Node-API Development Process
To implement cross-language interaction using Node-API, you need to register and load modules based on the Node-API mechanism first.
-
ArkTS/JS: Call C++ APIs by importing the related .so library.
-
Native: Implement module registration via a .cpp file. You need to declare the name of the library to register and define the mappings between the native and JS/ArkTS APIs in the callback registered.
The following demonstrates how to implement cross-language interaction by implementing add() in ArkTS/JS code and Add() in native code.
Creating a Native C++ Project
In DevEco Studio, choose New > Create Project, select the Native C++ template, click Next, select the API version, set the project name, and click Finish.
The main code of the project created consists of two parts: cpp and ets.
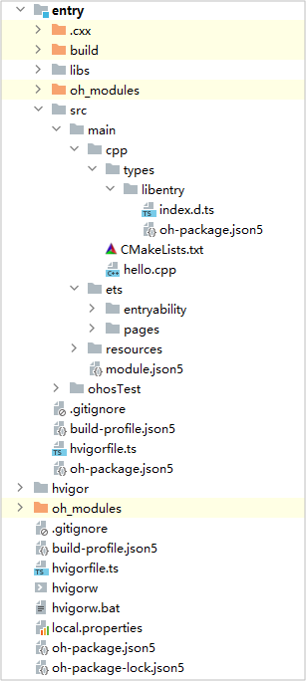
Project Directory Structure
-
entry > src > main > cpp > types: directory for C++ API description files.
-
entry > src > main > cpp > types > libentry > index.d.ts: file containing C++ APIs, including the API names, input parameters, and return values.
-
entry > src > main > cpp > types > libentry > oh-package.json5: file for configuring the entry and name of the third-party .so package.
-
entry > src > main > cpp > CMakeLists.txt: C++ source code configuration file, which provides the CMake build script.
-
entry > src > main > cpp > hello.cpp: file containing the C++ APIs of your application.
-
entry > src > main > ets: directory for ArkTS source code.
For details about more projects, see C++ Project Directory Structure.
Implementing Native APIs
-
Set module registration information.
When a native module is imported in ArkTS, the .so file will be loaded. During the loading process, the napi_module_register method is called to register the module with the system and call the module initialization function.
napi_module has two key attributes: .nm_register_func and .nm_modname. The former defines the module initialization function, and the latter specifies the module name, that is, the name of the .so file imported by ArkTS.
// entry/src/main/cpp/hello.cpp // Information about the module. Record information such as the Init() function and module name. static napi_module demoModule = { .nm_version = 1, .nm_flags = 0, .nm_filename = nullptr, .nm_register_func = Init, .nm_modname = "entry", .nm_priv = nullptr, .reserved = {0}, }; // When the .so file is loaded, this function is automatically called to register the demoModule module with the system. extern "C" __attribute__((constructor)) void RegisterDemoModule() { napi_module_register(&demoModule); } -
Initialize the module.
Implement the mappings between the ArkTS and C++ APIs.
// entry/src/main/cpp/hello.cpp EXTERN_C_START // Initialize the module. static napi_value Init(napi_env env, napi_value exports) { // Implement the mappings between the ArkTS and C++ APIs. napi_property_descriptor desc[] = { {"callNative", nullptr, CallNative, nullptr, nullptr, nullptr, napi_default, nullptr}, {"nativeCallArkTS", nullptr, NativeCallArkTS, nullptr, nullptr, nullptr, napi_default, nullptr}, }; // Embed the CallNative and NativeCallArkTS methods to the exports object. napi_define_properties(env, exports, sizeof(desc) / sizeof(desc[0]), desc); return exports; } EXTERN_C_END // Basic module information. static napi_module demoModule = { .nm_version = 1, .nm_flags = 0, .nm_filename = nullptr, .nm_register_func = Init, .nm_modname = "entry", .nm_priv = nullptr, .reserved = {0}, }; -
Add JS APIs in the index.d.ts file.
