Introduction to AVCodec Kit
Audio and Video Codec (AVCodec) Kit provides capabilities such as audio and video codec, media file muxing and demuxing, and media data input.
Capability Scope
- Media data input: Media applications can pass in the FD of a file or the URL of a stream for subsequent processing such as media information parsing.
- Media foundation: Basic types of media data processing, including AVBuffer and AVFormat, are provided.
- Audio encoding: Audio applications (such as audio calling and audio recording applications) can send uncompressed audio data to the audio encoder for encoding. The applications can set parameters such as the encoding format, bit rate, and sampling rate to obtain compressed audio files in desired formats.
- Video encoding: Video applications (such as video calling and video recording applications) can send uncompressed video data to the video encoder for encoding. The applications can set parameters such as the encoding format, bit rate, and frame rate to obtain compressed video files in desired formats.
- Audio decoding: Audio applications (such as audio calling application and audio player) can send audio streams to the audio decoder for decoding. The decoded data can be sent to audio devices for playback.
- Video decoding: Video applications (such as video calling application and video player) can send video streams to the video decoder for decoding. The decoded image data can be sent to display devices for display.
- Media file demuxing: Media applications (such as audio and video players) can parse media files stored locally or received from the Internet to obtain audio and video streams, presentation time, encoding formats, and basic file attributes.
- Media file muxing: Media applications (such as audio and video recording application) can mux stream data encoded by the encoder into media files (in MP4 or M4A format), and write the audio and video streams, presentation time, encoding format, and basic file attributes into the specified file in a certain format.
Highlights
-
Zero copy of internal data: During video decoding, the AVCodec provides an AVBuffer through a callback function. The application writes the sample data to be decoded to the AVBuffer. In this way, data in the AVCodec is directly sent to the decoder, rather than being copied from the memory.
-
Hardware acceleration for video codecs: H.264, H.265, and H.265 10-bit hardware codecs are supported.
Basic Concepts
- Media file: file that carries media data such as audio, video, and subtitles. Examples are .mp4 and .m4a files.
- Streaming media: media transmission mode that supports simultaneous download and playback. The supported download protocols include HTTP/HTTPS and HLS.
- Audio and video encoding: process of converting uncompressed audio and video data into another format, such as H.264 and AAC.
- Audio and video decoding: process of converting a data format into an uncompressed original sequence, such as YUV and PCM.
- Media file muxing: process of writing media data (such as audio, video, and subtitles) and description information to a file in a given format, for example, .mp4.
- Media file demuxing: process of reading media data (such as audio, video, and subtitles) from a file and parsing the description information.
Usage
-
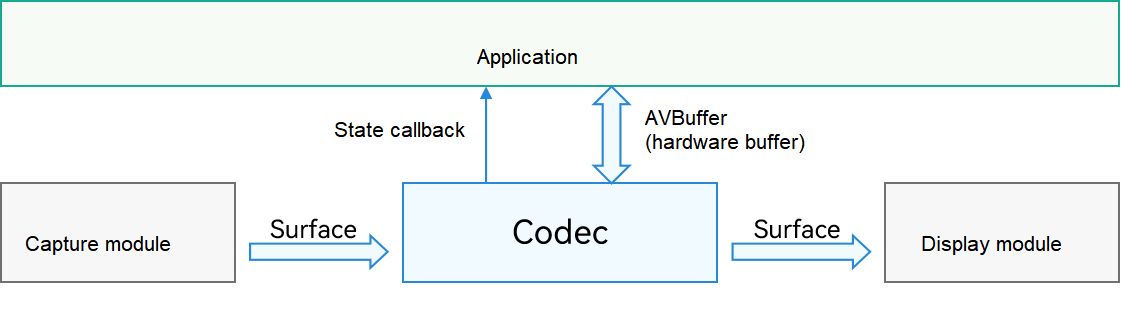
Video codec
The input of video encoding and the output of video decoding are in surface mode.
During encoding and decoding, an application is notified of the data processing status through a callback function. For example, during encoding, the application is notified once a frame is encoded and an AVBuffer is output. During decoding, the application is notified once a frame of stream arrives at the decoder. When the decoding is complete, the application is also notified and can perform subsequent processing on the data.
The following figure shows the video encoding and decoding logic.
-
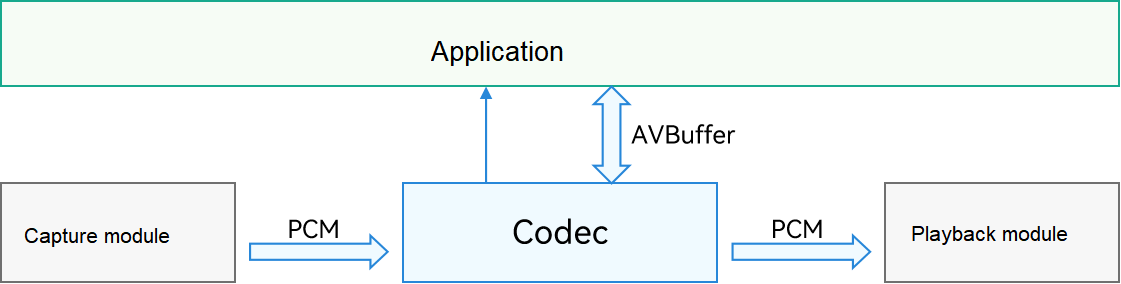
Audio codec
The input of audio encoding and the output of audio decoding are in PCM format.
During encoding and decoding, an application is notified of the data processing status through a callback function. For example, during encoding, the application is notified once a frame is encoded and an AVBuffer is output. During decoding, the application is notified once a frame of stream arrives at the decoder. When the decoding is complete, the application is also notified and can perform subsequent processing on the data.
The following figure shows the audio encoding and decoding logic.
-
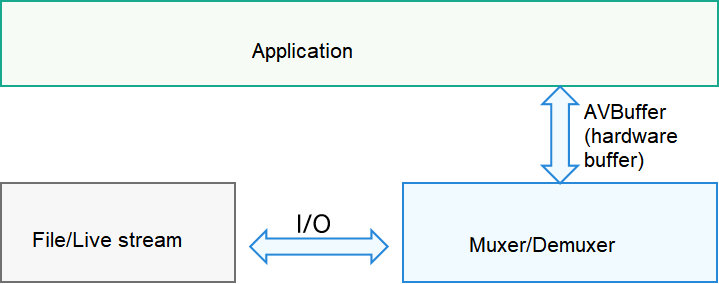
File muxing and demuxing
During file muxing, an application sends an AVBuffer to the corresponding interface of the AVCodec for muxing. The AVBuffer can be that output in the preceding encoding process or an AVBuffer created by the application. The AVBuffer must carry valid stream data and related time description. During file demuxing, the application obtains the AVBuffer that carries stream data from the corresponding interface of the AVCodec. The AVBuffer can be sent to the decoder for decoding.
The following figure shows the file muxing and demuxing logic.