Codec
Overview
Function
The OpenHarmony codec Hardware Device Interface (HDI) driver framework implements the video hardware codec driver based on OpenMAX. It provides APIs for the upper-layer media services to obtain component encoding and decoding capabilities, create a component, set parameters, transfer data, and destroy a component. The codec driver can encode video data in YUV or RGB format to H.264 or H.265 format, and decode raw stream data from H.264 or H.265 format to YUV or RGB format. This document describes the codec functionality developed based on the OpenHarmony Hardware Driver Foundation (HDF).
The codec HDI driver framework is implemented based on the HDF. The figure below shows the codec HDI driver framework.
Figure 1 Codec HDI driver framework
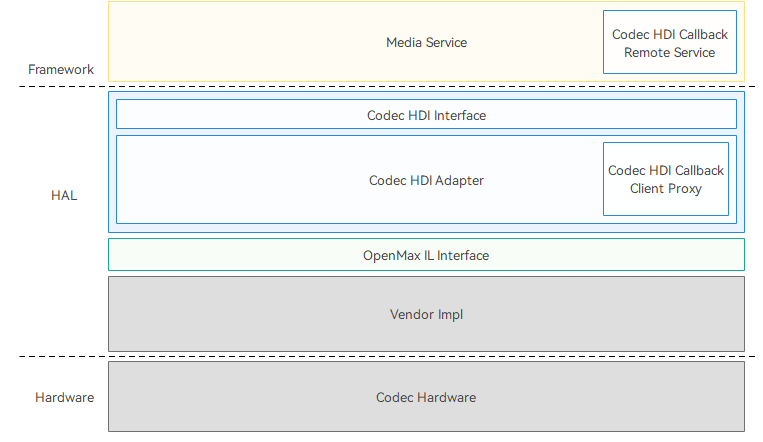
- Codec HDI Callback Remote Service: an anonymous callback service used to process callbacks.
- Codec HDI: provides standard APIs based on OpenMAX. The upper layer services call the APIs to implement hardware encoding and decoding.
- Codec HDI Adapter: HDI implementation layer, which implements HDI APIs and interacts with OpenMAX Integration layer (IL).
- OpenMAX IL interface: provides OpenMAX IL APIs to directly interact with the codec HDI driver.
- Vendor Impl: vendor adaptation layer, which is the OpenMAX implementation layer adapted by each vendor.
- Codec Hardware: hardware decoding device.
Basic Concepts
Before you get started, understand the following concepts:
-
Sampling rate
The number of samples taken from continuous signals every second to form discrete signals, in Hz.
-
OpenMAX IL
A standardized media component interface to enable applications and media frameworks to interact with multimedia codecs and supported components in a unified manner.
-
Frame rate
Number of frames of images transmitted per second, or the number of times that a GPU can refresh images per second. A higher frame rate indicates smoother motion, while a lower frame rate means choppier motion and blurry footage.
-
Bit rate
Number of bits transmitted or processed per unit of time, generally in kbit/s. A higher bit rate indicates clearer image, while a lower bit rate means blurry image with artifacts.
-
Component
An OpenMAX IL component, which is an abstraction of modules in video streams. The components in this document refer to codec components used for video encoding and decoding.
Constraints
The codec HDI applies only to the standard system.
For more details, see OpenMAX IL.
Development Guidelines
When to Use
The codec module implements hardware encoding and decoding of video data. It converts raw stream data such as H.264 data into YUV or RGB data, and converts YUV or RGB data into data formats such as H.264.