// entry/src/main/cpp/types/libentry/index.d.ts export const callNative: (a: number, b: number) => number; export const nativeCallArkTS: (cb: (a: number) => number) => number; -
Associate index.d.ts with .cpp in the oh-package.json5 file.
{ "name": "libentry.so", "types": "./index.d.ts", "version": "", "description": "Please describe the basic information." } -
Set CMake packaging parameters in the CMakeLists.txt file.
# entry/src/main/cpp/CMakeLists.txt cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 3.4.1) project(MyApplication2) set(NATIVERENDER_ROOT_PATH ${CMAKE_CURRENT_SOURCE_DIR}) include_directories(${NATIVERENDER_ROOT_PATH} ${NATIVERENDER_ROOT_PATH}/include) # Add a library named entry. add_library(entry SHARED hello.cpp) # Build the library to be linked to this executable. target_link_libraries(entry PUBLIC libace_napi.z.so) -
Implement CallNative and NativeCallArkTS. The code is as follows:
// entry/src/main/cpp/hello.cpp static napi_value CallNative(napi_env env, napi_callback_info info) { size_t argc = 2; // Declare the parameter array. napi_value args[2] = {nullptr}; // Obtain input parameters and put them into the parameter array in sequence. napi_get_cb_info(env, info, &argc, args, nullptr, nullptr); // Obtain the parameters in sequence. double value0; napi_get_value_double(env, args[0], &value0); double value1; napi_get_value_double(env, args[1], &value1); // Return the sum of the two numbers. napi_value sum; napi_create_double(env, value0 + value1, &sum); return sum; } static napi_value NativeCallArkTS(napi_env env, napi_callback_info info) { size_t argc = 1; // Declare the parameter array. napi_value args[1] = {nullptr}; // Obtain input parameters and put them into the parameter array in sequence. napi_get_cb_info(env, info, &argc, args , nullptr, nullptr); // Create an int() as the input parameter of ArkTS. napi_value argv = nullptr; napi_create_int32(env, 2, &argv ); // Invoke the callback that is passed in, and return the result. napi_value result = nullptr; napi_call_function(env, nullptr, args[0], 1, &argv, &result); return result; }
Calling C/C++ APIs on ArkTS
On ArkTS, import the .so file that contains the Native processing logic. This allows C/C++ methods to be called on ArkTS.
// entry/src/main/ets/pages/Index.ets
// Import the native APIs.
import nativeModule from 'libentry.so'
@Entry
@Component
struct Index {
@State message: string = 'Test Node-API callNative result: ';
@State message2: string = 'Test Node-API nativeCallArkTS result: ';
build() {
Row() {
Column() {
// Pressing the first button calls add(), which uses CallNative() in the native code to add the two numbers.
Text(this.message)
.fontSize(50)
.fontWeight(FontWeight.Bold)
.onClick(() => {
this.message += nativeModule.callNative(2, 3);
})
// Pressing the second button calls nativeCallArkTS, which corresponds to NativeCallArkTS in the native code. The ArkTS function is called on the native side.
Text(this.message2)
.fontSize(50)
.fontWeight(FontWeight.Bold)
.onClick(() => {
this.message2 += nativeModule.nativeCallArkTS((a: number)=> {
return a * 2;
});
})
}
.width('100%')
}
.height('100%')
}
}
Node-API Constraints
Naming Rules of .so Files
The case of the module name to import must be the same as that registered. For example, if the module name is entry, the .so file name must be libentry.so, and the nm_modname field in napi_module must be entry. When importing the module in ArkTS, use import xxx from 'libentry.so'.
Registration
-
To prevent conflicts with symbols in the .so file, add "static" to the function corresponding to nm_register_func. For example, the Init() function in this document.
-
The name of the module registration entry, that is, the function modified by attribute((constructor)) must be unique. For example, the RegisterDemoModule function in this document.
Multithread Processing
Each engine instance corresponds to a JS thread. The objects of an instance cannot be operated across threads. Otherwise, the application may crash. Observe the following rules:
-
The Node-API can be used only by JS threads.
-
The input parameter env of a native API can be bound to a JS thread only when the thread is created.