-
./hdi_impl/camera_host_config.hcs: defines the camera static capabilities, including the type and position of the lens, connection type, and supported exposure mode. Configure the camera static capabilities based on the specifications of your camera.
-
./pipeline_core/config.hcs: defines the pipeline connection mode. The pipeline configuration includes the supported pipeline types, nodes in each pipeline, and connections between the nodes.
After compilation, the congfig.c and congfig.h files are generated in the /drivers/periphera/camra/vdi_base/common/pipeline_core/pipeline_impl/src/strategy/config directory.
-
./pipeline_core/ipp_algo_config.hcs: provides algorithm configuration.
-
./pipeline_core/params.hcs: defines the scenarios, stream types, and stream IDs. The pipeline uses the stream ID to identify the stream type. Therefore, you need to configure the stream information here.
After compilation, the params.c and params.h files are generated in the /drivers/periphera/camra/vdi_base/common/pipeline_core/pipeline_impl/src/strategy/config directory.
Camera Dump
Function Overview
Camera dump can be used to test camera-related functions. You can enable this feature in the configuration file. Camera dump provides the following functionalities:
- Provides buffer dump in different phases to help quickly locate image problems and the related data.
- Dumps metadata to determine whether metadata parameters are correctly set and determine the impact of different parameters on image quality.
Directory Structure
/drivers/peripheral/camera/vdi_base/common/dump
├── include
│ └── camera_dump.h # Dump head file
└── src
└── camera_dump.cpp # Dump core code
Dump Configuration File
You can find the dump configuration dump.config in the /data/local/tmp directory of the device.
Table 1 Dump switch settings
| Switch | Value | Description | Application Scenarios | Output Data Format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| enableDQBufDump | true/false | The value true means to dump the data in the DequeueBuffer method defined in the v4l2_buffer.cpp file. | Preview, photo taking, and video recording | Onboard camera: YUV420 USB camera: YUV422 |
| enableUVCNodeBufferDump | true/false | The value true means to dump the data to be converted by the YUV422To420 method defined in the uvc_node.cpp file. | Preview, photo taking, and video recording | USB camera: YUV422 |
| enableUVCNodeConvertedBufferDump | true/false | The value true means to dump the converted data returned by the YUV422To420 method defined in the uvc_node.cpp file. | Preview, photo taking, and video recording | USB camera: YUV420 |
| enableExifNodeConvertedBufferDump | true/false | The value true means to dump the data in the DeliverBuffer method defined in the exif_node.cpp file. | Photo taking | JPEG |
| enableFaceNodeConvertedBufferDump | true/false | The value true means to dump the data in the DeliverBuffer method defined in the face_node.cpp file. | Reserved for future use | NA |
| enableForkNodeConvertedBufferDump | true/false | The value true means to dump the data in the DeliverBuffer method defined in the fork_node.cpp file. | Preview, photo taking, and video recording | YUV422 |
| enableRKFaceNodeConvertedBufferDump | true/false | The value true means to dump the data in the DeliverBuffer method defined in the rk_face_node.cpp file. | Reserved for future use | NA |
| enableRKExifNodeConvertedBufferDump | true/false | The value true means to dump the data in the DeliverBuffer method defined in the rk_exif_node.cpp file. | Photo taking | JPEG |
| enableCodecNodeConvertedBufferDump | true/false | The value true means to dump the data in the DeliverBuffer method defined in the codec_node.cpp file. | Preview, photo taking, and video recording | JPEG, YUV420, RGBA8888 |
| enableRKCodecNodeConvertedBufferDump | true/false | The value true means to dump the data in the DeliverBuffer method defined in the rk_codec_node.cpp file. | Preview, photo taking, and video recording | JPEG, H264, RGBA8888 |
| enableSreamTunnelBufferDump | true/false | The value true means to dump the data in the PutBuffer method defined in the stream_tunnel.cpp file. | Preview, photo taking, and video recording | JPEG, H264, YUV420, RGBA8888 |
| enableMetadataDump | true/false | The value true means to enable the dump metadata feature. | Preview, photo taking, and video recording | .meta |
You can also set the dump sampling interval, as described in the following table.
Table 2 Dump sampling interval
| Dump sampling interval | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| previewInterval | Integer greater than or equal to 1 | Interval for dumping preview. The default value is 1, which means to dump every frame. |
| videoInterval | Integer greater than or equal to 1 | Interval for dumping video recording. The default value is 1, which means to dump every frame. |
Configuration Example
Create a file named dump.config in any location on your PC and configure the related parameters.
Complete configuration:
enableDQBufDump=true
enableUVCNodeBufferDump=false
enableUVCNodeConvertedBufferDump=false
enableExifNodeConvertedBufferDump=false
enableFaceNodeConvertedBufferDump=false
enableForkNodeConvertedBufferDump=false
enableRKFaceNodeConvertedBufferDump=false
enableRKExifNodeConvertedBufferDump=false
enableCodecNodeConvertedBufferDump=false
enableRKCodecNodeConvertedBufferDump=false
enableSreamTunnelBufferDump=false
enableMetadataDump=true
previewInterval=3
videoInterval=1
Example:
Dump DequeueBuffer data and metadata with a dump sampling interval of 3.
Enabling Dump
-
Transfer the configuration file to the /data/local/tmp directory of the target device.
hdc file send dump.config /data/local/tmp -
Modify the permission on the dump directory.
hdc shell mount -o rw,remount /data hdc shell chmod 777 /data/ -R -
Enable the dump feature.
hdc shell "hidumper -s 5100 -a '-host camera_host -o'"- -s 5100: obtains all information about the ability whose ID is 5100. In this example, ability 5100 is camera.
- -a '-host camera_host -o': exports the specified ability information.
- For details about how to use HiDumper, see HiDumper.
-
Start the camera and perform operations, such as taking photos and videos, and previewing the photos and videos.
Dumping Data
After the dump feature is enabled, a file containing the data dumped will be generated in the /data/local/tmp directory of the device. You can view the file after sending it to a PC.
hdc file recv /data/local/tmp/xxxx.yuv ~/