Available APIs
- icodec_component_manager.h
| API | Description |
|---|---|
| int32_t CreateComponent(sptr const std::string& compName, int64_t appData, const sptr |
Creates a codec component instance. |
| int32_t DestoryComponent(uint32_t componentId) | Destroys a codec component instance. |
- icodec_component.h
| API | Description |
|---|---|
| int32_t SendCommand(CodecCommandType cmd, uint32_t param, const std::vector<int8_t>& cmdData) | Sends commands to a component. |
| int32_t GetParameter(uint32_t index, const std::vector<int8_t>& inParamStruct, std::vector<int8_t>& outParamStruct) | Obtains component parameter settings. |
| int32_t SetParameter(uint32_t index, const std::vector<int8_t>& paramStruct) | Sets component parameters. |
| int32_t GetState(CodecStateType& state) | Obtains the component status. |
| int32_t UseBuffer(uint32_t portIndex, const OmxCodecBuffer& inBuffer, OmxCodecBuffer& outBuffer) | Requests a port buffer for the component. |
| int32_t FreeBuffer(uint32_t portIndex, const OmxCodecBuffer& buffer) | Releases the buffer. |
| int32_t EmptyThisBuffer(const OmxCodecBuffer& buffer) | Empties this buffer. |
| int32_t FillThisBuffer(const OmxCodecBuffer& buffer) | Fills this buffer. |
- icodec_callback.h
| API | Description |
|---|---|
| int32_t EventHandler(CodecEventType event, const EventInfo& info) | Called to report an event. |
| int32_t EmptyBufferDone(int64_t appData, const OmxCodecBuffer& buffer) | Called to report an event indicating that the encoding or decoding in the input buffer is complete. |
| int32_t FillBufferDone(int64_t appData, const OmxCodecBuffer& buffer) | Called to report an event indicating that the output buffer is filled. |
For more information, see codec.
How to Develop
The codec HDI driver development procedure is as follows:
Registering and Initializing the Driver
Define the HdfDriverEntry struct (which defines the driver initialization method) and fill in the g_codeccomponentmanagerDriverEntry struct to implement the Bind(), Init(), and Release() pointers.
static struct HdfDriverEntry g_codeccomponentmanagerDriverEntry = {
.moduleVersion = 1,
.moduleName = "codec_component_manager_service",
.Bind = HdfCodecComponentManagerDriverBind,
.Init = HdfCodecComponentManagerDriverInit,
.Release = HdfCodecComponentManagerDriverRelease,
}; // Register the HdfDriverEntry struct of the codec HDI with the HDF.
-
HdfCodecComponentManagerDriverBind: binds the device in the HDF to the HdfCodecComponentManagerHost and registers the codec service with the HDF.
static int HdfCodecComponentManagerDriverBind(struct HdfDeviceObject *deviceObject) { CODEC_LOGI("HdfCodecComponentManagerDriverBind enter"); auto *hdfCodecComponentManagerHost = new (std::nothrow) HdfCodecComponentManagerHost; if (hdfCodecComponentManagerHost == nullptr) { CODEC_LOGE("failed to create create HdfCodecComponentManagerHost object"); return HDF_FAILURE; } hdfCodecComponentManagerHost->ioService.Dispatch = CodecComponentManagerDriverDispatch; hdfCodecComponentManagerHost->ioService.Open = NULL; hdfCodecComponentManagerHost->ioService.Release = NULL; auto serviceImpl = ICodecComponentManager::Get(true); if (serviceImpl == nullptr) { CODEC_LOGE("failed to get of implement service"); delete hdfCodecComponentManagerHost; return HDF_FAILURE; } hdfCodecComponentManagerHost->stub = OHOS::HDI::ObjectCollector::GetInstance().GetOrNewObject(serviceImpl, ICodecComponentManager::GetDescriptor()); if (hdfCodecComponentManagerHost->stub == nullptr) { CODEC_LOGE("failed to get stub object"); delete hdfCodecComponentManagerHost; return HDF_FAILURE; } deviceObject->service = &hdfCodecComponentManagerHost->ioService; return HDF_SUCCESS; } -
HdfCodecComponentManagerDriverInit: loads the attribute configuration from the HDF Configuration Source (HCS).
static int HdfCodecComponentManagerDriverInit(struct HdfDeviceObject *deviceObject) { CODEC_LOGI("HdfCodecComponentManagerDriverInit enter"); if (DevHostRegisterDumpHost(CodecDfxService::DevCodecHostDump) != HDF_SUCCESS) { CODEC_LOGE("DevHostRegisterDumpHost error!"); } return HDF_SUCCESS; } -
HdfCodecComponentTypeDriverRelease: releases the driver instance.
static void HdfCodecComponentManagerDriverRelease(struct HdfDeviceObject *deviceObject) { CODEC_LOGI("HdfCodecComponentManagerDriverRelease enter"); if (deviceObject->service == nullptr) { CODEC_LOGE("HdfCodecComponentManagerDriverRelease not initted"); return; } auto *hdfCodecComponentManagerHost = CONTAINER_OF(deviceObject->service, struct HdfCodecComponentManagerHost, ioService); delete hdfCodecComponentManagerHost; }
Configuring the Driver HCS
The HCS consists of the following:
- Device configuration
- Configuration of the supported components
The HCS includes the driver node, loading sequence, and service name. For details about the HCS syntax, see Configuration Management.
The following uses the RK3568 development board as an example. The configuration files of the standard system are in the vendor/hihope/rk3568/hdf_config/uhdf/ directory.
-
Configure the device.
Add the codec_component_manager_service configuration to codec_host in device_info.hcs.
Example:
codec :: host { hostName = "codec_host"; priority = 50; gid = ["codec_host", "uhdf_driver", "vendor_mpp_driver"]; codec_omx_idl_device :: device { device0 :: deviceNode { policy = 2; // Automatic loading, not lazy loading. priority = 100; // Priority. moduleName = "libcodec_driver.z.so"; // Dynamic library of the driver. serviceName = "codec_component_manager_service"; // Service name of the driver. deviceMatchAttr = "media_codec_capabilities"; // Attribute configuration. } } } -
Configure supported components.
Add the component configuration to the media_codec\media_codec_capabilities.hcs file.
Example:
/* node name explanation -- HDF_video_hw_enc_avc_rk: ** ** HDF____________video__________________hw____________________enc____________avc_______rk ** | | | | | | ** HDF or OMX video or audio hardware or software encoder or decoder MIME vendor */ HDF_video_hw_enc_avc_rk { role = 1; // Role of the audio and video codec. type = 1; // Codec type. name = "OMX.rk.video_encoder.avc"; // Component name. supportProfiles = [1, 32768, 2, 32768, 8, 32768]; // Supported profiles. maxInst = 4; // Maximum number of instances. isSoftwareCodec = false; // Whether it is software codec. processModeMask = []; // Codec processing mode. capsMask = [0x01]; // CodecCapsMask configuration. minBitRate = 1; // Minimum bit rate. maxBitRate = 40000000; // Maximum bit rate. minWidth = 176; // Minimum video width. minHeight = 144;; // Minimum video height. maxWidth = 1920; // Maximum video width. maxHeight = 1088; // Maximum video height. widthAlignment = 16; // Horizontal alignment. heightAlignment = 8; // Vertical alignment. minBlockCount = 0xFFFFFFFF; maxBlockCount = 0xFFFFFFFF; minBlocksPerSecond = 0xFFFFFFFF; maxBlocksPerSecond = 0xFFFFFFFF; blockSizeWidth = 0xFFFFFFFF; blockSizeHeight = 0xFFFFFFFF; supportPixelFmts = [28, 24, 20, 12]; // List of colors supported by the display. measuredFrameRate = [320, 240, 165, 165, 720, 480, 149, 149, 1280, 720, 73, 73, 1920, 1080, 18, 18]; bitRateMode = [1, 2]; // Bit rate mode. minFrameRate = 0; // Frame rate. maxFrameRate = 0; }
Development Example
After completing codec module driver adaptation, use the HDI APIs provided by the codec module for further development. The codec HDI provides the following features:
- Provides codec HDI APIs for video services to implement encoding and decoding for video services.
- Provides standard interfaces for device developers to ensure that the OEM vendors comply with the HDI adapter standard. This promises a healthy evolution of the ecosystem.
The development procedure is as follows:
- Initialize the driver, including initializing the instances, callbacks, and component.
- Set codec parameters and information such as the video width, height, and bit rate.
- Apply for input and output buffers.
- Flip codec buffers, enable the component to enter the CODEC_STATE_EXECUTING state, and process the callbacks.
- Deinitialize the interface instance, destroy the buffers, close the component, and releases all interface instances.
Initializing the Driver
Initialize the interface instance and callbacks, and create a component.
// Initialize the codec HDI ComponentManager instance.
omxMgr_ = ICodecComponentManager::Get(false);
if ((omxMgr_ == nullptr)) {
HDF_LOGE("%{public}s omxMgr_ is null", __func__);
return false;
}
// Initialize the callback.
callback_ = new CodecHdiCallback(shared_from_this());
if ((callback_ == nullptr)) {
HDF_LOGE("%{public}s callback_ is null", __func__);
return false;
}
// Create a component instance.
err = omxMgr_->CreateComponent(client_, componentId_, compName, reinterpret_cast<int64_t>(this), callback_);
if (err != HDF_SUCCESS) {
HDF_LOGE("%{public}s failed to CreateComponent", __func__);
return false;
}
Setting Codec Parameters and Configuration
Set the width and height of the input and output data, input data format, and output data format.
// Set the width and height of the input image.
OMX_PARAM_PORTDEFINITIONTYPE param;
if (util_->InitParam(param) != HDF_SUCCESS) {
return HDF_FAILURE;
}
param.nPortIndex = static_cast<uint32_t>(PortIndex::PORT_INDEX_INPUT);
std::vector<int8_t> inVec, outVec;
util_->ObjectToVector(param, inVec);
auto err = client_->GetParameter(OMX_IndexParamPortDefinition, inVec, outVec);
if (err != HDF_SUCCESS) {
HDF_LOGE("%{public}s failed PortIndex::PORT_INDEX_INPUT, index is OMX_IndexParamPortDefinition", __func__);
return err;
}
util_->VectorToObject(outVec, param);
HDF_LOGI("PortIndex::PORT_INDEX_INPUT: eCompressionFormat = %{public}d, eColorFormat = %{public}d ",
param.format.video.eCompressionFormat, param.format.video.eColorFormat);
util_->setParmValue(param, width_, height_, stride_);
util_->ObjectToVector(param, inVec);
err = client_->SetParameter(OMX_IndexParamPortDefinition, inVec);
if (err != HDF_SUCCESS) {
HDF_LOGE("%{public}s failed with PortIndex::PORT_INDEX_INPUT, index is OMX_IndexParamPortDefinition", __func__);
return err;
}
// Set the output width, height, and format.
if (util_->InitParam(param) != HDF_SUCCESS) {
return HDF_FAILURE;
}
param.nPortIndex = static_cast<uint32_t>(PortIndex::PORT_INDEX_OUTPUT);
util_->ObjectToVector(param, inVec);
err = client_->GetParameter(OMX_IndexParamPortDefinition, inVec, outVec);
if (err != HDF_SUCCESS) {
HDF_LOGE("%{public}s failed with PortIndex::PORT_INDEX_OUTPUT, index is OMX_IndexParamPortDefinition",
__func__);
return err;
}
util_->VectorToObject(outVec, param);
HDF_LOGI("PortIndex::PORT_INDEX_OUTPUT eCompressionFormat = %{public}d, eColorFormat=%{public}d",
param.format.video.eCompressionFormat, param.format.video.eColorFormat);
util_->setParmValue(param, width_, height_, stride_);
param.format.video.eColorFormat = AV_COLOR_FORMAT; // Set the output data format to YUV420SP.
err = client_->SetParameter(OMX_IndexParamPortDefinition, inVec);
if (err != HDF_SUCCESS) {
HDF_LOGE("%{public}s failed with PortIndex::PORT_INDEX_OUTPUT, index is OMX_IndexParamPortDefinition",
__func__);
return err;
}
// Set the input data format to H.264/H.265.
OMX_VIDEO_PARAM_PORTFORMATTYPE param;
if (util_->InitParam(param) != HDF_SUCCESS) {
return false;
}
param.nPortIndex = (uint32_t)PortIndex::PORT_INDEX_INPUT;
std::vector<int8_t> inVec, outVec;
util_->ObjectToVector(param, inVec);
auto err = client_->GetParameter(OMX_IndexParamVideoPortFormat, inVec, outVec);
if (err != HDF_SUCCESS) {
HDF_LOGE("%{public}s failed with PortIndex::PORT_INDEX_INPUT", __func__);
return false;
}
util_->VectorToObject(outVec, param);
HDF_LOGI("set Format PortIndex::PORT_INDEX_INPUT eCompressionFormat = %{public}d, eColorFormat=%{public}d",
param.eCompressionFormat, param.eColorFormat);
param.xFramerate = FRAME // Set the frame rate to 30.
if (codecMime_ == codecMime::AVC) {
param.eCompressionFormat = OMX_VIDEO_CodingAVC; // H264
} else {
param.eCompressionFormat = (OMX_VIDEO_CODINGTYPE)CODEC_OMX_VIDEO_CodingHEVC; // H265
}
util_->ObjectToVector(param, inVec);
err = client_->SetParameter(OMX_IndexParamVideoPortFormat, inVec);
if (err != HDF_SUCCESS) {
HDF_LOGE("%{public}s failed with PortIndex::PORT_INDEX_INPUT", __func__);
return false;
}
Applying for Input and Output Buffers
Perform the following steps:
- Use UseBuffer() to apply for input and output buffers and save the buffer IDs. The buffer IDs can be used for subsequent buffer flipping.
- Check whether the corresponding port is enabled. If not, enable the port first.
- Use SendCommand() to change the component status to CODEC_STATE_IDLE, and wait until the operation result is obtained.
// Apply for the input buffer.
auto err = UseBufferOnPort(PortIndex::PORT_INDEX_INPUT);
if (err != HDF_SUCCESS) {
HDF_LOGE("%{public}s UseBufferOnPort PortIndex::PORT_INDEX_INPUT error", __func__);
return false;
}
// Apply for the output buffer.
err = UseBufferOnPort(PortIndex::PORT_INDEX_OUTPUT);
if (err != HDF_SUCCESS) {
HDF_LOGE("%{public}s UseBufferOnPort PortIndex::PORT_INDEX_OUTPUT error", __func__);
return false;
}
// Enable the component to enter the OMX_StateIdle state.
std::vector<int8_t> cmdData;
auto err = client_->SendCommand(CODEC_COMMAND_STATE_SET, CODEC_STATE_IDLE, cmdData);
if (err != HDF_SUCCESS) {
HDF_LOGE("%{public}s failed to SendCommand with CODEC_COMMAND_STATE_SET:CODEC_STATE_IDLE", __func__);
return false;
}
Implement UseBufferOnPort() as follows:
int32_t CodecHdiDecode::UseBufferOnPort(PortIndex portIndex)
{
HDF_LOGI("%{public}s enter, portIndex = %{public}d", __func__, portIndex);
int bufferSize = 0;
int bufferCount = 0;
bool PortEnable = false;
// Obtain parameters of the port buffer.
OMX_PARAM_PORTDEFINITIONTYPE param;
if (util_->InitParam(param) != HDF_SUCCESS) {
return HDF_FAILURE;
}
param.nPortIndex = static_cast<OMX_U32>(portIndex);
std::vector<int8_t> inVec, outVec;
util_->ObjectToVector(param, inVec);
auto err = client_->GetParameter(OMX_IndexParamPortDefinition, inVec, outVec);
if (err != HDF_SUCCESS) {
HDF_LOGE("%{public}s failed to GetParameter with OMX_IndexParamPortDefinition : portIndex[%{public}d]",
__func__, portIndex);
return err;
}
util_->VectorToObject(outVec, param);
bufferSize = param.nBufferSize;
bufferCount = param.nBufferCountActual;
portEnable = param.bEnabled;
HDF_LOGI("buffer index [%{public}d], buffer size [%{public}d], "
"buffer count [%{public}d], portEnable[%{public}d], ret [%{public}d]",
portIndex, bufferSize, bufferCount, portEnable, err);
// Set the port buffer.
if (useBufferHandle_ && portIndex == PortIndex::PORT_INDEX_OUTPUT) {
err = UseBufferHandle(bufferCount, bufferSize);
} else {
err = UseBufferOnPort(portIndex, bufferCount, bufferSize);
}
// Check whether the port is available.
if (!portEnable) {
err = client_->SendCommand(CODEC_COMMAND_PORT_ENABLE, static_cast<uint32_t>(portIndex), {});
if (err != HDF_SUCCESS) {
HDF_LOGE("%{public}s SendCommand OMX_CommandPortEnable::PortIndex::PORT_INDEX_INPUT error", __func__);
return err;
}
}
return HDF_SUCCESS;
}
int32_t CodecHdiDecode::UseBufferOnPort(PortIndex portIndex, int bufferCount, int bufferSize)
{
if (bufferCount <= 0 || bufferSize <= 0) {
HDF_LOGE("UseBufferOnPort bufferCount <= 0 or bufferSize <= 0");
return HDF_ERR_INVALID_PARAM;
}
for (int i = 0; i < bufferCount; i++) {
std::shared_ptr<OmxCodecBuffer> omxBuffer = std::make_shared<OmxCodecBuffer>();
omxBuffer->size = sizeof(OmxCodecBuffer);
omxBuffer->version.s.nVersionMajor = 1;
omxBuffer->bufferType = CODEC_BUFFER_TYPE_AVSHARE_MEM_FD;
int fd = AshmemCreate(0, bufferSize);
shared_ptr<Ashmem> sharedMem = make_shared<Ashmem>(fd, bufferSize);
omxBuffer->fd = fd;
omxBuffer->bufferhandle = nullptr;
omxBuffer->allocLen = bufferSize;
omxBuffer->fenceFd = -1;
omxBuffer->pts = 0;
omxBuffer->flag = 0;
if (portIndex == PortIndex::PORT_INDEX_INPUT) {
omxBuffer->type = READ_ONLY_TYPE; // ReadOnly
sharedMem->MapReadAndWriteAshmem();
} else {
omxBuffer->type = READ_WRITE_TYPE;
sharedMem->MapReadOnlyAshmem();
}
OmxCodecBuffer outBuffer;
auto err = client_->UseBuffer((uint32_t)portIndex, *omxBuffer.get(), outBuffer);
if (err != HDF_SUCCESS) {
HDF_LOGE("%{public}s failed to UseBuffer with portIndex[%{public}d]", __func__, portIndex);
sharedMem->UnmapAshmem();
sharedMem->CloseAshmem();
sharedMem = nullptr;
return err;
}
omxBuffer->bufferId = outBuffer.bufferId;
omxBuffer->fd = -1;
HDF_LOGI("UseBuffer returned bufferID [%{public}d]", omxBuffer->bufferId);
std::shared_ptr<BufferInfo> bufferInfo = std::make_shared<BufferInfo>();
bufferInfo->omxBuffer = omxBuffer;
bufferInfo->avSharedPtr = sharedMem;
bufferInfo->portIndex = portIndex;
omxBuffers_.emplace(std::make_pair(omxBuffer->bufferId, bufferInfo));
if (portIndex == PortIndex::PORT_INDEX_INPUT) {
unUsedInBuffers_.push_back(omxBuffer->bufferId);
} else {
unUsedOutBuffers_.push_back(omxBuffer->bufferId);
}
}
return HDF_SUCCESS;
}
Flipping Codec Buffers
Set the component to the CODEC_STATE_EXECUTING state, fill the input buffer, read data from the output buffer, and flip the buffers.
// Set the component to the OMX_StateExecuting state and start buffer flipping.
HDF_LOGI("...command to CODEC_STATE_EXECUTING....");
auto err = client_->SendCommand(CODEC_COMMAND_STATE_SET, CODEC_STATE_EXECUTING, {});
if (err != HDF_SUCCESS) {
HDF_LOGE("%{public}s failed to SendCommand with CODEC_COMMAND_STATE_SET:CODEC_STATE_IDLE", __func__);
return;
}
// Set the output buffer to fill.
if (!FillAllTheBuffer()) {
HDF_LOGE("%{public}s FillAllTheBuffer error", __func__);
return;
}
// Fill the input buffer.
auto t1 = std::chrono::system_clock::now();
bool eosFlag = false;
while (!eosFlag) {
if (this->exit_) {
break;
}
int bufferID = GetFreeBufferId();
if (bufferID < 0) {
usleep(10000); // 10000 for wait 10ms
continue;
}
auto iter = omxBuffers_.find(bufferID);
if (iter == omxBuffers_.end()) {
continue;
}
auto bufferInfo = iter->second;
void *sharedAddr = const_cast<void *>(bufferInfo->avSharedPtr->ReadFromAshmem(0, 0));
eosFlag = this->ReadOnePacket(fpIn_, static_cast<char *>(sharedAddr), bufferInfo->omxBuffer->filledLen);
bufferInfo->omxBuffer->offset = 0;
if (eosFlag) {
bufferInfo->omxBuffer->flag = OMX_BUFFERFLAG_EOS;
}
err = client_->EmptyThisBuffer(*bufferInfo->omxBuffer.get());
if (err != HDF_SUCCESS) {
HDF_LOGE("%{public}s EmptyThisBuffer error", __func__);
return;
}
}
// Wait.
while (!this->exit_) {
usleep(10000); // 10000 for wait 10ms
}
// Enable the component to enter the OMX_StateIdle state after decoding.
auto t2 = std::chrono::system_clock::now();
std::chrono::duration<double> diff = t2 - t1;
HDF_LOGI("cost %{public}f, count=%{public}d", diff.count(), count_);
(void)client_->SendCommand(CODEC_COMMAND_STATE_SET, CODEC_STATE_IDLE, {});
return;
}
Automatic framing is not supported in rk OMX decoding. Therefore, you need to manually divide data into frames. Currently, data is divided into frames from code 0x000001 or 0x00000001 and sent to the server for processing. The sample code is as follows:
// Read a file by frame.
bool CodecHdiDecode::ReadOnePacket(FILE *fp, char *buf, uint32_t &filledCount)
{
// Read the start code.
size_t t = fread(buf, 1, START_CODE_SIZE_FRAME, fp);
if (t < START_CODE_SIZE_FRAME) {
return true;
}
char *temp = buf;
temp += START_CODE_SIZE_FRAME;
bool ret = true;
while (!feof(fp)) {
(void)fread(temp, 1, 1, fp);
if (*temp != START_CODE) {
temp++;
continue;
}
// Check the start code.
if ((temp[START_CODE_OFFSET_ONE] == 0) && (temp[START_CODE_OFFSET_SEC] == 0) &&
(temp[START_CODE_OFFSET_THIRD] == 0)) {
fseek(fp, -START_CODE_SIZE_FRAME, SEEK_CUR);
temp -= (START_CODE_SIZE_FRAME - 1);
ret = false;
break;
}
if ((temp[START_CODE_OFFSET_ONE] == 0) && (temp[START_CODE_OFFSET_SEC] == 0)) {
fseek(fp, -START_CODE_SIZE_SLICE, SEEK_CUR);
temp -= (START_CODE_SIZE_SLICE - 1);
ret = false;
break;
}
temp++;
}
filledCount = (temp - buf);
return ret;
}
The codec HDI provides the following callbacks:
- EventHandler: Called when a command is executed. For example, when the command for changing the component state from CODEC_STATE_IDLE to CODEC_STATE_EXECUTING is executed, this callback is invoked to return the result.
- EmptyBufferDone: Called when the input data is consumed. If the client needs to fill data to encode or decode, it must call EmptyThisBuffer() again.
- FillBufferDone: Called when the output data is filled. If the client needs to read the encoded or decoded data, it must call FillThisBuffer() again.
// EmptyBufferDone example
int32_t CodecHdiDecode::OnEmptyBufferDone(const struct OmxCodecBuffer &buffer)
{
HDF_LOGI("OnEmptyBufferDone, bufferId [%{public}d]", buffer.bufferId);
unique_lock<mutex> ulk(lockInputBuffers_);
unUsedInBuffers_.push_back(buffer.bufferId);
return HDF_SUCCESS;
}
// FillBufferDone example
int32_t CodecHdiDecode::OnFillBufferDone(const struct OmxCodecBuffer &buffer)
{
HDF_LOGI("OnFillBufferDone, bufferId [%{public}d]", buffer.bufferId);
if (exit_) {
return HDF_SUCCESS;
}
auto iter = omxBuffers_.find(buffer.bufferId);
if ((iter == omxBuffers_.end()) || (iter->second == nullptr)) {
return HDF_SUCCESS;
}
count_++;
// read buffer
auto bufferInfo = iter->second;
if (bufferInfo->avSharedPtr != nullptr) {
const void *addr = bufferInfo->avSharedPtr->ReadFromAshmem(buffer.filledLen, buffer.offset);
(void)fwrite(addr, 1, buffer.filledLen, fpOut_);
} else if (bufferInfo->bufferHandle != nullptr && gralloc_ != nullptr) {
gralloc_->Mmap(*bufferInfo->bufferHandle);
(void)fwrite(bufferInfo->bufferHandle->virAddr, 1, buffer.filledLen, fpOut_);
gralloc_->Unmap(*bufferInfo->bufferHandle);
}
(void)fflush(fpOut_);
if (buffer.flag == OMX_BUFFERFLAG_EOS) {
// end
exit_ = true;
HDF_LOGI("OnFillBufferDone the END coming");
return HDF_SUCCESS;
}
// call fillthisbuffer again
auto err = client_->FillThisBuffer(*bufferInfo->omxBuffer.get());
if (err != HDF_SUCCESS) {
HDF_LOGE("%{public}s FillThisBuffer error", __func__);
return HDF_SUCCESS;
}
return HDF_SUCCESS;
}
// EventHandler example
int32_t CodecHdiDecode::EventHandler(CodecEventType event, const EventInfo &info)
{
switch (event) {
case CODEC_EVENT_CMD_COMPLETE: {
CodecCommandType cmd = (CodecCommandType)info.data1;
if (CODEC_COMMAND_STATE_SET == cmd) {
HDF_LOGI("CODEC_COMMAND_STATE_SET reached, status is %{public}d", info.data2);
this->OnStatusChanged();
}
break;
}
case OMX_EventPortSettingsChanged: {
HDF_LOGI("OMX_EventPortSeetingsChanged reached");
this->HandleEventPortSettingsChanged(info.data1, info.data2);
}
default:
break;
}
return HDF_SUCCESS;
}
Destroying a Component
Change the component state to CODEC_STATE_IDLE, release the input and output buffers, change the component state to CODEC_STATE_LOADED, and call DestoryComponent to destroy the component.
Releasing Buffers
// Change the component state to OMX_StateLoaded.
client_->SendCommand(CODEC_COMMAND_STATE_SET, CODEC_STATE_LOADED, {});
// Release all buffers in use.
auto iter = omxBuffers_.begin();
while (iter != omxBuffers_.end()) {
auto bufferInfo = iter->second;
iter = omxBuffers_.erase(iter);
(void)client_->FreeBuffer((uint32_t)bufferInfo->portIndex, *bufferInfo->omxBuffer.get());
bufferInfo = nullptr;
}
unUsedInBuffers_.clear();
unUsedOutBuffers_.clear();
// After the buffers are released, the component enters the OMX_StateLoaded state.
CodecStateType status = CODEC_STATE_INVALID;
int32_t err = HDF_SUCCESS;
int32_t tryCount = 3;
do {
err = client_->GetState(status);
if (err != HDF_SUCCESS) {
HDF_LOGE("%s GetState error [%{public}x]", __func__, err);
break;
}
if (status != CODEC_STATE_LOADED) {
HDF_LOGI("Wait for OMX_StateLoaded status");
this->WaitForStatusChanged();
}
tryCount--;
} while ((status != CODEC_STATE_LOADED) && (tryCount > 0));
Destroying a Component Instance
// Destroy a component instance.
void CodecHdiDecode::Release()
{
omxMgr_->DestoryComponent(componentId_);
client_ = nullptr;
callback_ = nullptr;
omxMgr_ = nullptr;
}
FAQs
Green Screens Displayed During the Decoding Process
Symptom
Green screens are displayed during the decoding process.
Possible Causes
OpenMAX does not support framing.
Solution
When EmptyThisBuffer is call, only one frame can be passed in at a time.
Only Green Screen Displayed During the Decoding Process
Symptom
Decoding fails, and all the frames decoded cannot be played.
Possible Causes
For the data in AVCC format, the first frame to be processed must be extra_data.
Solution
Write sps and pps to the buffer in extra_data format, and set the buffer flag to OMX_BUFFERFLAG_EXTRADATA.
Failed to Play the Encoded Video
Symptom
After the generated video stream (H.264 stream) is written to a file, the video stream cannot be played by FFplay.
Possible Causes
- The xFramerate parameter of the output port is incorrectly set.
- The OMX_VIDEO_PARAM_AVCTYPE parameter is correctly set.
Solution
View the codec_host log generated during encoding, search for "encode params init settings", and check for incorrect parameters. If framerate is 0, xFramerate is incorrectly set. In this case, move the frame rate leftwards by 16 bits.
In other cases, correct the setting of OMX_VIDEO_PARAM_AVCTYPE.
Reference
For more information, see Codec.